Doropygusreticulatus, Kim & Boxshall, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/megataxa.4.1.1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5699847 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C487CB-EE14-3B7D-FCEF-FC57FA50F99D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Doropygusreticulatus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Doropygusreticulatus sp. nov.
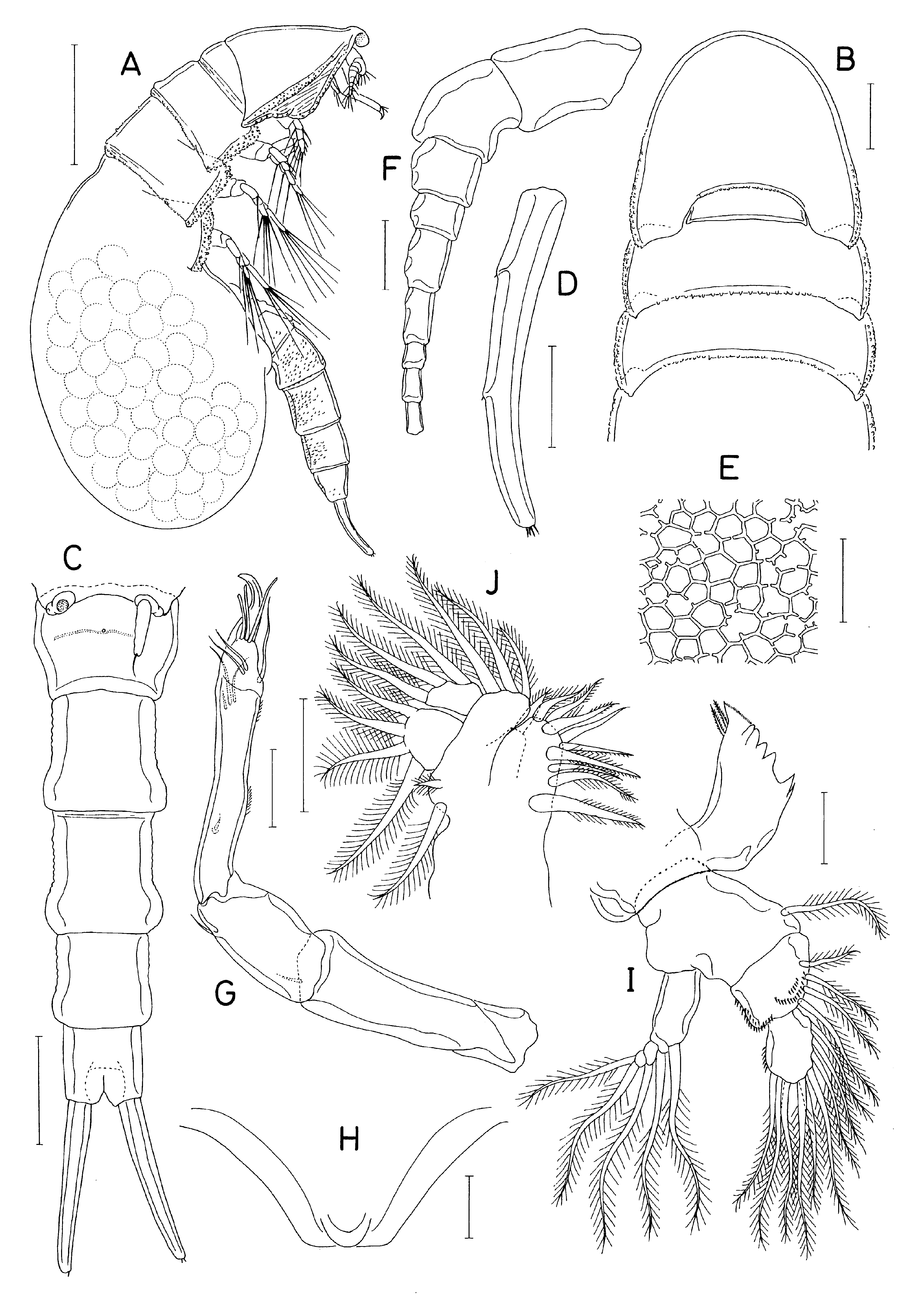
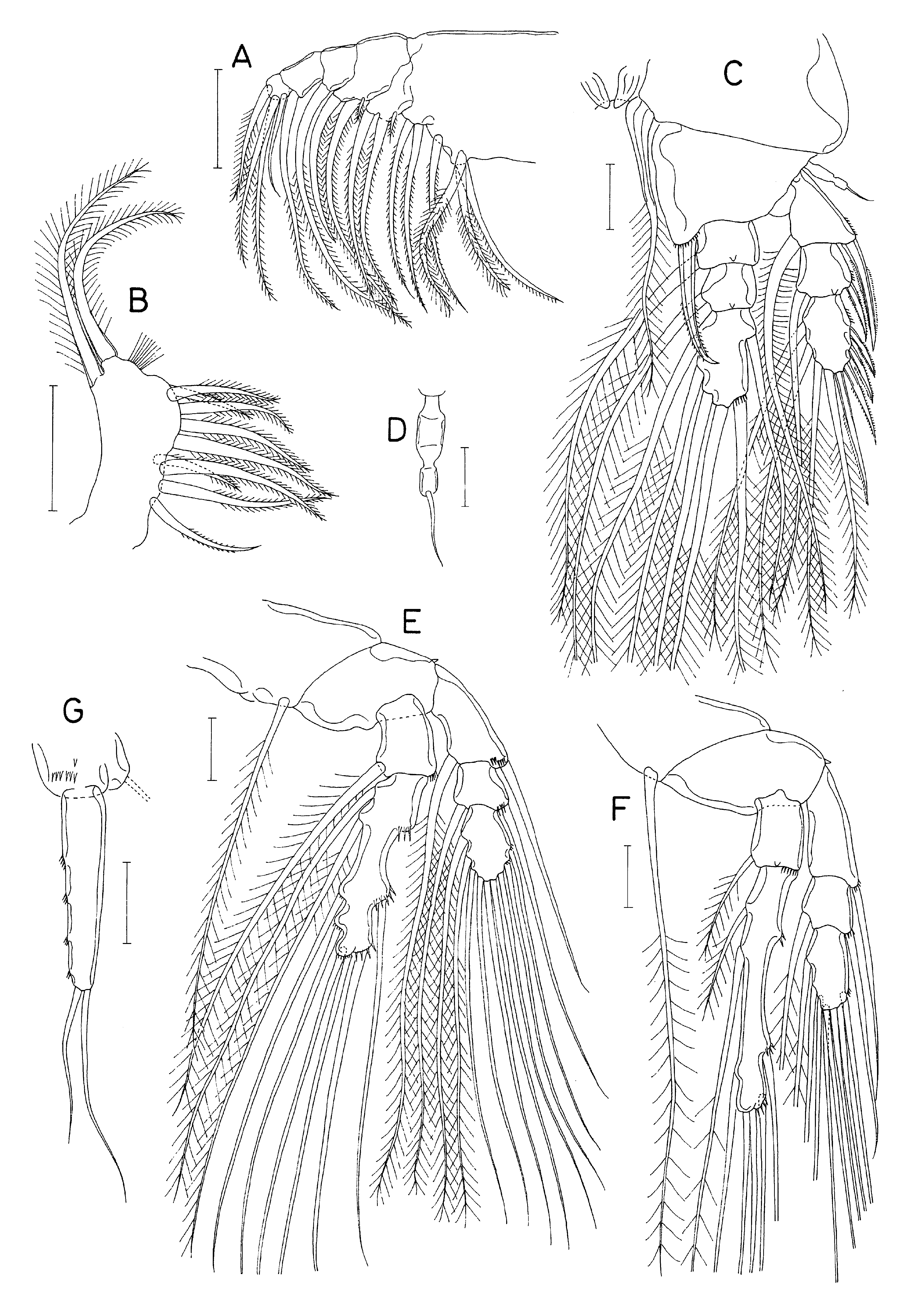
( Figs. 216 View FIGURE 216 , 217 View FIGURE 217 )
Type material. Holotype ♀ (dissected and mounted on a slide, MNHN-IU-2014-21308 ) and paratype ♀ (dissected and mounted on a slide, MNHN-IU-2014-21309) from Pyura arenosa (Herdman, 1881) (MNHN-IT-2008-7399 = MNHNS 2/ PUY /484), CRRF 0 PHG 1713-U, Vietnam (08°41.12 Ń, 106°36.80 É), depth 0-1 m, 29 July 2008.
Etymology. The specific name refers to the surface reticulation on the exoskeleton of the prosomites.
Descriptionoffemale. Body ( Fig. 216A View FIGURE 216 ) clearly segmented, length 3.04 mm; with thick, rigid exoskeleton. External surface of all prosomal somites reticulate, with polygonal sculpturing ( Fig. 216E View FIGURE 216 ). Cephalosome and first to third pedigerous somites dorsoventrally depressed. Posterolateral corners of dorsal cephalic shield extended posteriorlybeyond distalborder offirst pedigerous somite; corners angular in dorsal view ( Fig. 216B View FIGURE 216 ), but tapering and pointed in lateral view. First pedigerous somite small ( Fig. 216B View FIGURE 216 ), half as wide as cephalic shield. Second to fourth pedigerous somites each with well-developed epimera. Cephalic shield and epimera of second to fourth pedigeroussomites thickened laterally, ornamented with minute surface granulation along lateral margins. Posterodorsal margins of second and third pedigerous somites concave and fringed with surface granulation. Fourth pedigerous somite expanded to form nearly oval brood pouch, longer than cephalosome plus anterior pedigerous somites combined, its epimera confined to anterior 20% of somite length, near base of leg 4. Freeurosome ( Fig. 216C View FIGURE 216 ) slender, 5-segmented, with thick exoskeleton and surface granulation (not shown in Fig. 216C View FIGURE 216 , but visible in Fig. 216A View FIGURE 216 ). Genital somite 192×269 μm, narrow in posterior half. Four abdominal somites 212×269, 231×223, 173×188, and 138×150 μm, respectively, with first to third abdominal somites expanded posteriorly. Caudal ramus ( Fig. 216D View FIGURE 216 ) slender, slightly archedventrally, about 7.4 timeslongerthan wide (340×46 μm) and about 2.5 times longer than anal somite; carrying vestiges of 6 setae, 2 proximal setae located at 27 and 64% of ramus length.
| Leg 1 | Coxa Basis Exopod 0-1 1-I I-1; I-1; III, I, 4 | Endopod 0-1; 0-1; 1, 2, 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Legs 2 & 3Leg 4 | 0-1 0-1 | 1-0 1-0 | 1-1; 1-1; 3, 2, 4 1-0; 1-1; 2, 2, 4 | 0-1; 1, 2, 5 0-1; 2, 2, 3 |
Rostrum represented by broad, blunt apical lobe of cephalosome. Antennule ( Fig. 216F View FIGURE 216 ) slender and 9- segmented; setae strongly entangled, not countable. Antenna ( Fig. 216G View FIGURE 216 ) slender, 4-segmented; coxa short and unarmed; basis 99×53 μm, with 1 smallseta distally; first endopodal segment 83×50 μm, with 1 small seta on inner margin; compound distal endopodal segment 5.2 times longer than wide (162×31 μm) and twice as long as first endopodal segment, ornamented with 2 groups of minute spinules on outer margin; armed with 10 small setae plus small terminal claw, about one-third as long as segment.
Labrum ( Fig. 216H View FIGURE 216 ) with smooth sides, strongly tapering to narrow, linear free posterior margin, with small posteromedial lobe. Mandible ( Fig. 216I View FIGURE 216 ) with 5 major teeth, 1 distalsubsidiarytooth, and 2 smallproximal setae on coxal gnathobase; basis with 1 seta on medial margin; exopod with 5 setae, distal outer seta slightly shorter than other 4; first endopodal segment bearing 4 setae and spinules near outer distal and medioventral surfaces; second endopodal segment with 9 setae and spinules on outer margin. Maxillule ( Fig. 216J View FIGURE 216 ) with 9 setae on arthrite, 1 on coxal endite, 2 on epipodite, 3 on basis, 4 onexopodand 3 on endopod. Maxilla ( Fig. 217A View FIGURE 217 ) 5-segmented; syncoxawith 9 setae (grouped as 3, 1, 2, and 3); basiswith 3 setae; endopodwith 1, 1, and 4 setae on first to third segments, respectively. Maxilliped ( Fig. 217B View FIGURE 217 ) unsegmented, elongate, armedwith 9 setae on medial margin and 2 subequal setae apically.
Leg 1 ( Fig. 217C View FIGURE 217 ) with 3-segmented rami. Inner coxal seta broadened and highly sclerotized in proximal part, extending beyond tip of inner distal spine on basis. Outer seta ( Fig. 217D View FIGURE 217 ) on basis spiniform, constricted proximally and in distal third, with slender flagellate tip. Inner distal spine on basis extending to middle of third endopodal segment, curved, spinulose along distal half. Outer spine on first exopodal segment large, twice as long as outer spine on second segment.
Legs 2–4 with 3-segmented exopods and 2- segmented endopods ( Fig. 217E, F View FIGURE 217 ); endopods distinctly longer than exopods. Legs 2 and 3 with same setation. Inner coxal seta elongate, much longer than endopod. Outersetaonbasis rudimentary, scarcely visible. Outer setae on exopods longerthan ramus. Proximal 2 inner setae on endopod of leg 4 shorter than other endopodal setae. Second endopodal segment of legs 2–4 elongated, with uneven lateral margins. Second endopodal segment of leg 4 longerthan exopod. First exopodal segment of leg 4 lacking inner seta. Armature formula for legs 1–4 as follows:
Leg 5 ( Fig. 217G View FIGURE 217 ) 2-segmented: protopod short, with several spinules near base of exopod and 1 outer distal seta (this seta missing in observed specimens); free exopodal segment slender, graduallynarrowing distally, 4.5 times longer than wide (126×28 μm), with 2 long setae distally (outer seta 140 μm long, inner 103 μm) and 4 rows of spinules on dorsomedial surface.
Male. Unknown.
Remarks. In the genus Doropygus there are ten species currently known to have a maxillule combining the presence of 4 setae on the exopod with 3 setae on the endopod, as found in D. reticulatus sp. nov. Among these species, D. rigidus Ooishi, 1962 and probably D. platythorax Jones, 1974 have, like the new species, a highly sclerotized, rigid exoskeleton but the surface reticulationof the prosomites, as found in the newspecies, has not been reported in any of those ten species.
These ten species typically have elongate caudal rami and three are known to have caudal rami which are more than 6 times as long as wide, as in D. reticulatus sp. nov. These three species are D. kerguelensis , D. platythorax , and D. rigidus . However, all three of these species have a much broader free exopodal segment of leg 5, which is up to 3.5 times as long as wide in contrast to 4.5 times in D. reticulatus sp. nov. In two other species, D. spiniferus Schellenberg, 1922 and D. trisetosus Schellenberg, 1922 the information available on their caudal rami is incomplete but it is reported that in both species the caudalramus is 1.5 timeslongerthan the anal somite. Fortunately, Doropygus reticulatus sp. nov. is readily distinguishable from these two species because its caudal ramus is 2.5 times longer than the anal somite.
The characteristic shape of the outer seta on the basis of leg 1 may be a diagnostic feature of D. reticulatus sp. nov. allowing it to be differentiated from its congeners.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
SubPhylum |
Tunicata |
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |