Dorylaimellus (D.) japonicus, Ahmad & Naz, 2010
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1080/00222931003690706 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C24C64-FFD2-7F62-8EAA-FB537965FE1F |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Dorylaimellus (D.) japonicus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
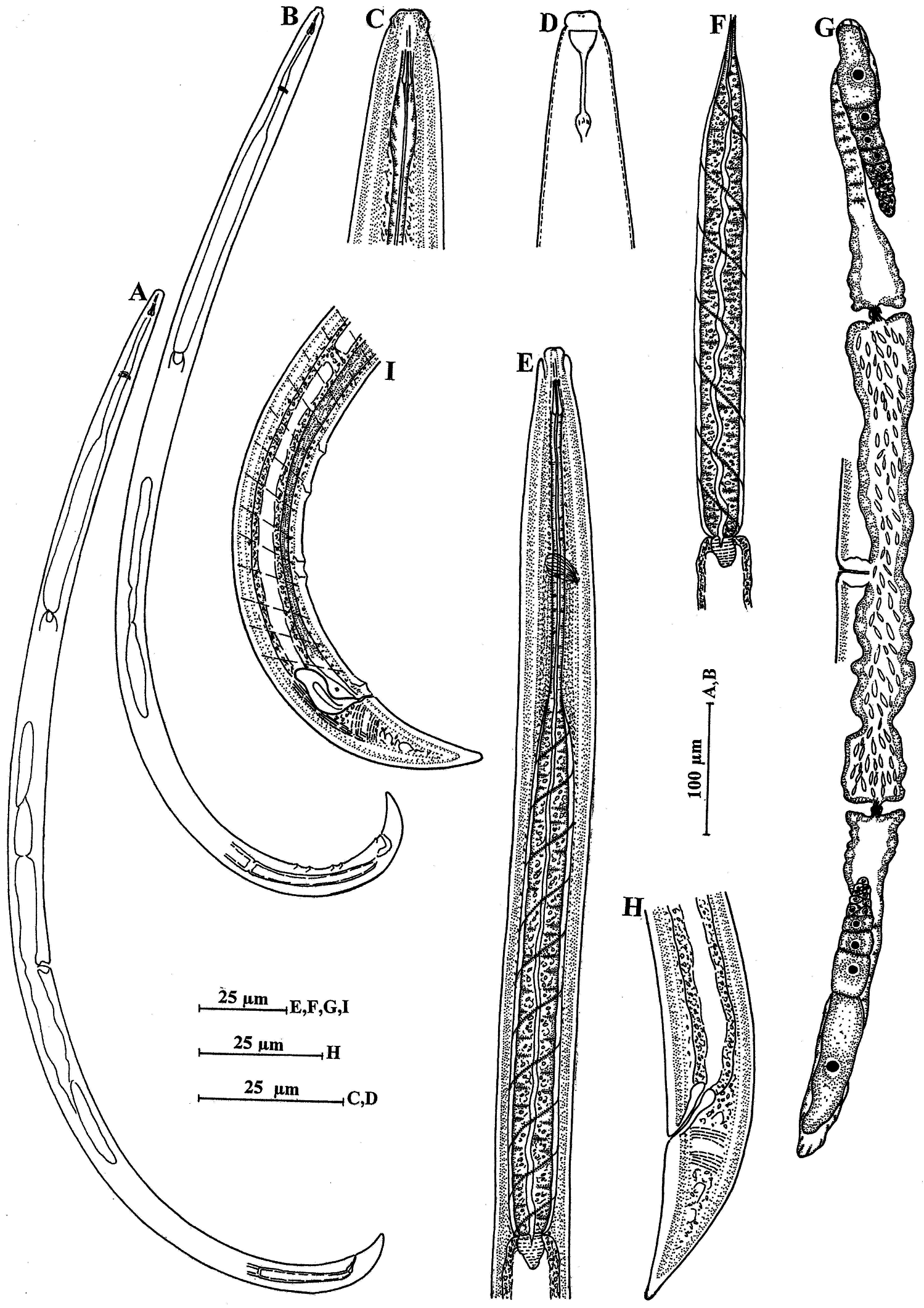
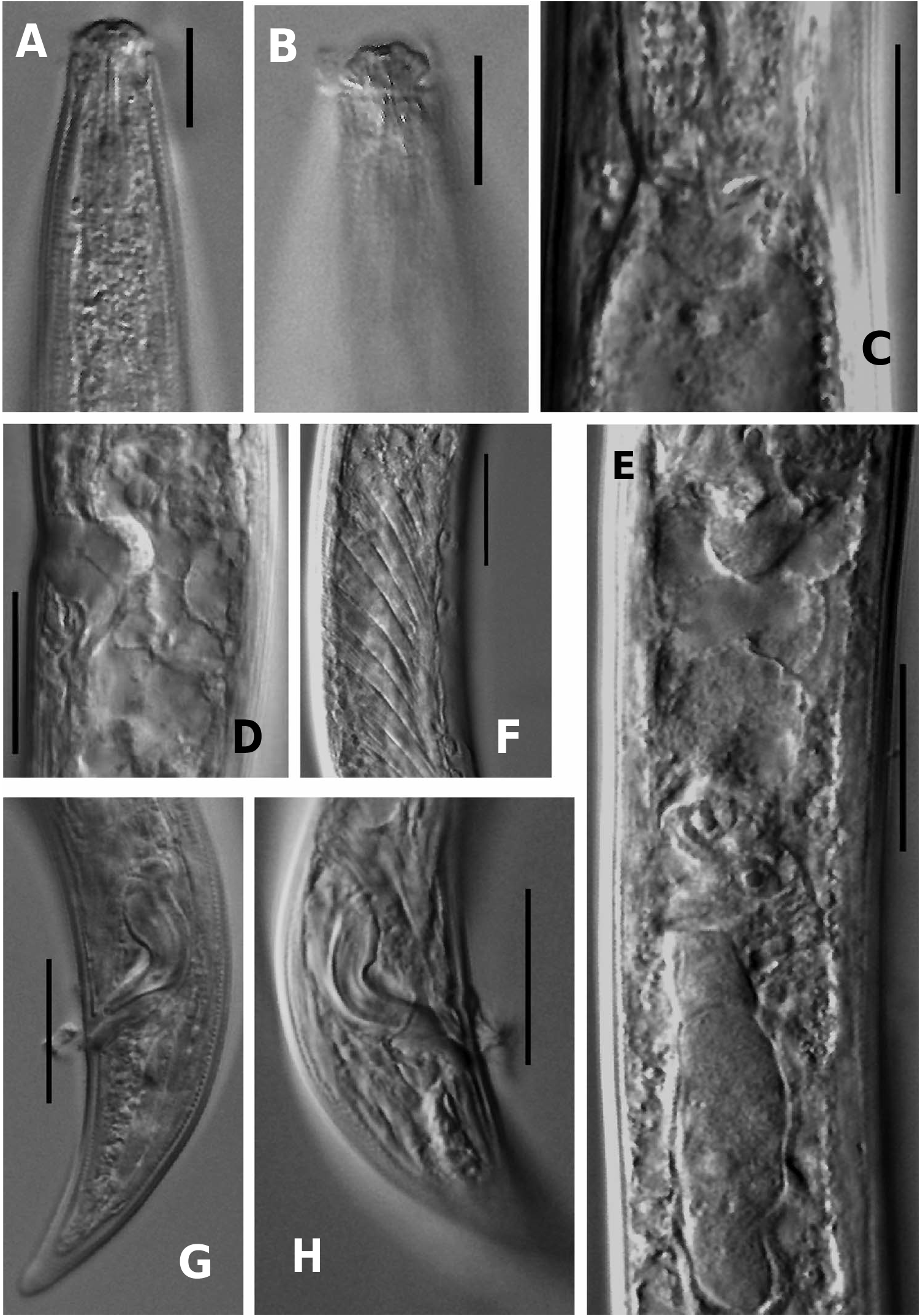
Dorylaimellus (D.) japonicus sp. nov.
( Figures 5A–I View Figure 5 , 6A–H View Figure 6 ; Table 3)
Description
Female. Body curved ventrad upon fixation, tapering towards both extremities. Cuticle with fine transverse striations, 1.5 µm thick at mid-body and 2–3 µm at tail. Lateral chords about one-third of body width at mid-body, with indistinct glandular organs. Lateral, dorsal and ventral body pores indistinct. Lip region distinctly offset by constriction, about twice as wide as high or about one-quarter as wide as body width at neck base. Four cuticularized pieces present around oral opening. Amphids large stirrup-shaped, their aperture about as wide as lip region width. Odontostyle slender, about 0.6–0.7 times lip region width long, its aperture about one-third of its length. Guiding ring obscure. Odontophore poorly flanged, 1.5–1.6 times the odontostyle length. Nerve ring encircling the anterior part of pharynx at 25–30% of neck length from anterior end. Pharyngeal expansion gradual; expanded part occupying about 54–65% of total neck length, enclosed in a thick sheath of dextrally spiral muscles. Cardia short, rounded, about one-quarter to one-third of corresponding body width long. Genital system didelphic–amphidelphic; both the sexual branches almost equally developed. Ovaries reflexed, not reaching or surpassing the oviduct–uterus junction, measuring 50–60 µm (anterior) and 60–85 µm (posterior) with oocytes arranged in a single row except near tip. Oviduct joining ovary subterminally, measuring 10–15 µm (anterior) and 10–14 µm (posterior), consisting of a long slender part with prismatic cells and a slightly wider pars dilatata with wide lumen. Sphincter present between oviduct–uterus junction. Uterus a small tube, measuring 10–15 µm (anterior) and 10–16 µm (posterior), differentiated into an expanded distal part with wide lumen filled with spermatozoa and a comparatively narrower proximal part. Vulva longitudinal. Vagina extending inward, about one-third of corresponding body width; pars proximalis vaginae 6–7 µm, with convex walls; pars refringens vaginae absent; pars distalis vaginae 1.0 1.2 µm, with rounded walls. Prerectum about 4–5 anal body widths long. Rectum about as long as anal body width. Tail elongate, conoid with rounded terminus, ventrally almost straight, dorsally convex, 1.9–2.0 anal body widths long. Caudal pores two on each side.
Male. Similar to female in general morphology, except for posterior region being more curved ventrad because of the presence of copulatory muscles. Supplements, an adanal pair and four spaced ventromedians, starting above the range of spicules. Spicules stout, relatively broad in proximal half and strongly ventrally bent near middle, about 1.1–1.3 anal body widths long. Lateral guiding pieces absent. Prerectum 5.0–5.5 anal body widths long. Tail elongate, conoid with rounded terminus, ventrally slightly concave, dorsally convex, 1.6–2.0 anal body widths long. Caudal pores two on each side.
Type habitat and locality
Grassland from Hirakubozaki, Iriamote Island, south Japan, Japan.
Type specimens
Holotype female on slide Dorylaimellus ( D.) japonicus sp. nov. / 1; paratype females and males on slides Dorylaimellus ( D.) japonicus sp. nov. / 2–5; deposited with the nematode collection of the Department of Zoology, Aligarh Muslim University, India.
Diagnosis and relationships
Dorylaimellus ( D.) japonicus sp. nov. is characterized by having 0.9–1.0 mm long body; 4–5 µm long odontostyle; poorly flanged odontophore about 1.5–1.6 times the odontostyle length; long pharynx, its expanded part 54–65% of total neck length; 22–25 µm long strongly ventrally arcuate spicules; four ventromedian supplements and elongate conoid tail with subacute terminus.
The new species belongs to the subgenus Dorylaimellus Jairajpuri and Ahmad, 1980 and comes close to Dorylaimellus virginianus Cobb, 1913 in tail shape. However, it differs, from it in having shorter body length (0.9–1.0 vs 1.2–1.4 mm), shorter odontostyle (4–5 vs 7–7.5 µm), shorter and poorly flanged odontophore (vs longer, twice the odontostyle length and broadly flanged odontophore), longer pharynx (b = 2.5–3.5 vs 4.0–5.1) and shorter spicules lacking lateral guiding pieces (spicules 22–25 vs 29–30 µm; lateral guiding pieces present).
The new species comes close to Dorylaimellus monticolus Clark, 1963 in the size of pharynx, but differs from it in having longer body (0.9–1.0 vs 0.6–0.7 mm), distinctly striated cuticles (vs cuticle smooth), shorter odontostyle (4–5 vs 7.5 µm), and in the tail shape (convex–conoid with subacute terminus vs convex–conoid with bluntly rounded or subdigitate terminus). Andrássy (1967) synonymized Dorylaimellus directus Heyns, 1963 with D. monticolus . Heyns and Jordan (1985) made a detailed study of Dorylaimellus directus , D. monticolus as well as Dorylaimellus montenegricus Andrássy, 1959 and concluded that the three species can be distinguished on the basis of relative length of basal pharyngeal bulb and the total stylet length. Our new species, although it belongs to this group, has a smaller odontostyle (vs 7.5 µm in D. monticolus ; 8.5 µm in D. montenegricus and about 9.0 µm in D. directus ).
The new species is also close to Dorylaimellus graminus Kruger, 1965 in having short odontostyle and shape and size of spicules, but differs in having shorter and poorly flanged odontophore (vs odontophore broadly flanged, about twice the length of odontostyle), longer pharynx (b = 2.5–3.5 vs 4.1–4.8), longer expanded part of pharynx (50–52% vs 54–65%) and in having differently shaped female tail (subacute terminus vs sharply rounded terminus).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.