Heliophanus xerxesi Logunov, 2009
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.35929/RSZ.0003 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5752202 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03BDA37E-FFF7-FFB6-FC65-3EB5B3A69346 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Heliophanus xerxesi Logunov, 2009 |
| status |
|
Heliophanus xerxesi Logunov, 2009 View in CoL
Figs 1-13 View Figs 1-8 View Figs 9-12 View Fig
Heliophanus xerxesi Logunov, 2009: 905 View in CoL , figs 13-17.
Material examined: MMUE G7635.1 View Materials ; 1 male, 1 female; IRAN, Ilam Province, Darrekh Shank, Kabirkuh , c. 32°54’N, 47°44’E; III.2015; collector unknown. – ISEA 001.8437 ; 1 male; IRAN, Markazi Province, Tafresh County, c. 8 km SW of Tafresh, river valley, 34°37’30-37”N, 49°56’46-49”E, 2300-2312 m a.s.l.; 29.V.2017; leg. O.E. Kosterin.
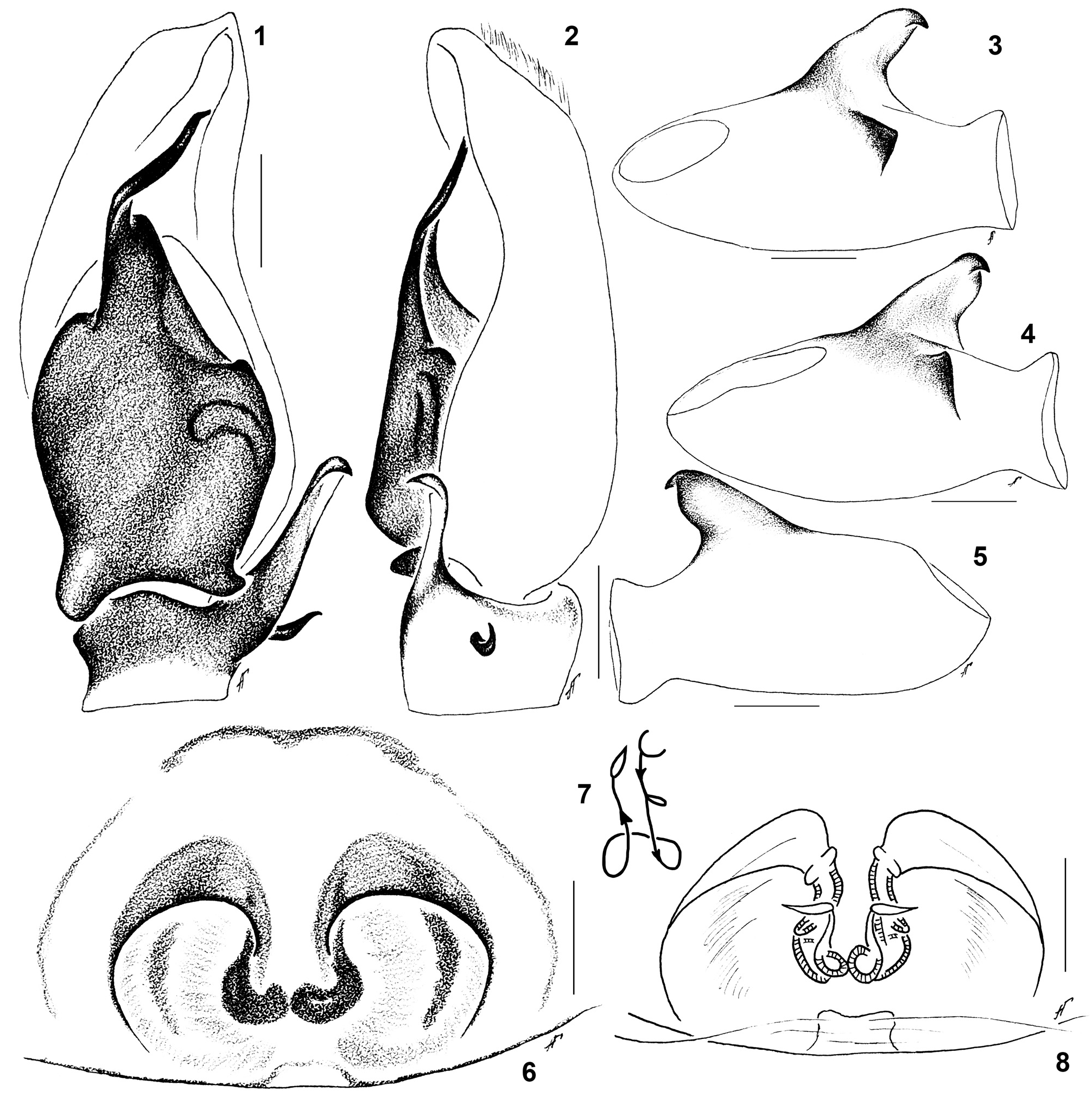
Extended diagnosis: The female copulatory organs of H. xerxesi are similar to those of H. forcipifer Kulczyński, 1895 , but differ in having larger epigynal wings ( Fig. 1 View Figs 1-8 cf. Rakov & Logunov, 1997: fig. 81) and markedly smaller spermathecae ( Fig. 3 View Figs 1-8 cf. Rakov & Logunov, 1997: figs 82-83). For the diagnosis of the male, see Logunov (2009).
Description:
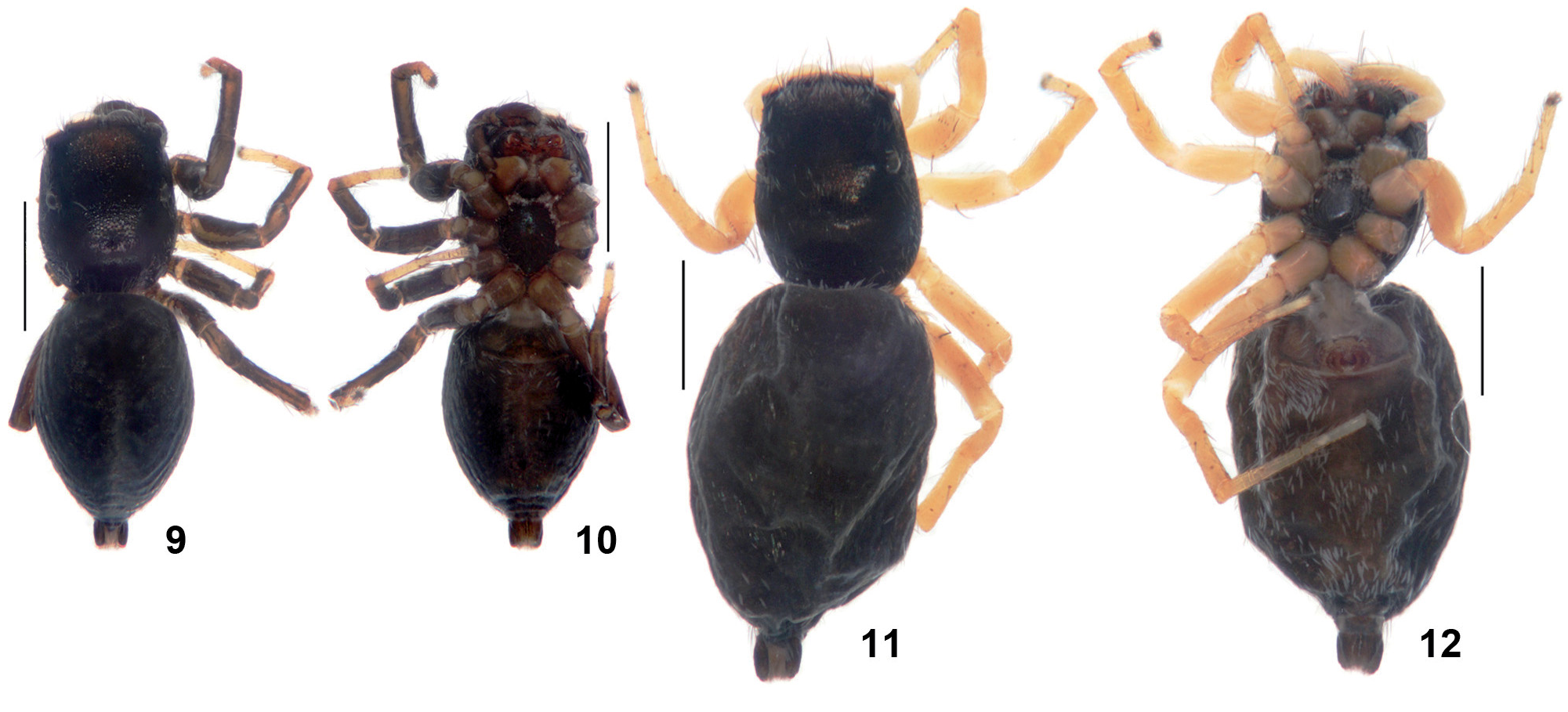
Male: See Logunov (2009). The studied male is illustrated in Figs 1-5 View Figs 1-8 , 9-10 View Figs 9-12 .
Female: Carapace 1.70 long, 1.30 wide, 0.75 high at PLE. Ocular area 0.75 long, 1.05 wide anteriorly and 1.05 wide posteriorly. Diameter of AME 0.35. Abdomen 2.70 long, 1.90 wide. Cheliceral length 0.50. Clypeal height 0.05. Length of leg segments: I 2.65 (0.80 + 0.50 + 0.55 + 0.45 + 0.35); II 2.45 (0.80 + 0.40 + 0.50 + 0.45 + 0.30); III 3.00 (0.90 + 0.50 + 0.55 + 0.65 + 0.40); IV 3.85 (1.15 + 0.55 + 0.85 + 0.80 + 0.50). Leg spination: I: Fm d 1-1-1; Tb pr 0-1, v 2-0; Mt v 2-2 ap. II: Fm d 1-1-1; Tb pr 0-1, v 1-0; Mt v 2-2 ap. III: Fm d 1-1-2; Tb pr and rt 0-1, v 2 ap; Mt pr 2 ap, rt 2 ap, v 2 ap. IV: Fm d 1-1-1; Tb pr and rt 1-1, v 2 ap; Mt pr and rt 1-2 ap, v 1-0-2 ap. Coloration: Carapace dark brown, almost black, shiny, covered with sparse white scales ( Fig. 11 View Figs 9-12 ). Sternum dark brown ( Fig. 12 View Figs 9-12 ). Labium and endites brown, with pale apexes. Chelicerae dark brown. Clypeus and cheeks brown, covered with short white hairs. Abdomen brown ventrally, covered with white scales; dorsum dark brown, covered with white and iridescent scales ( Fig. 11 View Figs 9-12 ). Book-lung covers brown. Spinnerets dark brown. Palps yellow, covered with white hairs. Palpal coxa dark brown, palpal tibia covered with brown hairs. All legs yellow. Coxa IV dark brown retrolaterally. Fm I with four stridulatory hairs. Epigyne and spermathecae as in Figs 6-8 View Figs 1-8 : copulatory openings hidden under C-shaped epigynal wings ( Fig. 6 View Figs 1-8 ), spermathecae small, with two short accessory glands ( Fig. 8 View Figs 1-8 ).
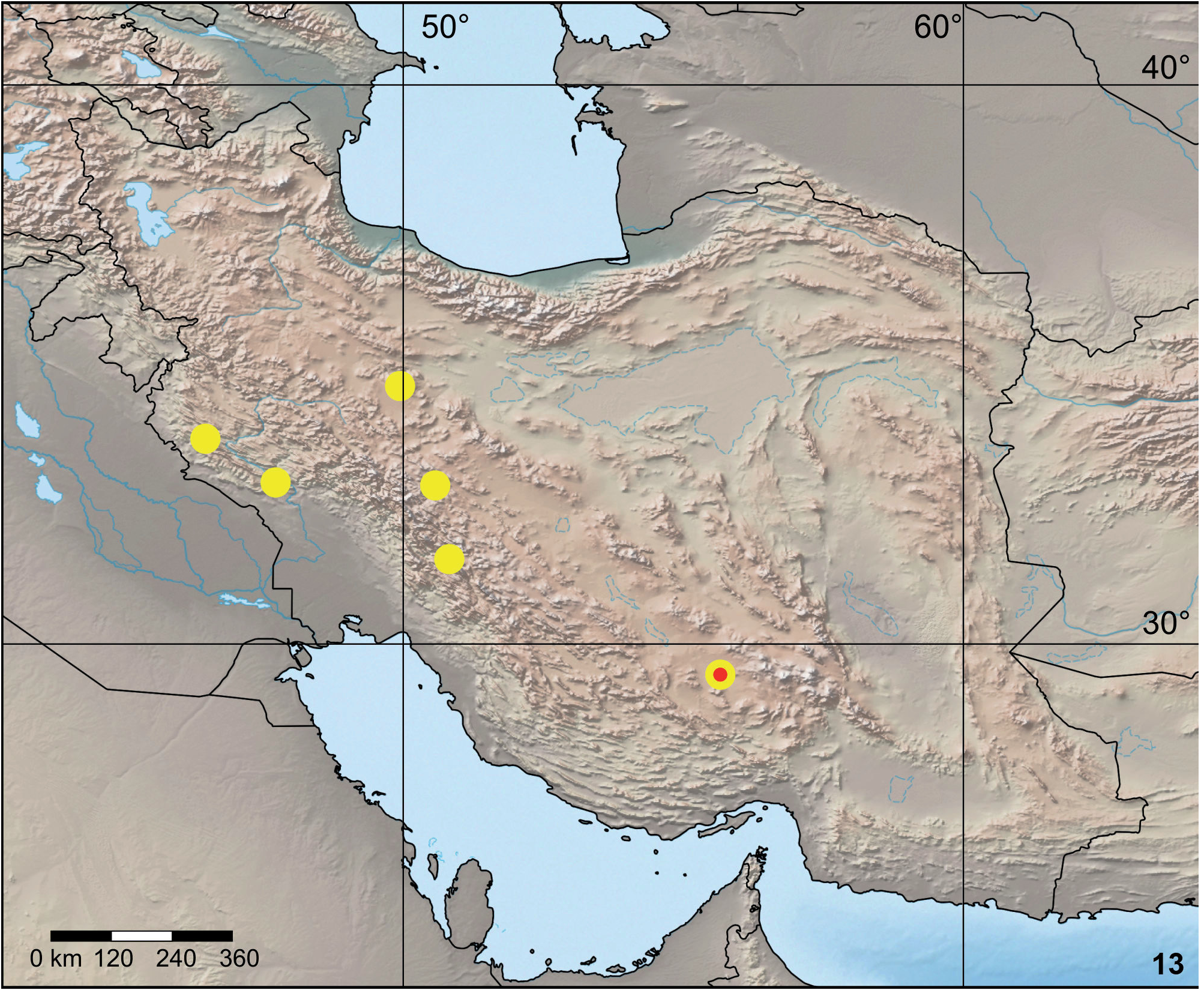
Distribution: Heliophanus xerxesi is an Iranian endemic, known from Chaharmahal & Bakhtiari, Ilam, Isfahan, Markazi and Kerman provinces, western to southeastern Iran ( Fig. 13 View Fig ) ( Logunov, 2009; Zamani et al., under review; present data).
| MMUE |
Museum of Manchester University |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Salticinae |
|
Tribe |
Chrysillini |
|
Genus |
Heliophanus xerxesi Logunov, 2009
| Azarkina, Galina N. & Zamani, Alireza 2020 |
Heliophanus xerxesi
| Logunov D. V. 2009: 905 |