Hipposideros griffini, Thong, Puechmaille, Denzinger, Dietz, Csorba, Bates, Teeling & Schnitzler, 2012
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.3739808 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6617540 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03BD87A2-C67D-A20F-FF31-F64EFB1C5151 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Hipposideros griffini |
| status |
|
28. View Plate 17: Hipposideridae
Griffin’s Leaf-nosed Bat
Hipposideros griffini View in CoL
French: Phyllorhine de Griffin / German: Griffin-Rundblattnase / Spanish: Hiposidérido de Griffin
Other common names: Griffin's Roundleaf Bat
Taxonomy. Hipposideros griffini Thong et aL, 2012 View in CoL ,
“Cat Ba National Park, Cat Ba Island, Ha Long Bay, Vietnam, 20°48’N, 107°01'E, 248 m above sea level (m a.s.l.).” GoogleMaps
Hipposideros griffini is in the armiger species group. Monotypic.
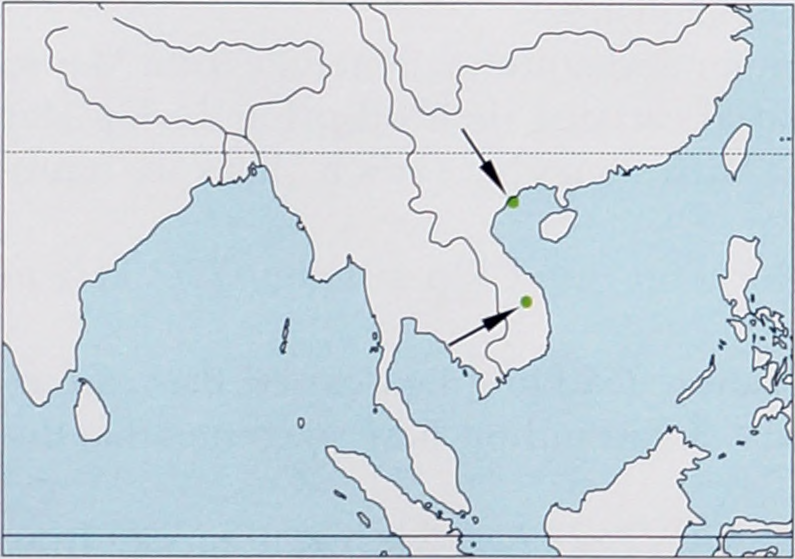
Distribution. NE & C Vietnam, known only from Cat Ba I, Ha Long Bay (Haiphong Province) and Chu Mom Ray National Park (Kon Turn Province). View Figure
Descriptive notes. Ear 27-5-30 mm, hindfoot 14-1-15-8 mm, forearm 83-3-90 mm; weight 44 g. Pelage of Griffin’s Leaf-nosed Bat is brownish or grayish, being darker on dorsum than on ventral area; on each hair, distal part is also darker than basal portion. This species presents four pairs of supplementary lateral leaflets. Second pair of leaflets is longest and widest. Fourth pair of leaflets is shortest and least pronounced, whereas posterior part of third leaflet is merged with an excrescence. Upper edge of posterior leaf is cusp-shaped. Ears are triangular and tail is long. Males present a noticeable excrescence and a sexual sac, which become more pronounced during breeding season.
Habitat. Both primary and degraded forest. Griffin’s Leaf-nosed Bat has been reported in karstic mountain areas, as well as in lowlands.
Food and Feeding. Foraging behavior and diet are still unknown for Griffin’s Leafnosed Bat, but it probably forages in primary as well as disturbed forests; its diet may be based on insects.
Breeding. One young was captured in June. Males have been reported breeding in August at Chu Mom Ray National Park.
Activity patterns. Griffin’s Leaf-nosed Bat has been reported roosting in rock piles, crevices, caves, old mines, and hollow trees. Echolocation call frequency is c.76-6— 79-2 kHz.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. Griffin’s Leaf-nosed Bat roosts alone or in pairs.
Status and Conservation. Not assessed on 7%e IUCNRed List due to its recent recognition as a species. More research on the ecology and population size and trends of Griffin’s Leaf-nosed Bat is needed to permit the establishment of adequate conservation and management measures.
Bibliography. Thong Vu Dinh, Puechmaille, Denzinger, Dietz et al. (2012)
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Hipposideros griffini
| Don E. Wilson & Russell A. Mittermeier 2019 |
Hipposideros griffini Thong et aL, 2012
| Thong, Puechmaille, Denzinger, Dietz, Csorba, Bates, Teeling & Schnitzler 2012 |