Hipposideros ridleyi, H. C. Robinson & Kloss, 1911
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3739808 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3810878 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03BD87A2-C669-A21B-FF29-FED2FC1F4BD6 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Hipposideros ridleyi |
| status |
|
87. View Plate 19: Hipposideridae
Ridley’s Leaf-nosed Bat
Hipposideros ridleyi View in CoL
French: Phyllorhine de Ridley / German: Ridley-Rundblattnase / Spanish: Hiposidérido de Ridley
Other common names: Ridley's Roundleaf Bat, Singapore Roundleaf Horseshoe Bat
Taxonomy. Hipposideros ridleyi H. C. Robinson & Kloss, 1911 View in CoL ,
“Botanic Gardens, Singapore.”
Hipposideros ridleyi was formerly included in the bicolor species group but is now placed in the new ater species group. Monotypic.
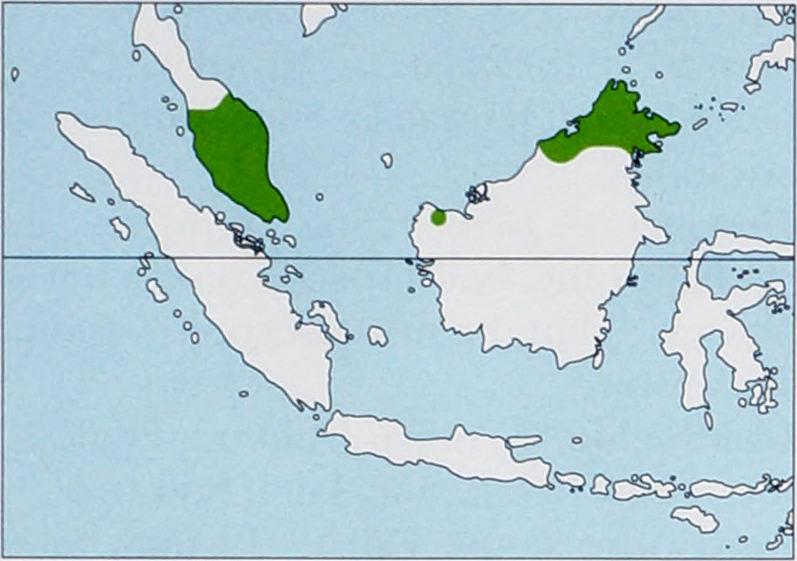
Distribution. Malay Peninsula and N & SW Borneo ( Sabah, Sarawak, and Brunei); probably also occurs in the rest of Borneo (Kalimantan), but this has not yet been confirmed. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Tail 25-29 mm, ear 24-28 mm, forearm 47-51 mm; weight 7-5-13-5 g. Ears of Ridley’s Leaf-nosed Bat is large. Pelage is uniformly dark brown, slightiy paler on ventral side. Noseleaf is wide and rounded, with deep emargination on anterior leaf. It has no lateral supplementary leaflet. Intemarial septum forms a large disk shape.
Habitat. Ridley’s Leaf-nosed Bat was captured in flat lowland primary rainforests.
Food and Feeding. No information.
Breeding. In Peninsular Malaysia, females were found pregnant with one embryo in March-May, and lactating in May-October.
Activity patterns. Ridley’s Leaf-nosed Bat was captured c.0-5-3 m aboveground in gaps of lowland forest understory. It roosts in hollow trees, pipes, and old houses. Call frequency is 61-62 kHz (Malay Peninsula) and 65-67 kHz ( Sabah).
Movements, Home range and Social organization. Ridley’s Leaf-nosed Bats roost in small groups of up to 15 individuals in very large fallen trees with deep hollows. The roost is sexually segregated for the most part. The species was reported to share a hollow tree with Malayan Tailless Leaf-nosed Bats ( Coelops robinsoni ).
Status and Conservation. Classified as Vulnerable on The IUCN Red List. The population of Ridley’s Leaf-nosed Bat is generally declining. The major threat is deforestation.
Bibliography. Corbet & Hill (1992), Francis (2008a), Francis, Kingston & Bumrungsri (2008), Kingston et al. (2006), Phillipps & Phillipps (2016), Simmons (2005).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Hipposideros ridleyi
| Don E. Wilson & Russell A. Mittermeier 2019 |
Hipposideros ridleyi
| H. C. Robinson & Kloss 1911 |