Elginus bispinus, Stiller, M., 2009
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.2135.1.1 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03BD0C4B-FFBE-D17D-FF46-FF71FCBC28C6 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Elginus bispinus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Elginus bispinus View in CoL sp.n.
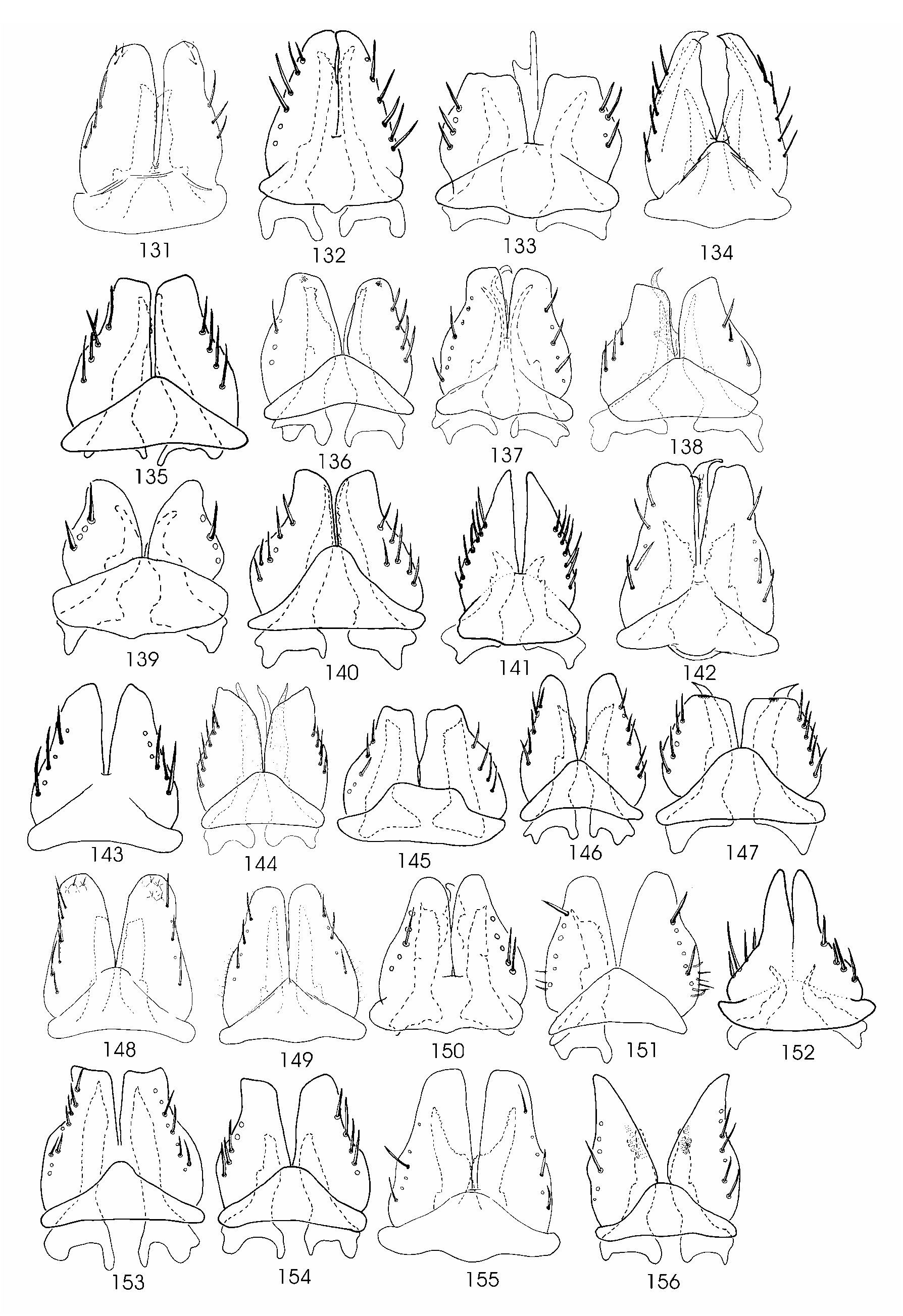
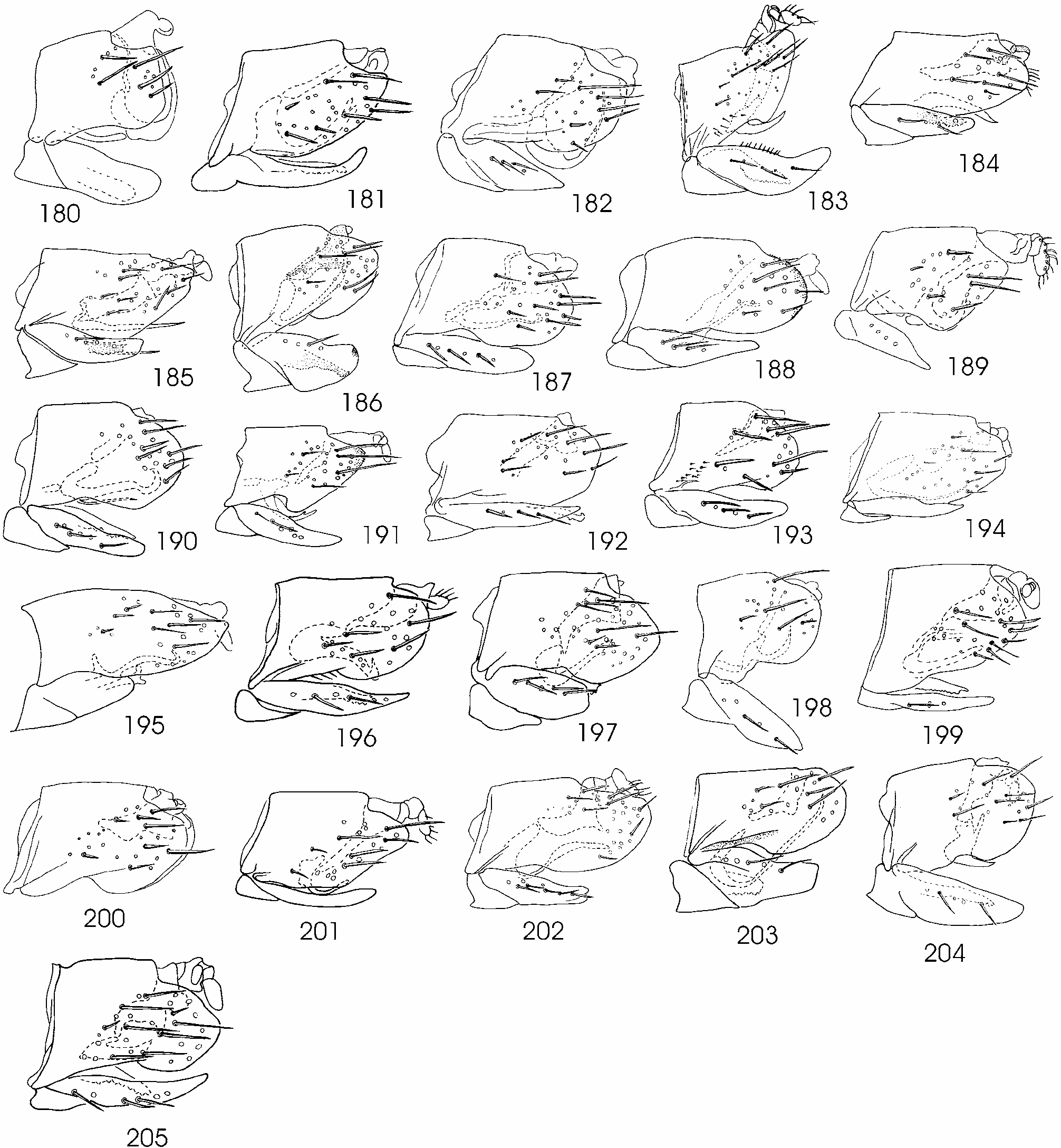
( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1–8 , 52 View FIGURES 51–77 , 79 View FIGURES 78–104 , 106 View FIGURES 105–130 , 132 View FIGURES 131–156 , 181 View FIGURES 180–205 , 207 View FIGURES 206–232 , 233 View FIGURES 233–258 )
Diagnosis. Aedeagus with apex of shaft bifurcate and flattened dorsoventrally, and apophysis of style elongate.
Etymology. Latin, to describe the forked apex of the aedeagal shaft.
Colour. Male & female. Vertex indistinctly marked, without wedge-shaped mark. Fuscous markings in the central cells of the tegmina ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1–8 ).
Dimensions. Male (n = 6). Lengths: apex of vertex to apex of tegmina 2.7–2.9 mm, apex of vertex to apex of abdomen 2.3–2.4 mm; vertex medially 0.4 mm; vertex laterally next to eye 0.2–0.3 mm; pronotum medially 0.3 mm; scutellum medially 0.2–0.3 mm. Maximum widths: head 0.8–0.9 mm; pronotum 0.7 mm; scutellum 0.4 mm. Ocellus: diameter 17–27 µm; ocellocular distance 41–55 µm.
Genital capsule. Male. Aedeagal shaft flattened dorso-ventrally; shaft short, 1.8 times as long as dorsal apodeme; apex with gonopore flanked by spines; gonopore dorsad ( Figs 52 View FIGURES 51–77 , 79 View FIGURES 78–104 ). Connective elongate ( Fig. 106 View FIGURES 105–130 ). Plate elongate, apex rounded, fused with valve ( Fig. 132 View FIGURES 131–156 ). Pygofer lobe apex bluntly pointed ( Fig. 181 View FIGURES 180–205 ). Style apophysis narrow, as long as anterior lateral lobe, up to 7 teeth ventrally; extending through most of plate ( Fig. 207 View FIGURES 206–232 ).
Dimensions. Female (n = 3). Lengths: apex of vertex to apex of tegmina 3.1–3.2 mm, apex of vertex to apex of abdomen 3.1–3.2 mm; vertex medially 0.5 mm; vertex laterally next to eye 0.3–0.4 mm; pronotum medially 0.3–0.4 mm; scutellum medially 0.3 mm. Maximum widths: head 1.0 mm; pronotum 0.8 mm; scutellum 0.4 mm. Ocellus: diameter 28 µm; ocellocular distance 39–59 µm.
Genital capsule. Female. Sternite VII apical margin triangular, apex with narrow V-shaped notch ( Fig. 233 View FIGURES 233–258 ).
Material examined. Holotype male. South Africa, Western Cape. Bokfontein Ceres , 32°25ʹS 19°15ʹE, 3.viii.1985, J.G. Theron ( SANC) GoogleMaps . Paratypes (5♂, 3♀). Western Cape . 5♂, 2♀, ibid. holotype ; 1♀, Goudiniweg Station Worcester, 33°36ʹ07.74ʺS 19°19ʹ59.88ʺE, 258 m, 13.xii.2004, M. Stiller ( SANC, USIC) GoogleMaps .
Remarks. This species is not closely related to species in the Fynbos or Grassland Biomes. No other species has a similarly flattened aedeagal shaft and complex apex of the shaft. Known mainly from one locality in the Fynbos Biome at which E. saltus also occurs. The latter species is larger, with the vertex more pointed, and it has a more variable colour pattern, that is, it either has fuscous paired markings on the vertex or it is darker with most cells of tegmina fuscous and the pronotum and vertex have dark makings. Elginus theroni also appears to occur more widely in the Fynbos Biome and can be recognized because its colouration that is even less distinct or it is without markings on the body.
| SANC |
Agricultural Research Council-Plant Protection Research Institute |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |