Cf. tyrannosaurus, Osborn, 1905, Osborn, 1905
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.3374/014.054.0202 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5233794 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03BA87C4-FFBD-FFDE-F5DE-FA04FE991C41 |
|
treatment provided by |
Jeremy |
|
scientific name |
Cf. tyrannosaurus |
| status |
|
FAMILY Tyrannosauridae Osborn, 1906
GENUS Tyrannosaurus Osborn, 1905
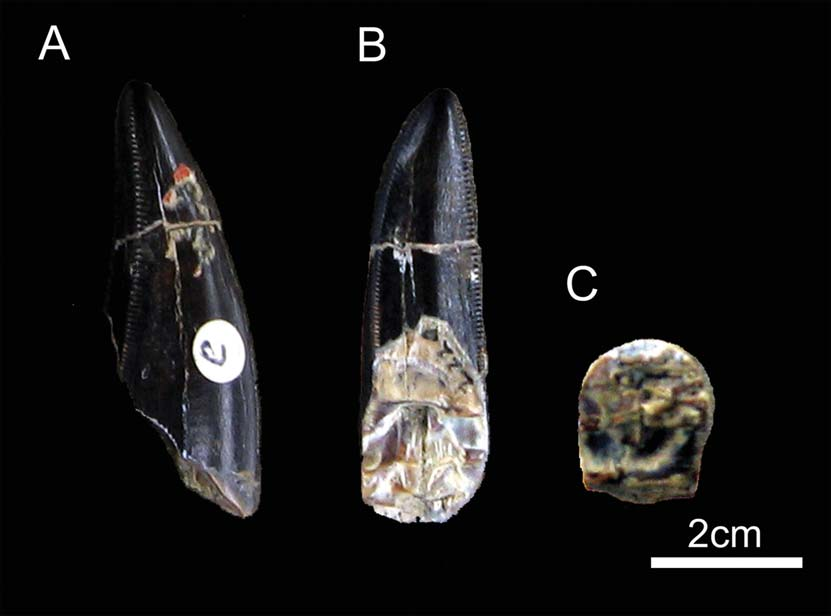
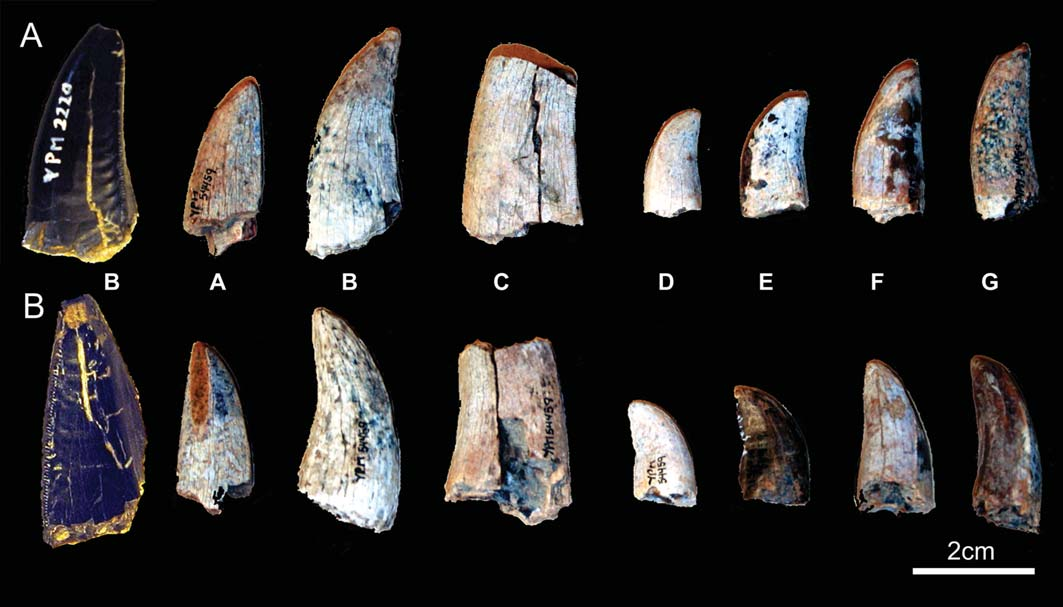
Material. YPM VP 002220(A, B) , one dentary tooth and one lateral tooth without roots and YPM VP 054459(A–G), seven lateral teeth without roots. Horizon and locality. Upper Cretaceous Lance Formation, Buck Creek, 37 km north of Lusk , Wyoming, USA .
Description.In this description nine teeth,specimens YPM VP 002220(A, B) and YPM VP 054459(A–G) are referred to cf. Tyrannosaurus .
The dentary tooth YPM VP 002220(A) ( Figure 9 View FIGURE 9 A–C) has a crown height of 4.8 cm and is missing the root. The crown has a D-shaped cross section, a characteristic of the first dentary tooth of Tyrannosaurus rex ( Brochu 2003; Smith 2005;N.L. Larson 2008). The labial face of the tooth is convex anteriorly, whereas the mesial and distal faces are flattened and elongated ( Smith and Dodson 2003; Smith 2005). The lingual face is rounded and apically and it resembles the premaxillary teeth ( Smith 2005). The basal long axis of the tooth is mesiodistally oriented the same way as it is in the known examples of T. rex ( Smith 2005) .The carinae are linguomesially and linguodistally oriented, whereas their bases are labially oriented ( Carr and Williamson 2004; Smith 2005).
The lateral teeth YPM VP 002220(B) and YPM VP 054459(A–G) ( Figure 10 View FIGURE 10 A–B) are significantly smaller when compared to teeth of an adult Tyrannosaurus rex . Their relatively small size suggests that these teeth belong to juveniles or subadult individuals. The teeth are laterally compressed, re-curved, serrated and have elliptical bases. In all the teeth the mesial carina has a linguomesial orientation and is situated close to the lingual face of the crown, whereas the distal carina is situated along the labiodistal edge of the crown ( Currie 2003a; Smith 2005). Both carinae meet and are contiguous over the tip of the crown ( Smith 2005). The labial and lingual faces of the tooth crown YPM VP 002220(B) have distinctive enamel wrinkles that are perpendicular to the apicobasal axis of the tooth crown as in some other examples of Tyrannosaurus teeth such as MOR 555 ( Brusatte et al. 2007).
| YPM |
YPM |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |