Singillatus, Nielson, 2015
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5181587 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:E574C53C-B3FF-4030-94F9-447B68595ABF |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03BA1722-D841-9676-7DAE-FE82FA21FB96 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Singillatus |
| status |
|
Key to species of Singillatus View in CoL (males)
1.
— Subgenital plate with 1 or 2 apical spines .................................................................................... 2 Subgenital plate without such spines ........................................................................................... 3 2(1).
—
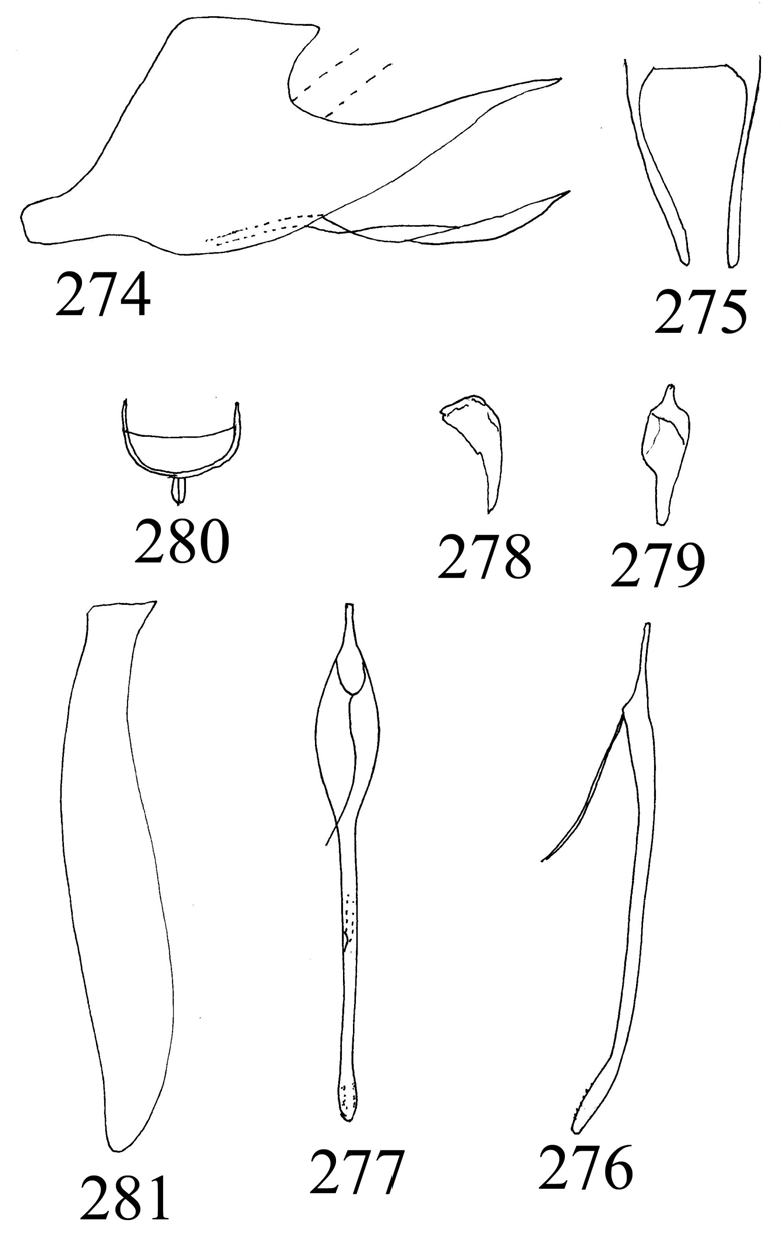
Subgenital plate with single apical spine ( Fig. 278 View Figures 274-281 , Nielson 1982); aedeagus with short subapical process (fig. 279, 280, Nielson 1982) ( India) ............................................ S. curtus (Nielson) View in CoL
Subgenital plate with 1 apical, 1 subapical spine (Fig. I, Zhang 1994); aedeagus with long, slender medial process (fig. M, L, Zhang 1994) ( China) .................... S. xanthopronotatus (Zhang)
3(1).
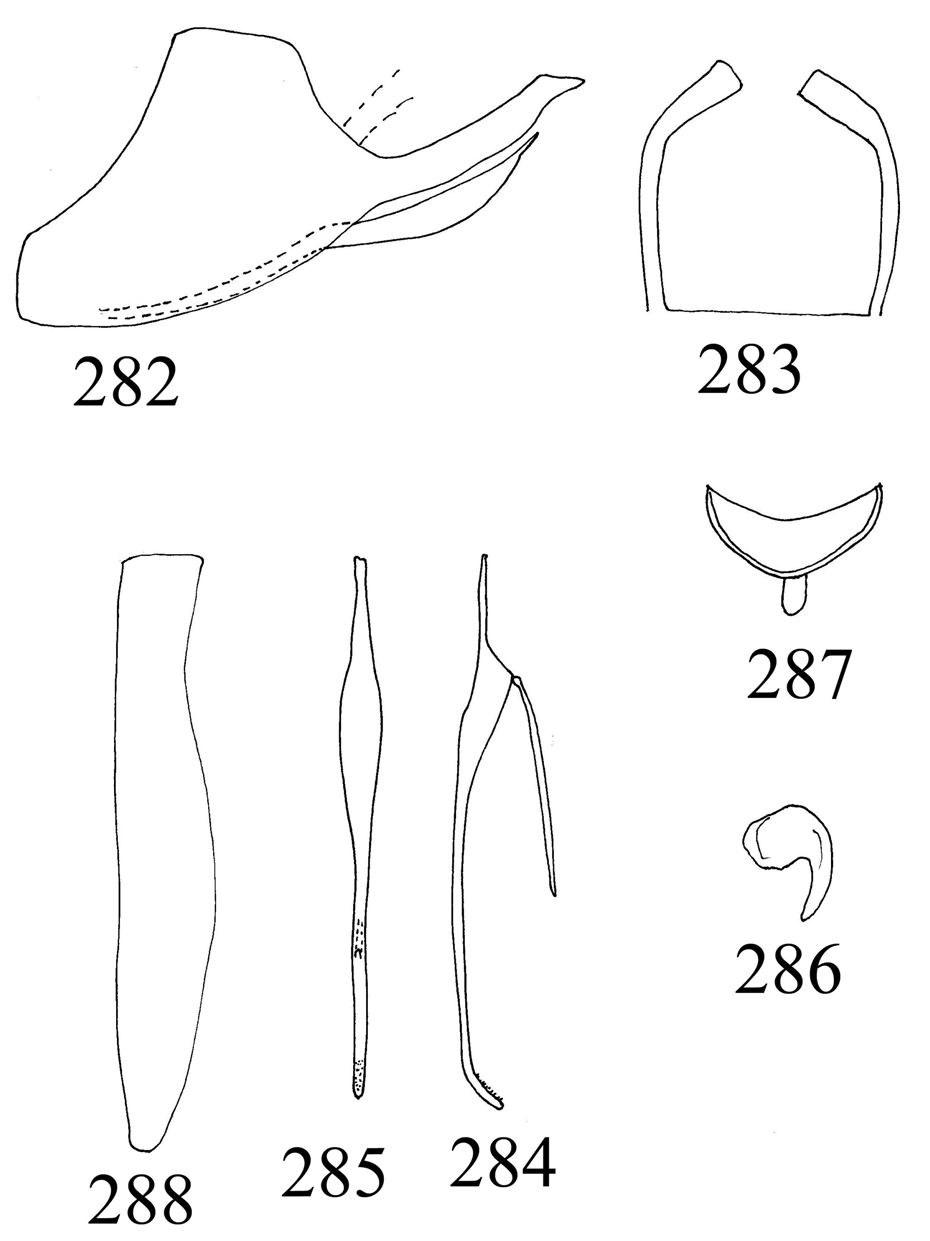
— Style with short to long, glabrous apophysis ............................................................................... 4 Style with very long apophysis with row of spines in distal half ( Fig. 287 View Figures 282-288 , Nielson 1982) ( Malaysia)
.................................................................................................................... S. unicus (Nielson) View in CoL
4(3).
— Pygofer in lateral view with long prominent caudoventral process ............................................ 5 Pygofer in lateral view without such process or with small digitate lobe .................................. 8
5(4).
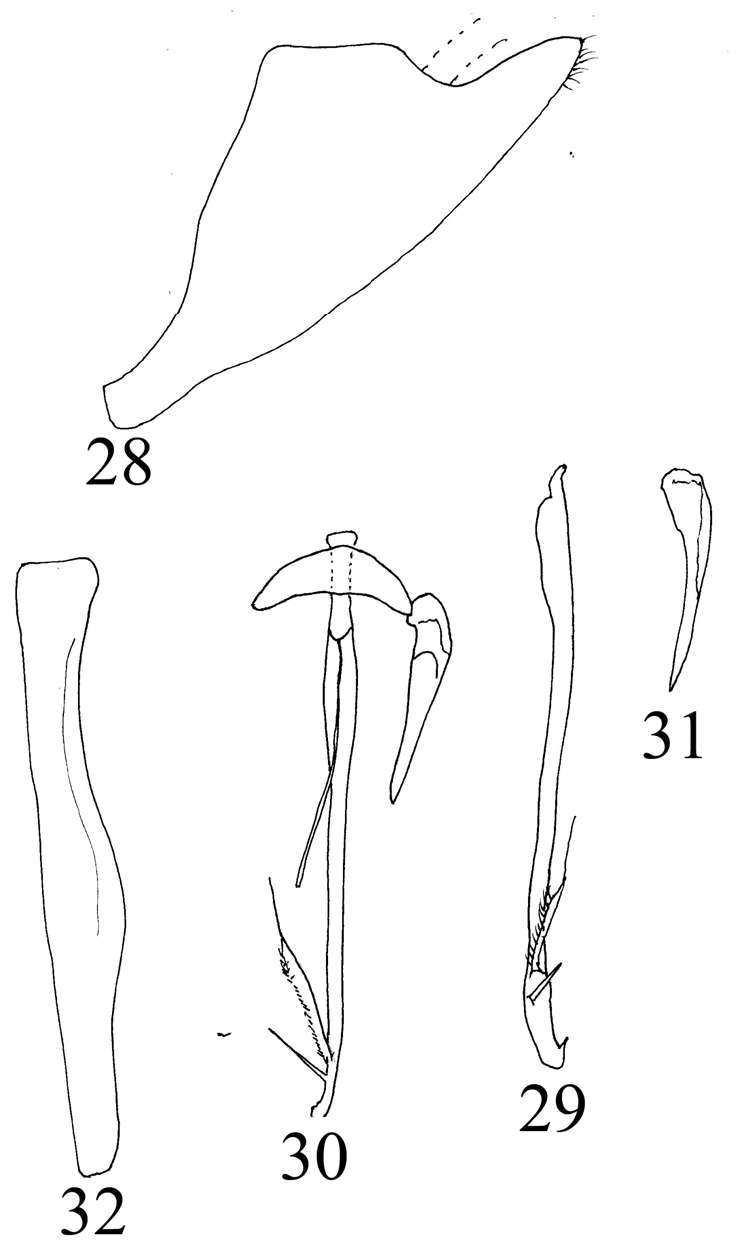
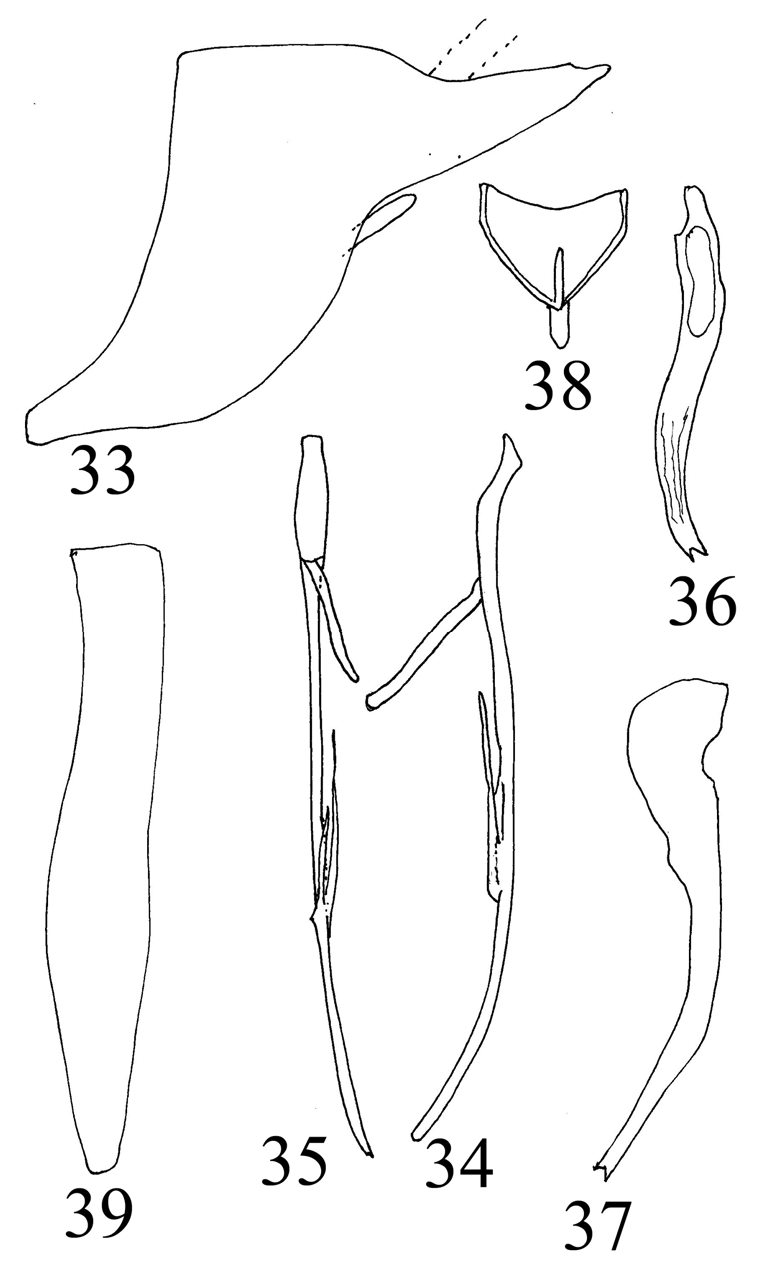
— Pygofer caudoventral process with accessory process(es) ........................................................... 6 Pygofer caudoventral process entire ( Fig. 31 View Figures 28-32 , Nielson 1990); subgenital plate obliquely truncate apically ( Fig. 35 View Figures 33-39 , Nielson 1990) ( India) ............................................. S. singularis (Nielson) View in CoL
6(5).
— Pygofer caudoventral process very broad with 2 accessory processes ........................................ 7 Pygofer caudoventral process very narrow with 1 subapical process ( Fig. 26 View Figures 20-27 , Nielson 1990)
( India) ...................................................................................................... S. furcatus (Nielson) View in CoL 7(6).
—
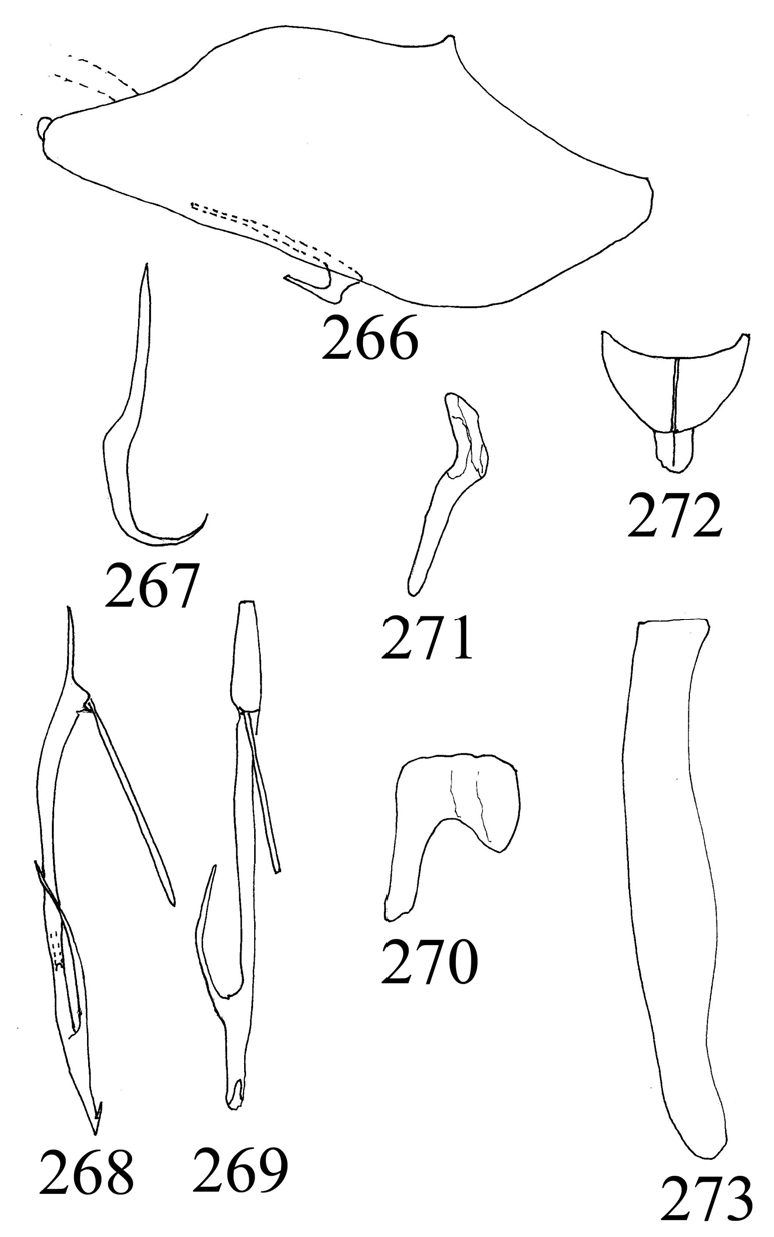
Aedeagus with very short subapical process ( Fig. 274 View Figures 274-281 , Nielson 1982); pygofer caudoventral process with 1 subbasal and 1 apical process ( Fig. 270 View Figures 266-273 , Nielson 1982) ( China, Laos) ........................... ................................................................................................................. S. laminus (Nielson) View in CoL
Aedeagus with very long subapical process (fig. 268, 269) ( India) ................................................ ........................................................................................................ S. ventrospinatus , sp. nov.
8(4).
— Style with moderately long, digitate apophysis, not exceeding midlength of aedeagal shaft ..... 9 Style with very long, sharply pointed apophysis exceeding midlength of aedeagal shaft ( Fig. 2 View Figures 1-12 ,
Freytag 2011) ( Thailand) ....................................................................... S. anisotus (Freytag) View in CoL 9(8).
—
Aedeagus with process arising subapically, distance between base of process and apex of shaft shorter than length of process ................................................................................................. 10
Aedeagus with process arising subapically, distance between base of process and apex of shaft greater than length of process ( Fig. 260, 261 View Figures 259-265 ) ( Indonesia ( Sumatra)) ....................................... .................................................................................................................. S. gracilius , sp. nov.
10(9).
—
Aedeagal process short, not reaching to or slightly extending basad of midlength of aedeagal shaft ........................................................................................................................................... 11
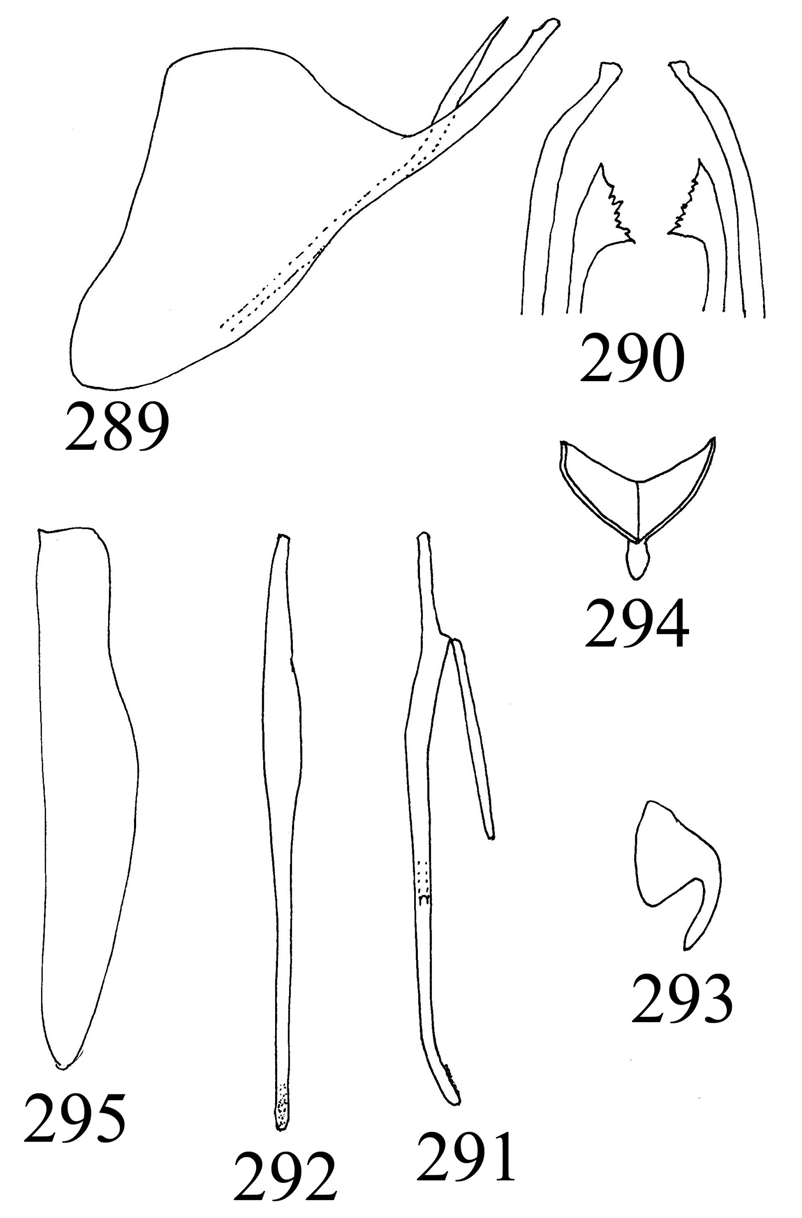
Aedeagal process very long, extending basad much beyond midlength of aedeagal shaft, shaft in lateral view with small, globular, subapical, serrated lobe ( Fig. 294 View Figures 289-295 , Nielson 1982) ( Malaysia, Raja Ampat Isl., Sabah) ................................................................. S. marginifrons (Walker)
11(10). Aedeagal process closely appressed to shaft ............................................................................... 12
— Aedeagal process not appressed to shaft, curved from base to apex ......................................... 13
12(11). Large species, length 8.60-10.00 mm.; aedeagus with short process, not reaching midlength of aedeagal shaft (fig. 339, 340, Nielson 1982) ( Malaysia Peninsula, ( Sarawak)) ......................... .................................................................................................................. S. mundus (Nielson)
— Small species, length 6.40-7.80 mm.; aedeagus with moderately long process, reaching to midlength of aedeagal shaft (fig. 333, 334, Nielson 1982) ( Laos, Thailand, Vietnam) ............................... ....................................................................................................................... S. reidi (Nielson)
13(11). Aedeagus in lateral view with subapical process arising from dorsal margin .......................... 14
— Aedeagus in lateral view with subapical process arising from ventral margin ( Fig. 12 View Figures 1-12 , Freytag 2011) ( Thailand) ......................................................................................... S. nudus (Freytag)
14(13). Pygofer in lateral view glabrous ................................................................................................. 15
— Pygofer in lateral view setose apically ........................................................................................ 16
15(14). Aedeagus in lateral view with very short subapical process, process about 1/5 as long as length of aedeagus, gradually tapered apically ( Fig. 329 View Figures 325-331 , Nielson 1982) ( Malaysia, Indonesia) .............. .................................................................................................................. S. apertus (Nielson)
— Aedeagus in lateral view with moderately long subapical process, process about ¼ as long as length of aedeagus, abruptly tapered about midlength (Fig. M, Zhang 1994) ( China) ............. ................................................................................................................... S. signatus (Zhang)
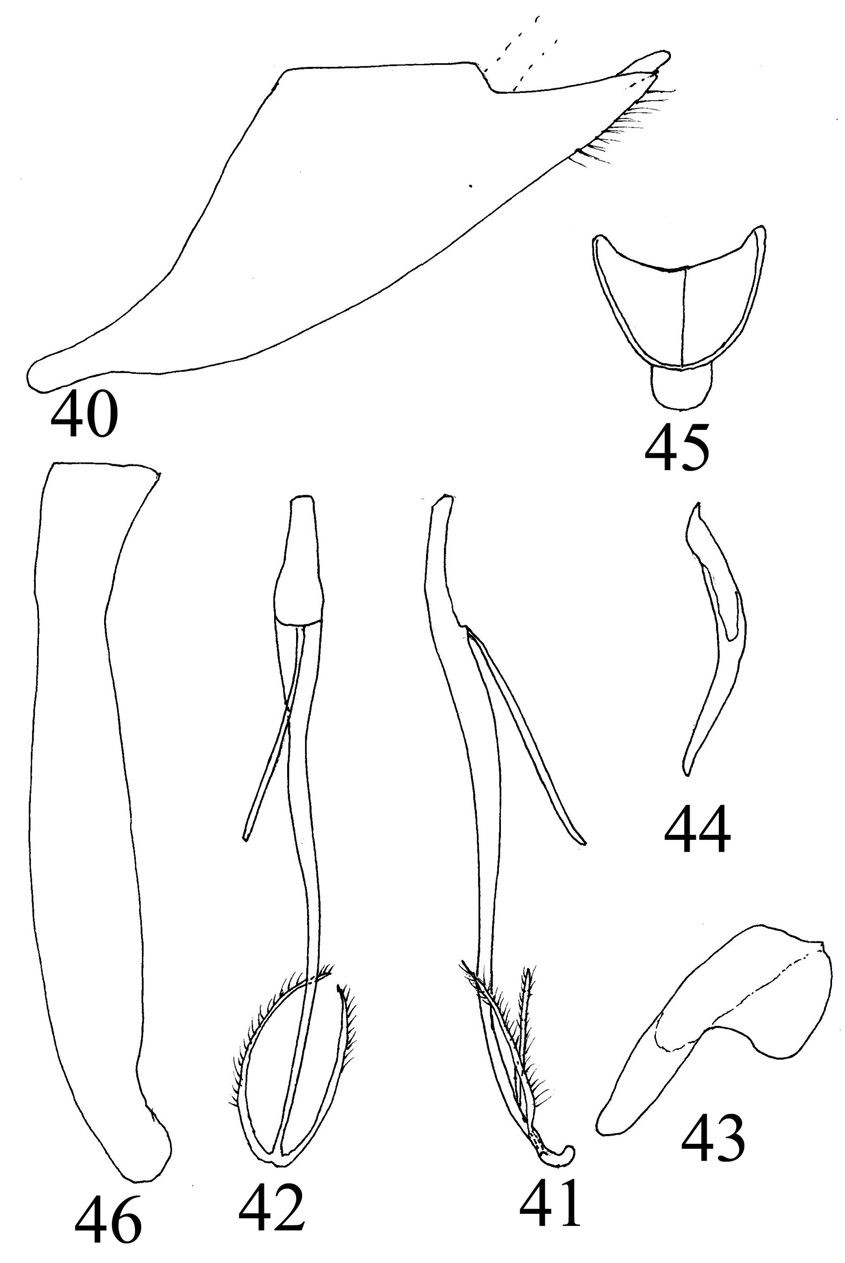
16(14). Aedeagus in dorsal or ventral view with shaft abruptly narrowed subapically ( Fig. 38 View Figures 33-39 , Nielson 1990); subgenital plate slightly constricted medially ( Fig. 40 View Figures 40-46 , Nielson 1982) ( Malaysia) ......... ........................................................................................................ S. viraktamathi (Nielson)
— Aedeagus in dorsal or ventral view with shaft not abruptly narrowed subapically ( Fig. 320 View Figures 318-324 , Nielson 1982); subgenital plate slightly inflated medially ( Fig. 319 View Figures 318-324 , Nielson 1982) ( Malaysia) ............................................................................................................ S. ventrosolus (Nielson)
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.