Teucrium ekimii Duman (1998: 125)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/phytotaxa.566.3.1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7140380 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B9879C-4764-FFB9-FF3B-CE60FEFCF787 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Teucrium ekimii Duman (1998: 125) |
| status |
|
Teucrium ekimii Duman (1998: 125)
Stem: In stem basal potion, the transition between primary and secondary structures was observed. Stem cross-sections revealed the characteristic four-cornered shape of Lamiaceae . The epidermis consists of a single layer of oblong or oval cells that are fragmented and covered by a thick cuticle layer. There are glandular and non- glandular trichomes on the epidermis. Epidermis cells are 15.77–54.78 × 11.19–20.86 μm in size. Under the epidermis, there are 6–8 rows of parenchymatic cortex. The parenchymatic cells are quadrangular-flat with the size of 15.63–42.23 × 9.30–17.82 μm. The endodermis is conspicuous and consists of a single row of rectangular cells. The endodermis cells are 10.07–19.37 × 4.65–10.87 μm in size. Phloem and xylem are prominent and 2–3 rows of cambium are distinguished between the two. The tracheal elements of protoxylem are larger than those of metaxylem. Tracheal cells of xylem elements are 6.98–87.33 μm in size. Pith rays are composed of 1–2 rows of cells. In the middle part of the stem, there is a pith composed of large parenchymatic cells. The diameter of the parenchyma cells is between 3.10–19.37 μm ( Fig. 1B View FIGURE 1 ).
Leaf: In leaf cross-section, there is an epidermis layer consisting of a single row of oval or oblong cells. Upper epidermis cells are considerably larger than the lower epidermis cells. Upper epidermis cells are 13.52–61.05 × 10.14– 42.80 μm and lower epidermis cells are 3.38–24.56 × 3.38–11.22 μm in size. Both epidermis layers are covered with cuticle. There are glandular and non-glandular trichomes in both surface of the leaf blade, but trichome density is higher in the lower epidermis. Leaves are dorsiventral (bifacial). There is a palisade parenchyma consisting of 2–3 layers under the upper epidermis. Palisade parenchyma cells are cylindrical. Palisade parenchyma cells are 3.26–12.12 × 13.98–27.03 μm in size. The portion of the mesophyll occupied by the palisade parenchyma is 51–67%. Below the palisade parenchyma, there is a sponge parenchyma consisting of 3-4 rows of ovoid or circular cells. Sponge parenchyma cells are 4.55–16.78 μm in diameter. The mesophyll tissue is 87.41–139.10 µm thick. Both parenchyma cells contain starch grains ( Fig. 1C View FIGURE 1 ).
Leaves are amphistomatic as stomata are observed on both surfaces. However, number of stomata on the upper surface is less than the lower surface. The stomatal index is 21.49 on the upper surface and 24.13 on the lower surface. The stoma index ratio was calculated as 0.89. The walls of the epidermis cells are undulated.
Midrib: The midrib shape is circular. This has 1–2 rows of collenchyma and 3–4 rows of parenchyma under the lower epidermis. Collenchyma cells are 12.67–26.05 × 14.21–25.35 μm in size. The vascular bundles are collateral and surrounded by single layer parenchymatic bundle sheath and the cells are 5.61–34.38 × 4.51–25.96 μm in size. The xylem is located on the adaxial side and the phloem is on the abaxial side. Below the phloem are the sclerenchymatic elements. The xylem tissue is well-developed and the tracheal elements are oval and hexagonal. Phloem tissue is not very dense and consists of small cells ( Fig. 1D View FIGURE 1 ).
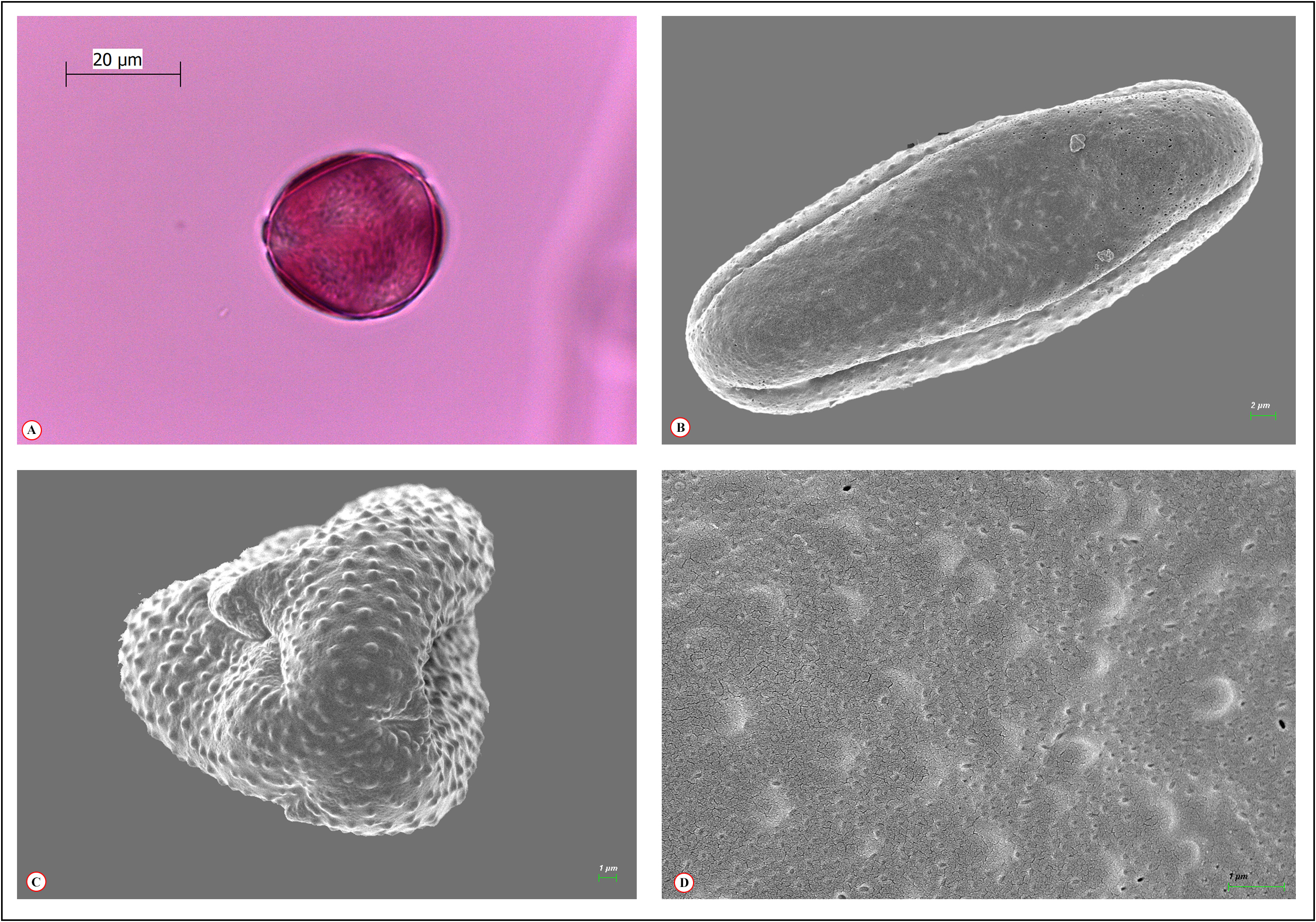
Pollen: Pollen grains of Teucrium ekimii are radially symmetrical, isopolar and tricolpate. Pollen shape is prolate, medium sized, polar axis is 32.96±3.50 μm and equatorial axis is 21.30±2.80 μm long. AMB is circular, ornamentation is microverrucate-perforate. Colpus elongated 20.54±2.35 μm. Exine is 1.71±0.29 μm and intine is 1.06±0.17 μm long ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 , Table 3 View TABLE 3 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Teucrium ekimii Duman (1998: 125)
| Atasagun, Bayram 2022 |
Teucrium ekimii
| Duman, H. 1998: ) |