Lernaeascus kabuto, Uyeno & Tang & Nagasawa, 2015
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.12782/sd.20.2.159 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:1D309B8D-92CA-4048-B8BD-70DE10A9B3E8 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5737537 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6E4C545D-FD8C-4E45-B22F-4099F235CE59 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:6E4C545D-FD8C-4E45-B22F-4099F235CE59 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Lernaeascus kabuto |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Lernaeascus kabuto View in CoL sp. nov.
( Figs 1–4 View Fig View Fig View Fig View Fig )
Type material. Holotype male (NSMT-Cr 24277) and allotype female (NSMT-Cr 24278), ex Centropyge venusta (Yasuda and Tominaga) ( Perciformes : Pomacanthidae ), East China Sea, off Torishima Islet (26°19′N, 126°49′E), Kumejima Island, Ryukyu Islands, Japan, 40 m depth, 19 November 2009, leg. D. Uyeno. Paratypes: 2 males and 1 female (NSMT-Cr 24279), collection data as for holotype and allotype; 1 male (KAUM-AT-211), collection data as for holotype and allotype; 1 male (NSMT-Cr 24280), ex C. heraldi Woods and Schultz ( Perciformes : Pomacanthidae ), East China Sea, off Torishima Islet (26°5′N, 127°42′E), Kumejima Island, Ryukyu Islands, Japan, 8 m depth, 16 November 2009, leg. D. Uyeno; 1 male ( RUMF-ZC 03913), ex C. venusta , East China Sea, off Shichugama (26°20′N, 126°50′E), Kumejima Island, Ryukyu Islands, Japan, 15 m depth, 25 August 2010, leg. D. Uyeno, Y. Fujita and I. Nakayoshi.
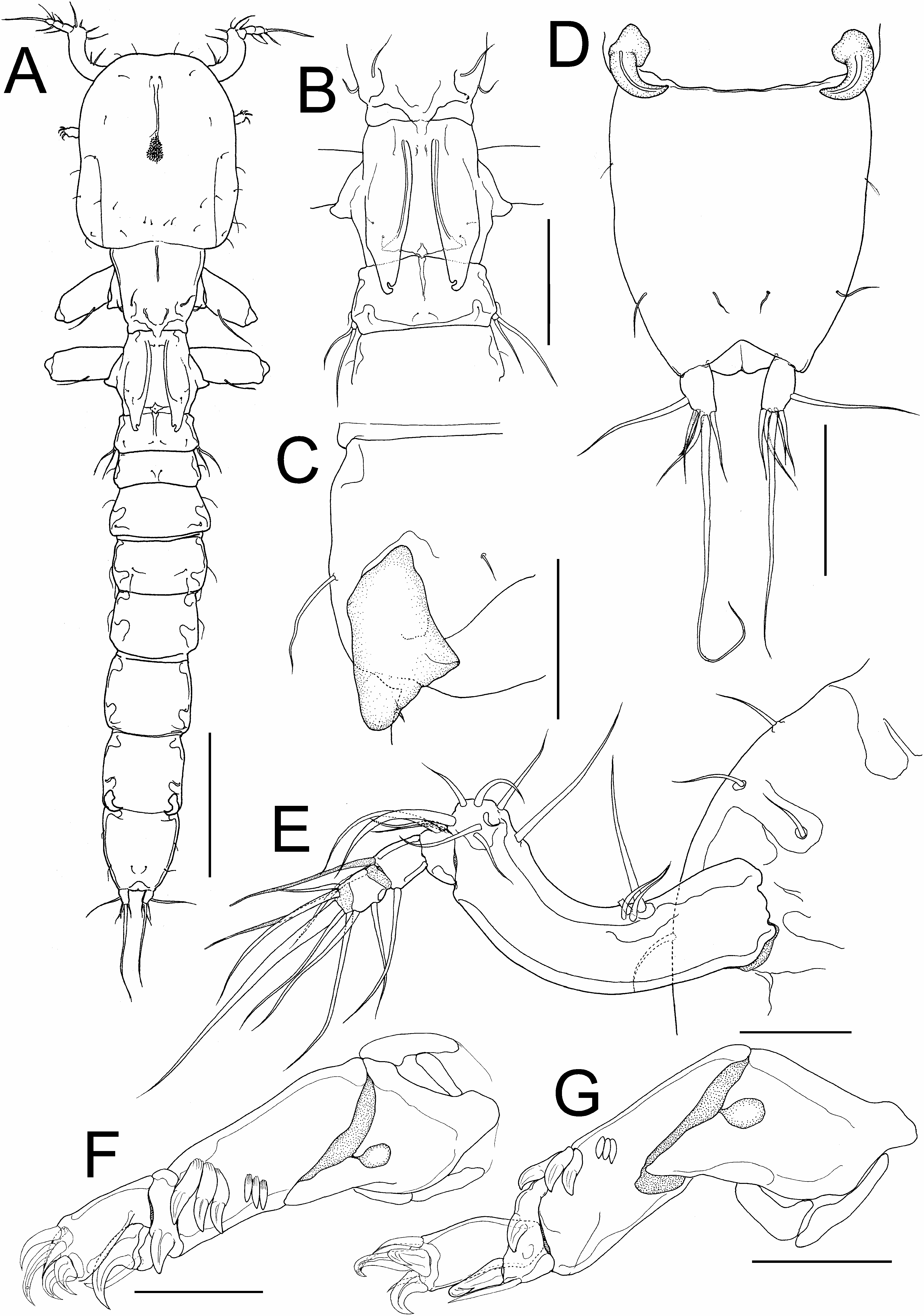
Description of holotype male. Body ( Fig. 1A View Fig ) dorsoventrally compressed, 1179 long (including caudal rami), composed of 11 somites. Cephalosome ( Fig. 1A View Fig ) subquadrate, slightly constricted at mid-length, longer than wide 273×222. Second pedigerous somite ( Fig. 1B View Fig ) bearing paired wing-like dorsal plates, each with inner subterminal notch. Urosome 586 long, composed of fifth pediger, genital somite, and four abdominal somites. Genital somite wider than long 79×132. Third abdominal somite ( Fig. 1D View Fig ) bearing dorsal hamulus on each posterolateral corner. Caudal ramus ( Fig. 1D View Fig ) bearing six setae.
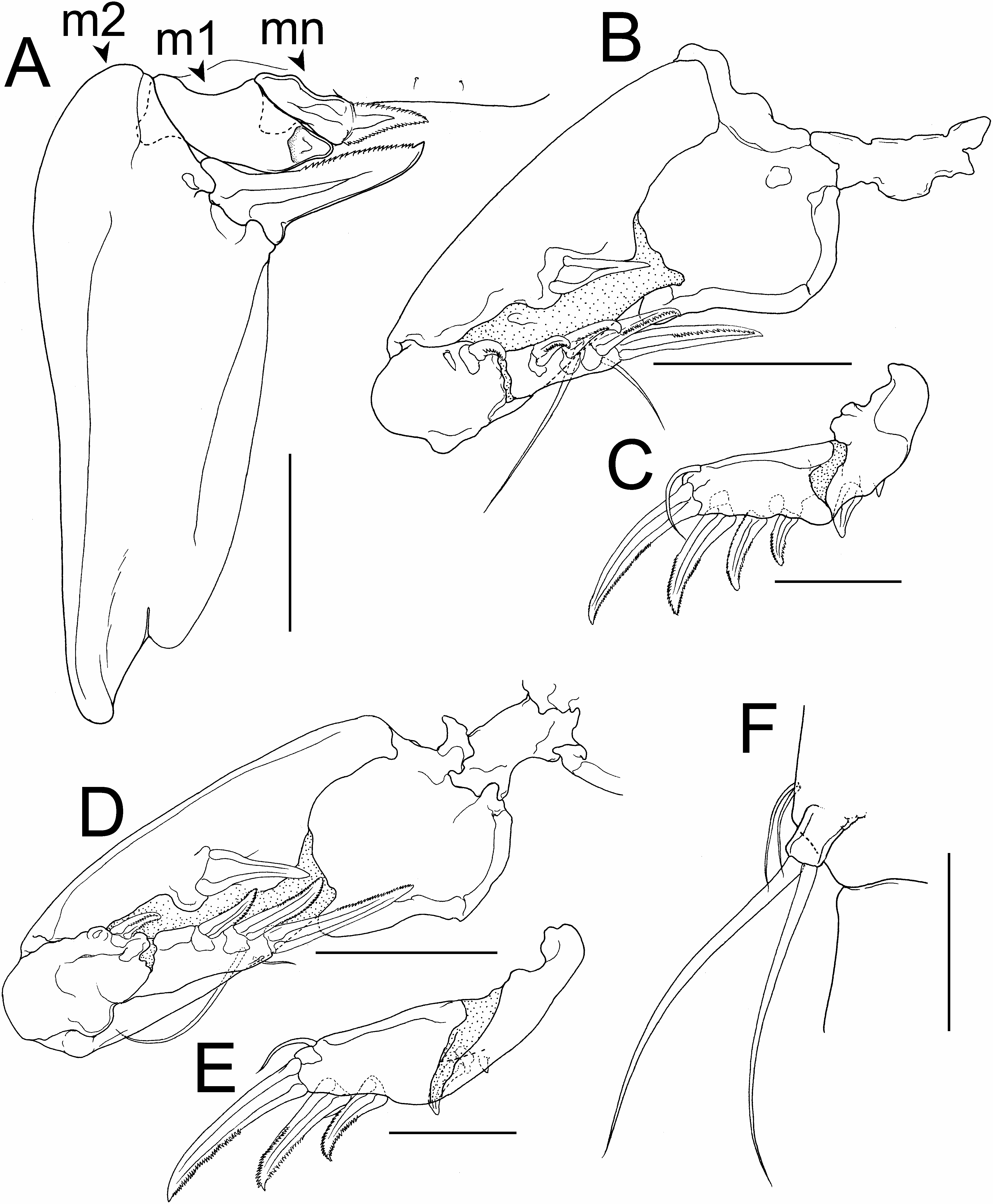
Antennule ( Fig. 1E View Fig ) 4-segmented; proximal segment robust, elongate and anteriorly curved; armature formula 12, 3, 2+1 aesthetasc, 7+1 aesthetasc. Antenna ( Fig. 1F, G View Fig ) 4-segmented, consisting of coxobasis and 3-segmented endopod; coxobasis rod-like, unarmed; proximal endopodal segment rod-like, bearing three small and three large, highly sclerotised, squamate denticles on anterior surface; middle endopodal segment small, bearing large claw-like spine, seta, and large denticulate process; terminal endopodal segment bearing three claw-like spines and three setae on tip. Labrum ( Fig. 2A View Fig ) broad, slightly indented in middle of posterior margin. Mandible ( Fig. 2A View Fig ) unsegmented, bearing serrate apical blade. Paragnath absent. Maxillule ( Fig. 2A View Fig ) small, conical, with subterminal process and blunt tip. Maxilla ( Fig. 2A View Fig ) 2-segmented, comprising syncoxa and basis; syncoxa robust and elongate; basis represented by terminal blade with serrate anterior margin. Maxilliped absent.
Legs 1 and 2 ( Fig. 2B, D View Fig ) biramous, composed of coxa, basis, 2-segmented exopod, and spiniform endopod; armature formula of legs shown in Table 1. First exopodal segment of legs 1 and 2 ( Fig. 2C, E View Fig ) ornamented with small process on outer margin. Endopods of legs 1 and 2 ( Fig. 2B, D View Fig ) rudimentary, each represented by robust spine. Leg 3 ( Fig. 2F View Fig ) fused to third pediger, comprising two basal setae and unsegmented, exopod armed with two long, simple terminal setae. Legs 4 and 5 absent. Leg 6 ( Fig. 1C View Fig ) represented by posteroventral genital operculum ( Fig. 1C View Fig ), armed with minute subterminal seta.
Variability of male morphology. Morphology of body parts of paratypes as in holotype. Measurements of body parts of paratypes (n=5) as follows: body length 1037–1375 (1206±144); cephalosome length 225–346 (294±50); cephalosome width 159–335 (268±74); urosome length 518–658 (570±68); genital somite length 68–84 (78±6); genital somite width 107–146 (131±15).
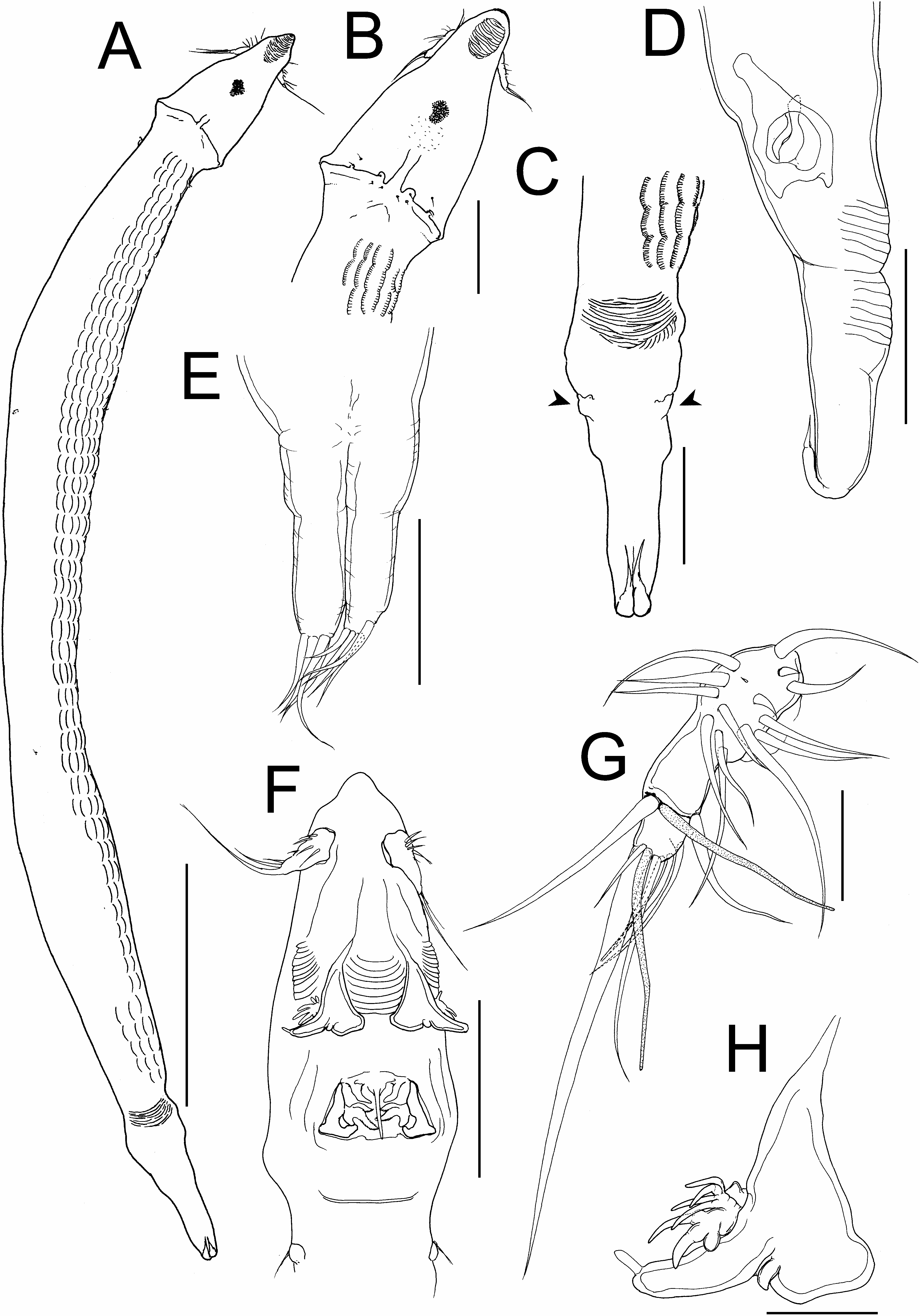
Description of allotype female. Body ( Fig. 3A View Fig ) vermiform, 2210 long (including caudal rami), composed of cephalosome and trunk. Cephalosome ( Fig. 3B, F View Fig ) conical, longer than wide 234×159, with blunt frontal margin, having elliptical corrugated pad on dorso-apical surface and corrugated surface medial and lateral to antenna. Trunk ( Fig. 3A, C View Fig ) slightly curved, terminating in small abdomen, ornamented with longitudinal dorsal rows of serrate, crescentic plates on right side and patch of dorsal corrugations near posterior end. Genital field ( Fig. 3D View Fig ) with laterally paired copulatory pores. Caudal ramus ( Fig. 3C, E View Fig ) fused with abdomen, bearing five setae.
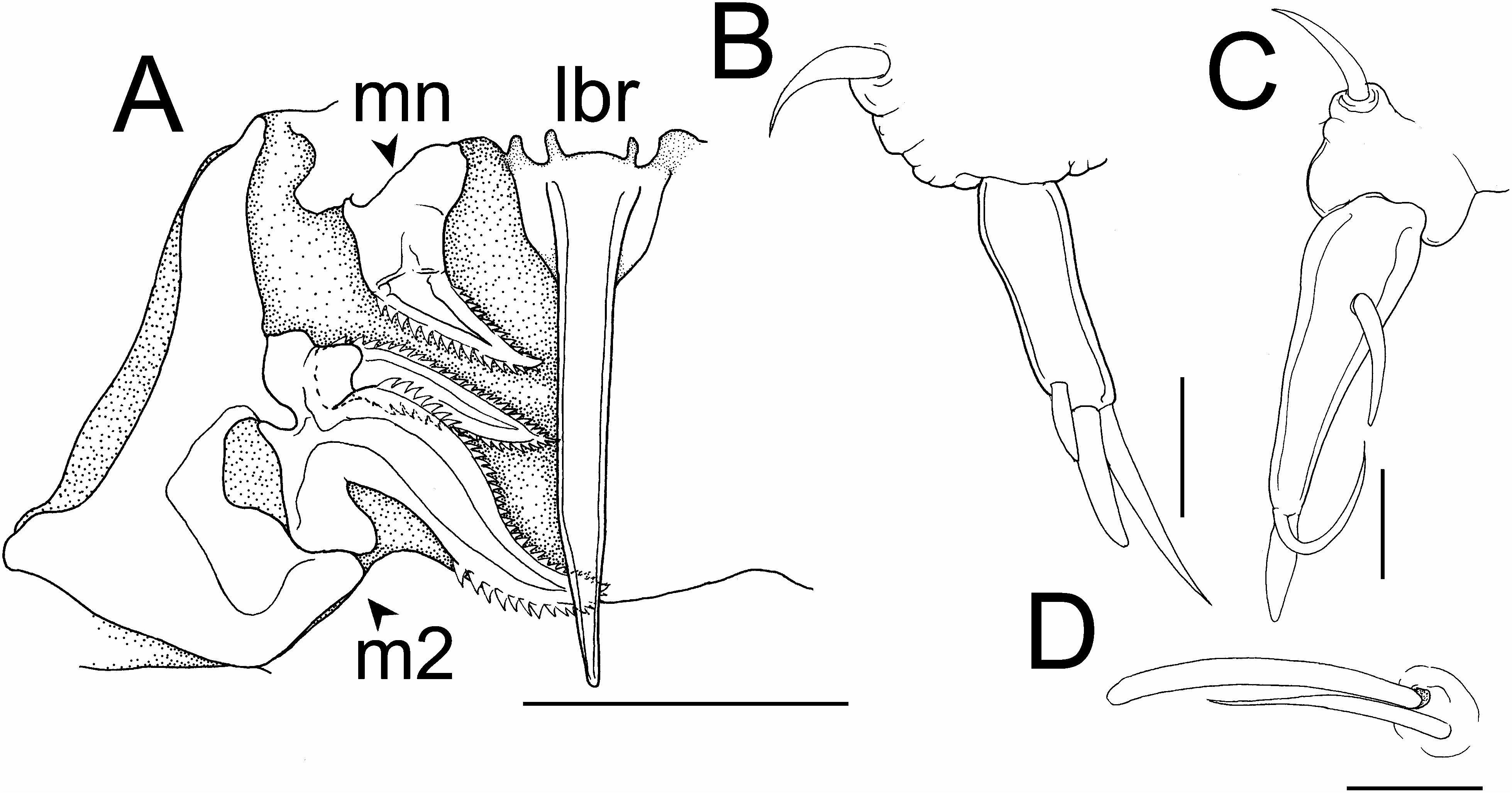
Antennule ( Fig. 3G View Fig ) 2-segmented; proximal segment longest and slightly constricted at mid-length; armature formula 17+1 aesthetasc, 6+1 aesthetasc. Antenna ( Fig. 3F, H View Fig ) apparently 1-segmented, arising from mid-ventral surface of cephalosome, triangular with medial conical process, lateral digitate process, and apical spine. Labrum ( Fig. 4A View Fig ) with broad base produced into postero-median styliform process. Mandible ( Fig. 4A View Fig ) unsegmented, bearing serrate apical blade. Paragnath and maxillule absent. Maxilla ( Fig. 4A View Fig ) 2-segmented; proximal segment (syncoxa) triangular, unarmed; terminal segment (basis) armed with 2 subequal serrate blades. Maxilliped absent.
Legs 1 and 2 ( Fig. 4B, C View Fig ) each comprising knob-like protopod carrying lateral seta and rod-like, 1-segmented exopod, latter bearing three distal setae on leg 1 and single medial and two distal setae on leg 2. Leg 3 ( Fig. 4D View Fig ) vestigial, represented by two setae. Legs 4 and 5 absent.
Variability of female morphology. Morphology of body parts of paratype as in allotype. Measurements of paratype (n=1) as follows: body length 1964; cephalosome length 217; cephalosome width 118.
Etymology. The specific name kabuto , a noun in apposition, the Japanese name for the helmets worn by Japanese warlords and alludes to the shape of the male cephalothorax and the associated curved, elongate antennules.
Infection site. Unknown.
Remarks. The new species is included in Lernaeascus , as it shares a number of characters in common with L. nematoxys , such as a vermiform body in females that is composed of a cephalosome, a long trunk embossed with multiple rows of scale-like cuticular structures, and a short abdomen and in males a pair of dorsal plates on the second pediger. Lernaeascus kabuto sp. nov. is easily distinguishable from L. nematoxys by differences in (1) the proportions, segmentation, and ornamentation of the urosomites and the structure of the dorsal plates, antennule, labrum, maxillule, maxilla, leg 1, and leg 6 of the male, as well as (2) the ornamentation of the cephalosome and structure of the antenna, labrum, and first two pairs of legs of the female ( Table 2).
Newly established Japanese name for both the genus and the species. Senchu-modoki
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |