Cosmolaelaps ceylonensis, Joharchi & Ermilov & Khaustov, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4743.2.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:624E410F-A208-46D4-BF6B-5331B39582F9 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3688002 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B58785-DE03-1E31-5EA4-70B3FDAE8442 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Cosmolaelaps ceylonensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Cosmolaelaps ceylonensis sp. nov.
( Figures 1–24 View FIGURES 1–6 View FIGURES 7–14 View FIGURE 15–18 View FIGURES 19–20 View FIGURES 21–24 )
Type material: Holotype, female, Sri Lanka, Sabaragamuwa Province, Polgampola , 06°27’ N, 080°12’ E, alt. 42 m, 24 January 2019, O. Joharchi, S.G. Ermilov & A.A. Khaustov coll., from forest soil-litter near the Thambadola Ella waterfall (in TSUMZ) GoogleMaps . Paratypes, three females and seven males same data as holotype (two females and four males in TSUMZ, one female and three males in ZISP) GoogleMaps .
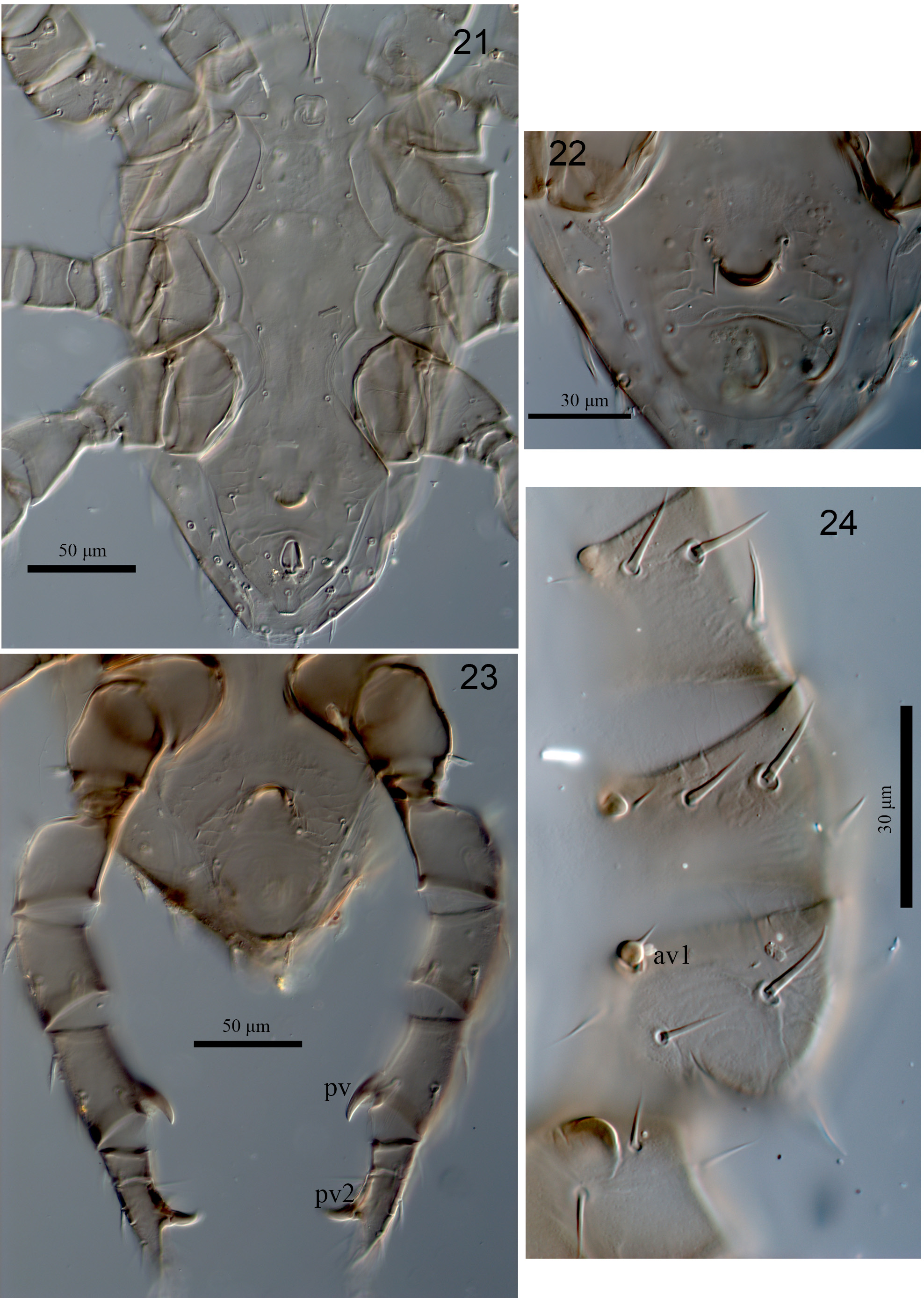
Diagnosis (adult female and male). Dorsal shield with well reticulate ornamentation over whole surface, covering most of the idiosoma, narrowing from level of setae r3, progressively tapering until rounded posteriorly, bearing 39 pairs of subequal oblong-mucronate setae (22 pairs of podonotal setae and 17 pairs of opisthonotal setae, including two pairs of Zx setae) except j1, z1 and Z5 foliate-dentate and shorter. Adult female sternal shield smooth almost throughout; anterior margin hardly conspicuous and posterior margin concave, bearing three pairs of setae and two pairs of large slit shape pore-like structures, st1 long enough to reach base of st2, ratio of shield length/width (at broadest level) 1. Genital shield ratio of length/width (at broadest level) 2.4, surface without any distinct reticulation, almost≃completely smooth, except two diagonal lines in posterior part ≃ which confluence with another horizontal line and forming semi-triangular in posterior part of surface.Anal shield ratio of length/width (at broadest level) 1.4, cribrum well developed. Peritreme long, reaching mid-level of coxa I (near s1). Fixed digit of chelicera with 10 ≃–11 teeth of various sizes. Some dorsal setae on tibia and genu of legs I–IV and pd2, pd3 on tarsi III–IV feather-like. Male with holoventral shield; shield with a strongly sclerotised median circular shape projection; spermatodactyl short and apically curved dorsally; av1 on femur of leg II lanceolate, pv on tibia IV and av2 on tarsus II, IV, pv2 on tarsus III, IV spur-like (apically blunt) and trochanter bearing a large bump shape spur ( Fig. 24 View FIGURES 21–24 ).
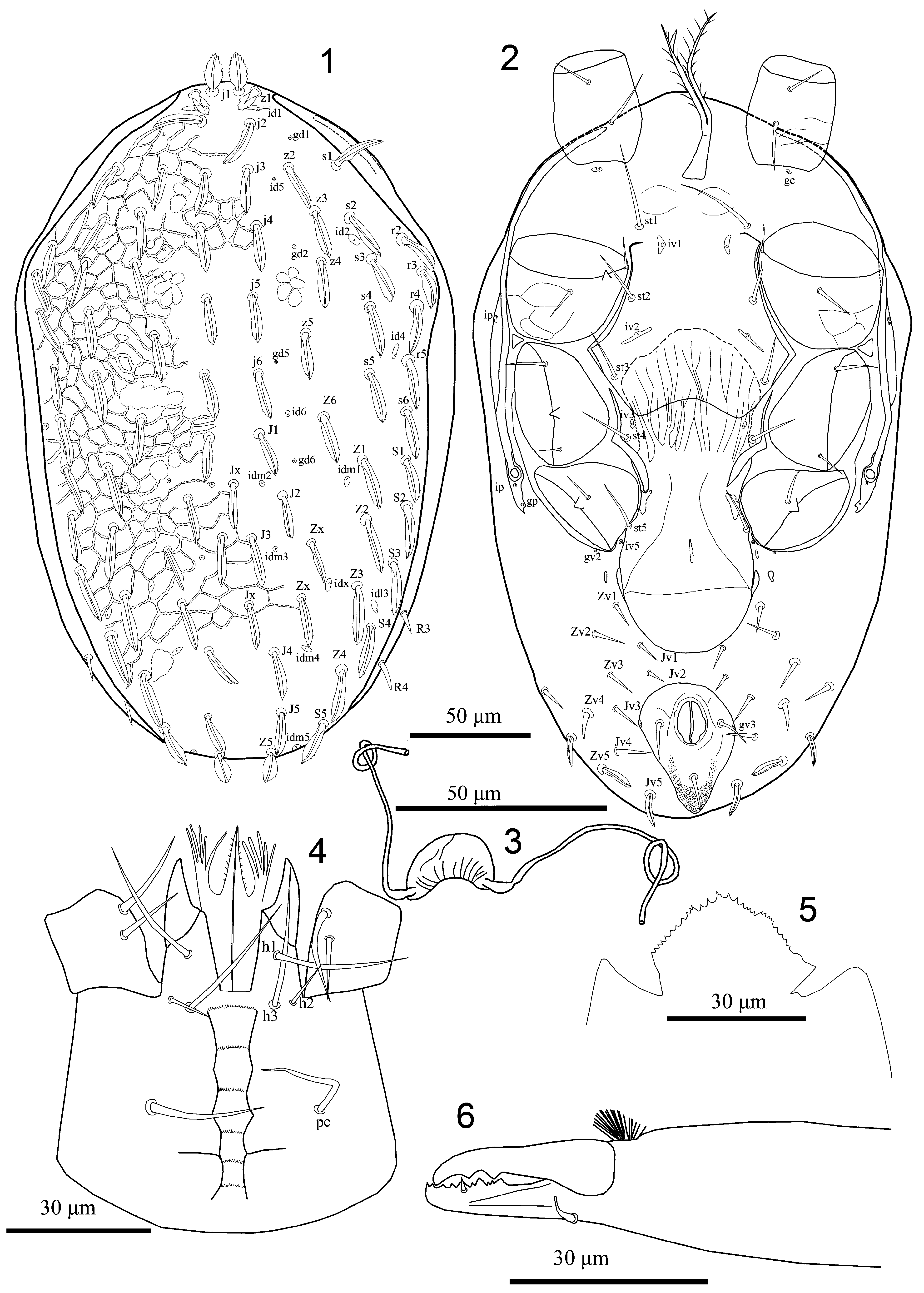
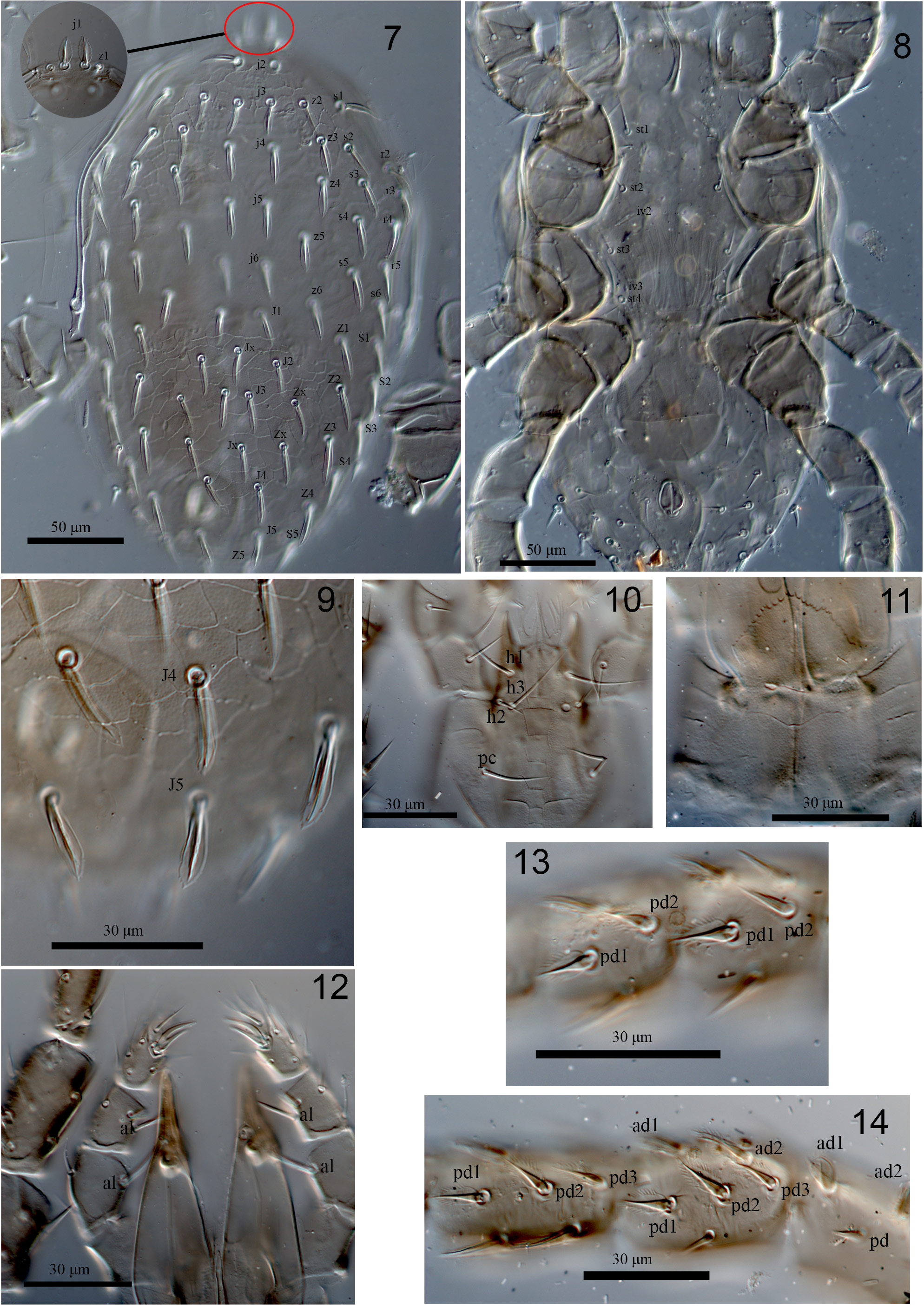
Description. Female (n=4). Dorsal idiosoma ( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1–6 , 7 & 9 View FIGURES 7–14 ). Dorsal shield 295–305 long, 180–190 wide, covering most of dorsal idiosoma, well reticulated over whole surface, narrowing from level of setae r3, progressively tapering until rounded posteriorly. Shield with 39 pairs of oblong-mucronate setae, 22 pairs of podonotal setae (j1–6; z1–6; s1–6; r2–5), and 17 pairs of opisthonotal setae (J1–5; Z1–5; S1–5 and two pairs of Zx setae) except j1, z1 and Z5 foliate-dentate; two unpaired supernumerary setae (Jx) present ( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1–6 , 7 & 9 View FIGURES 7–14 ). Almost all setae with 2–4 minute barbs ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 7–14 ) and uniform in length (21–26) and thickness, except Z5 (13–15), z1 (8–10) and j1 (15–17) length of setae slightly increasing from central to lateral ( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1–6 , 7 & 9 View FIGURES 7–14 ). Narrow strip of soft cuticle surrounding dorsal shield with two pairs of R setae (R3, R4). Shield with about 16 pairs of discernible pore-like structures, including 15 poroids (id1, id2, id4, id5, id6, idm1, idm2, idm3, idm4, idm5, idx, idl3) and four gland openings (gd1, gd2, gd5, gd6), others indistinct ( Figures 1 View FIGURES 1–6 and 7 View FIGURES 7–14 ).
Ventral idiosoma ( Figs 2 View FIGURES 1–6 & 8 View FIGURES 7–14 ). Tritosternum with paired pilose laciniae (53–58), fused basally (2–4), columnar base 20–24 × 8–11 wide; presternal area poorly sclerotised. Sternal shield (length 86–90) narrowest between coxae II (58–60), widest (88–90), anterior margin completely indistinct and posterior margin concave; shield with three pairs of smooth pointed setae (st1 32–34, st2 22–24, st3 22–24, st1 reaching base of next setae) and two pairs of large slit-shaped pore-like structures (iv1 adjacent to setae st1; iv2 between st2 and st3); sternal shield smooth almost throughout and without distinct reticulation. Metasternal setae st4 (19–21) and metasternal poroids located on soft integument; metasternal platelets absent. Endopodal plates II/III completely fused to sternal shield, endopodal plates III/IV elongate, narrow and curved. Genital shield broad, flask-shaped, not adjacent to anal shield, expanded laterally behind setae st5, length 137–139, maximum width 54–58, posterior margin rounded, shield smooth almost throughout, except two diagonal lines in posterior part that fuse with another horizontal line and forming a faintly semi-triangular shape; bearing a pair of simple setae st5 (19–21); paragenital poroids iv5 located on soft cuticle lateral to shield near seta st5. Shield flanked by two pairs of irregular small platelets. Anal shield subtriangular, rounded anteriorly, length 55–57, width 40–44, anterior half lineate-reticulate, para-anal setae and post-anal seta subequal in length (14–16), cribrum consisting of a terminal tuft and pair of anterior arms reaching about to midlevel of distance between post-anal and para-anal setae; anal poroids gv3 on anterolateral margin of anal shield. Soft opisthogastric cuticle surrounding genital and anal shields with 12 pairs of subequal setae (12–16) (Jv1–Jv5, Zv1–Zv5, UR1, UR2). Setae Jv5, Zv5 and UR2 spatulate, metapodal plates absent. Exopodal and parapodal platelets not fused, strip-like, extending narrowly behind coxae IV. Peritreme extending anteriorly to mid-level of coxa I; peritrematal shield narrow, free from exopodal shields, protrusion band of cuticle lateral to the peritreme at the level of coxae II–III, a lyrifissure ip at level of coxa II, post-stigmatic section bearing two pore-like structures, a lyrifissures ip and a gland pore gp ( Figs 2 View FIGURES 1–6 & 8 View FIGURES 7–14 ).
Gnathosoma ( Figs 4–6 View FIGURES 1–6 , 10–12 View FIGURES 7–14 ). Hypostomal groove with six transverse rows of denticles, each row with about 11–25 small teeth ( Figs 4 View FIGURES 1–6 & 10 View FIGURES 7–14 ), groove wider anteriorly. Hypostome with four pairs of setae, h1 (28–30), h2 (10–12), h3 (28–30), palpcoxal setae (pc) (24–26) ( Figs 4 View FIGURES 1–6 & 10 View FIGURES 7–14 ). Epistome trapezoidal, central part irregularly denticulate ( Figs 5 View FIGURES 1–6 , 11 View FIGURES 7–14 ). Corniculi robust and horn-like, extending slightly beyond palp trochanter. Internal malae with median and lateral projections, fringed, inner lobes touching with outer lobes; labrum with pilose surface. Chaetotaxy of palps: trochanter 2, femur 5, genu 6, tibia 14, tarsus 15, all setae smooth and needle-like except al on palp femur and genu thickened and apically spatulate, palp tarsal apotele two-tined ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 7–14 ). Fixed digit of chelicera with an offset and most distal large tooth (gabelzhan) followed by 9–10 variously sized teeth, 4nd, 6th, 9th larger, a setaceous pilus dentilis, dorsal cheliceral setae prostrate, arthrodial membrane with a rounded flap and normal filaments and cheliceral lyrifissures indistinct, movable digit with two teeth ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 1–6 ).
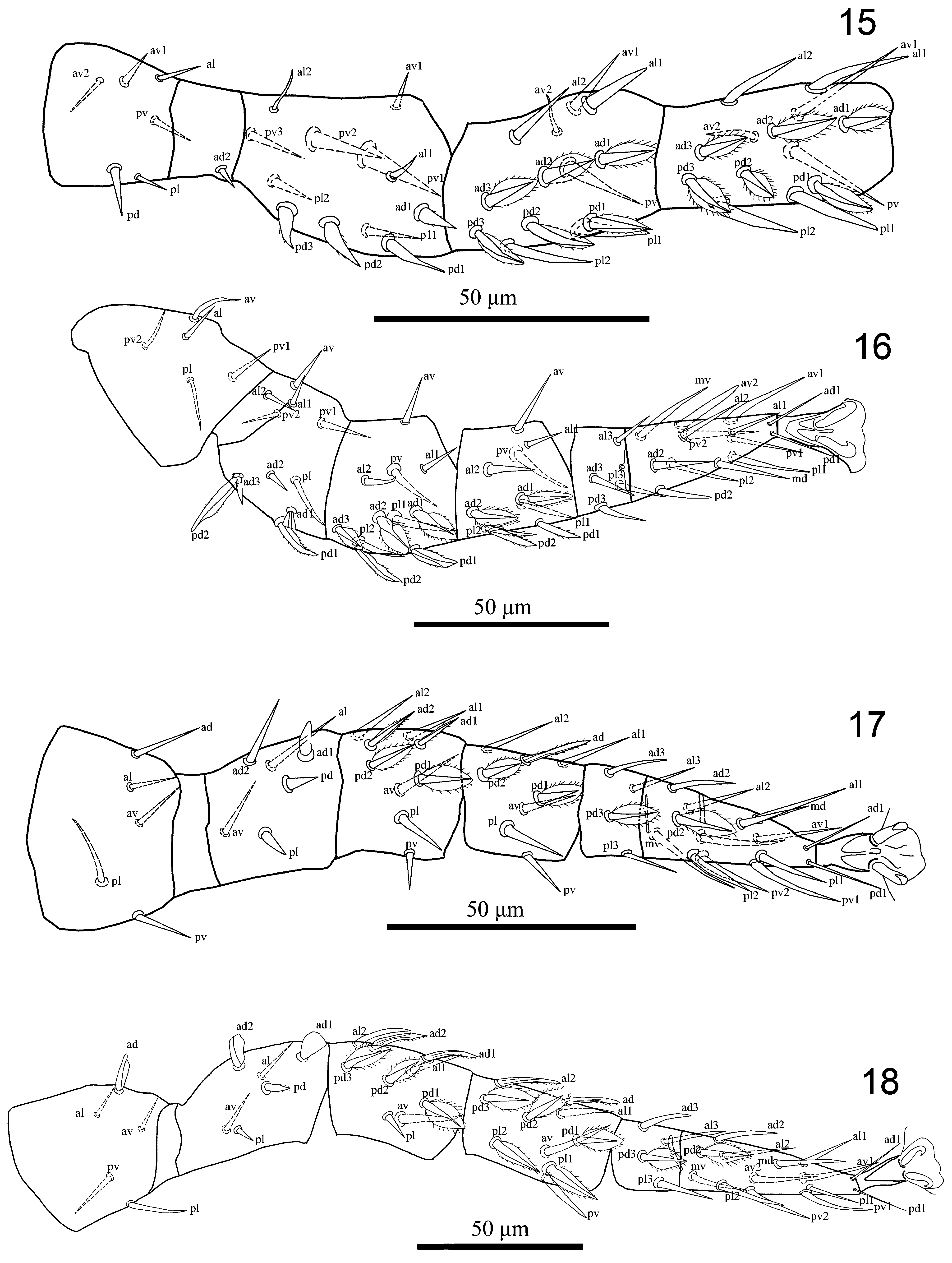
Legs ( Figs 13–18 View FIGURES 7–14 View FIGURE 15–18 ). Legs II and III short (213–217, 195–204), I and IV longer (273–296, 294–301). Chaetotaxy normal for free-living Laelapidae : Leg I ( Fig. 15 View FIGURE 15–18 ): coxa 0-0/1, 0/1-0, trochanter 1-0/2, 1/1-1, femur 2-2/1, 3/3-2 (pv1, pv2, ad1, pd1, pd2, pd3 thickened, all dorsal setae with minute barbs), genu 2-3/2, 3/1-2 (all dorsal setae feather-like, lateral and ventral setae thickened except av2), tibia 2-3/2, 3/1-2 (all dorsal setae feather-like, lateral setae thickened). Leg II ( Fig. 16 View FIGURE 15–18 ): coxa 0-0/1, 0/1-0, trochanter 1-0/1, 0/2-1, femur 2-3/1, 2/2-1 (ad1 truncate, pd1, pd2 falcate and with minute barbs), genu 2-3/1, 2/1-2 (ad1, ad2, ad3 feather-like, pd1, pd2 falcate and with minute barbs), tibia 2-2/1, 2/1-2 (ad1, ad2 feather-like, pd1, pd2 thickened and with minute barbs). Leg III ( Fig. 17 View FIGURE 15–18 ): coxa 0-0/1, 0/1-0, trochanter 1-1/1, 0/1-1, femur 1-2/1, 1/0-1 (ad1, pd, pl thickened, ad1 apically blunt), genu 2-2/1, 2/1-1 (pd1, pd2 feather-like, ad1, ad2 lanceolate, with minute barbs, pl thickened, Fig. 13 View FIGURES 7–14 ), tibia: 2-1/1, 2/1-1 (pd1, pd2 feather-like, ad1 lanceolate, with minute barbs, pl thickened, Fig. 13 View FIGURES 7–14 ). Leg IV ( Fig. 17 View FIGURE 15–18 ): coxa 0-0/1, 0/0-0, trochanter 1-1/1, 0/1-1 (ad spatulate), femur 1-2/1, 1/0-1 (ad1, ad2 spatulate, pd thickened with minute barbs, Fig. 14 View FIGURES 7–14 ), genu 2-2/1, 3/0-1 (pd1, pd2, pd3 feather-like, ad1, ad2 lanceolate, with minute barbs, av thickened, Fig. 14 View FIGURES 7–14 ), tibia 2-1/1, 3/1-2 (pd1, pd2, pd3 feather-like, ad1, ad2 lanceolate, with minute barbs, av, al, pv thickened, Fig. 14 View FIGURES 7–14 ). Tarsi II-IV with 18 setae (3-3/2, 3/2-3 + mv, md). All pretarsi with well-developed paired claws and rounded pulvilli and a long thin stalk, ventral and lateral setae on tarsus II and III thickened, pd2, pd3 on tarsi III-IV feather-like.
Insemination structures ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1–6 ). Laelapid-type sperm access system, tubulus long, wider at the solenostome level of coxa III and entering sacculus via a pair of circular openings. Sacculus reniform, the proximal ends of the tubulus slightly swollen at junction with ramus.
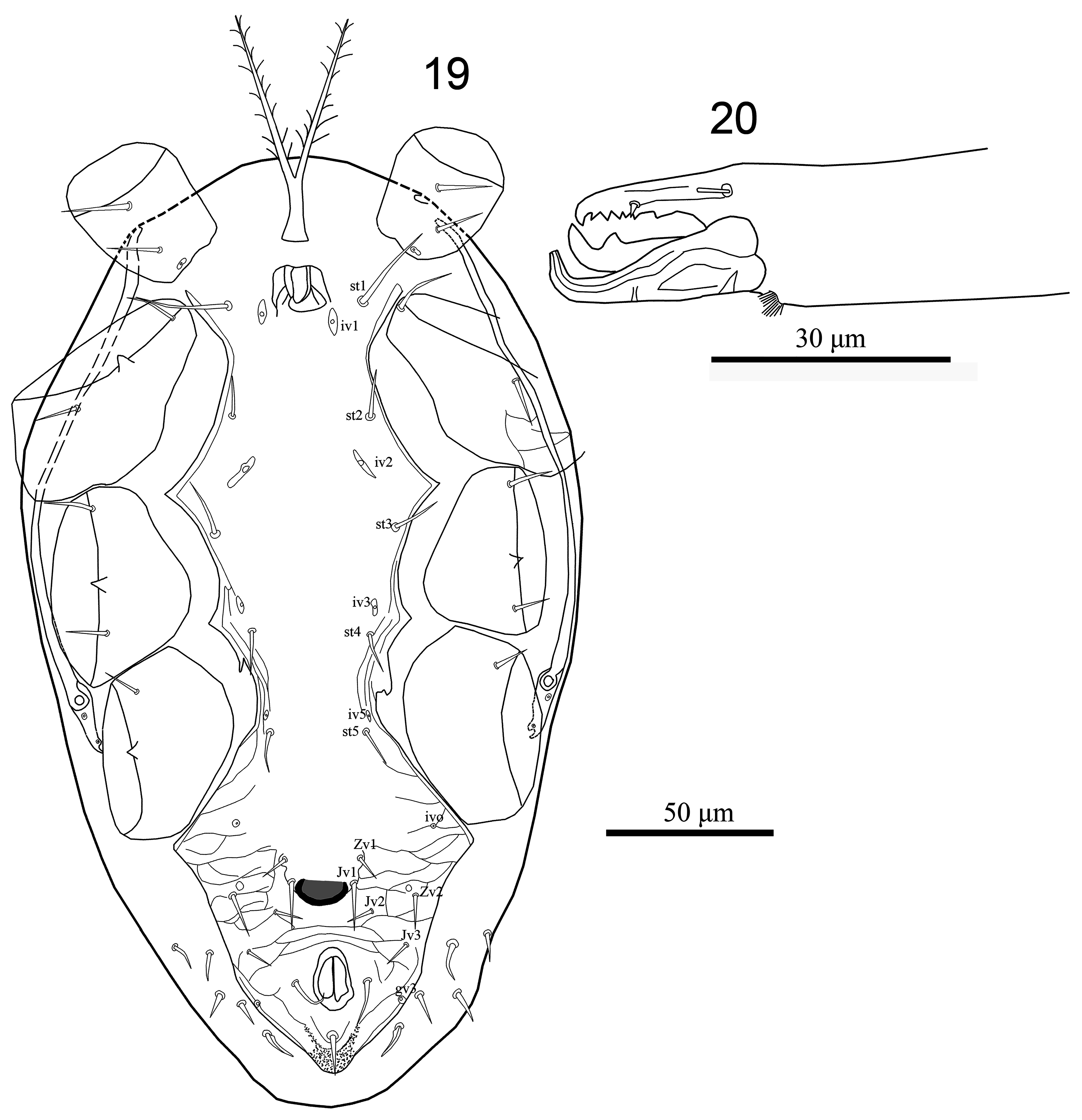
Male (n=7). ( Figs 19–24 View FIGURES 19–20 View FIGURES 21–24 ). Dorsal idiosoma. Dorsal shield (268–295) long, (154–172) wide; ornamentation and chaetotaxy as in female.
Ventral idiosoma ( Figs 19 View FIGURES 19–20 , 21 & 23 View FIGURES 21–24 ). Sternal, genital, endopodal, ventral and anal shields fused into holoventral shield, weakly reticulate, more distinct behind ZV1, bearing st1–5, five pairs of opisthogastric setae (Jv1–Jv3, Zv1, Zv2) in addition to circumanal setae; six pairs of poroids and a pore-like (gv3) laterad of para-anal setae, gland pore gv2 behind coxa IV not discerned; shield with a strongly sclerotised median circular shape projection ( Fig. 22 View FIGURES 21–24 ), cribrum with 3–4 irregular rows of spicules and a pair of anterior arms reaching about to mid-level of distance between post-anal and para-anal setae. Soft opisthogastric cuticle with five pairs setae.
Gnathosoma . Epistome and subcapitulum similar to female. Fixed digit of chelicera with seven teeth of various sizes, pilus dentilis setaceous. Movable digit of chelicera with one tooth, spermatodactyl short and apically curved dorsally, with blunt tip, free portion of spermatodactyl shorter than movable digit, fringed hyaline arthrodial process at base of movable digit ( Fig. 20 View FIGURES 19–20 ). Palps similar to those of female.
Legs. Chaetotaxy as in female. Seta av1 on femur of leg II lanceolate ( Fig. 24 View FIGURES 21–24 ), pv on tibia IV ( Fig. 23 View FIGURES 21–24 ) and av2 on tarsus II, IV, pv2 on tarsus III, IV spur-like (apically blunt) and tochanter II bearing a large dome-shaped spur ( Fig. 24 View FIGURES 21–24 ).
Etymology. Named after the type locality, Sri Lanka, previously known as Ceylon.
Differential diagnosis. The dorsal setae in Cosmolaelaps ceylonensis are similar in shape to those of C. rectangularis Sheals, 1962 , C. serratus Trägårdh, 1952 , C. claviger ( Berlese, 1883) , C. diversus ( Karg, 1994) and C. bengalensis ( Bhattacharyya, 1968) , described from Argentina, Saint Lucia, Tahiti, Galápagos Islands and India, respectively. It differs from all these species by the different shape of j1, z1 and Z5 setae, foliate-dentate in C. ceylonensis ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1–6 ) (vs. j1, z1 and Z5 setae obovate-spatulate or simple and smooth in the other species, never foliate-dentate). The sternal and genital setae (st1–st3 and st5) are simple and the shields are smooth, without distinct reticulation, except for two diagonal lines in the posterior part of the genital shield which fuse with another horizontal line to form a semi-triangular figure in posterior part of the genital shield surface) in C. ceylonensis ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1–6 ). Both or at least one of the sternal or genital shields have distinct reticulation in C. rectangularis , C. serratus , C. claviger , C. diversus ; and setae st1–st3 and st5 are spatulate and with some barbs respectively in C. bengalensis . Some dorsal setae on the tibia and genu of legs I–IV and pd2, pd3 on tarsi III–IV are feather-like in C. ceylonensis ( Figs 13–18 View FIGURES 7–14 View FIGURE 15–18 ); while the dorsal setae on tibia and genu of legs I–IV in all the other species mentioned are sometimes spatulate or thickened but never feather-like, and pd2, pd3 on tarsi III–IV simple.
In the classification of Karg (1981), C. ceylonensis falls into the claviger species group of Hypoaspis (Cosmolaelaps) , because almost all dorsal shield setae oblong-mucronate, but C. ceylonensis is distinguished easily from all species in the claviger species group by the following combination of unique characters: (1) dorsal shield with well reticulate ornamentation over whole surface and narrowing from level of setae r3, progressively tapering until rounded posteriorly, bearing 39 pairs of oblong-mucronate setae and almost all setae with 2–4 minute barbs and uniform in length and thickness except j1, z1 and Z5 foliate-dentate and shorter; (2) both sternal and genital shields obviously smooth and without distinct reticulation (except two diagonal lines in posterior part of genital shield which confluence with another horizontal line and forming semi-triangular in posterior part of genital shield surface) and sternal shield bearing two pairs of large slit shape pore-like structures and st1 length enough to well reach base of st2, (3) fixed digit of chelicera with 10–11 various size of teeth; (4) some dorsal setae on tibia and genu of legs I–IV (antero-dorsals and postero-dorsals setae on tibia and genu I–II and postero-dorsals setae on tibia and genu III–IV) and pd2, pd3 on tarsi III–IV feather-like; (5) Male with holoventral shield; shield with a strongly sclerotised median circular shape projection and spermatodactyl short and apically curved dorsally; (6) ad on tibia IV and ad2, pd2 on tarsus IV spur-like (apically blunt) in male.
| ZISP |
Zoological Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |