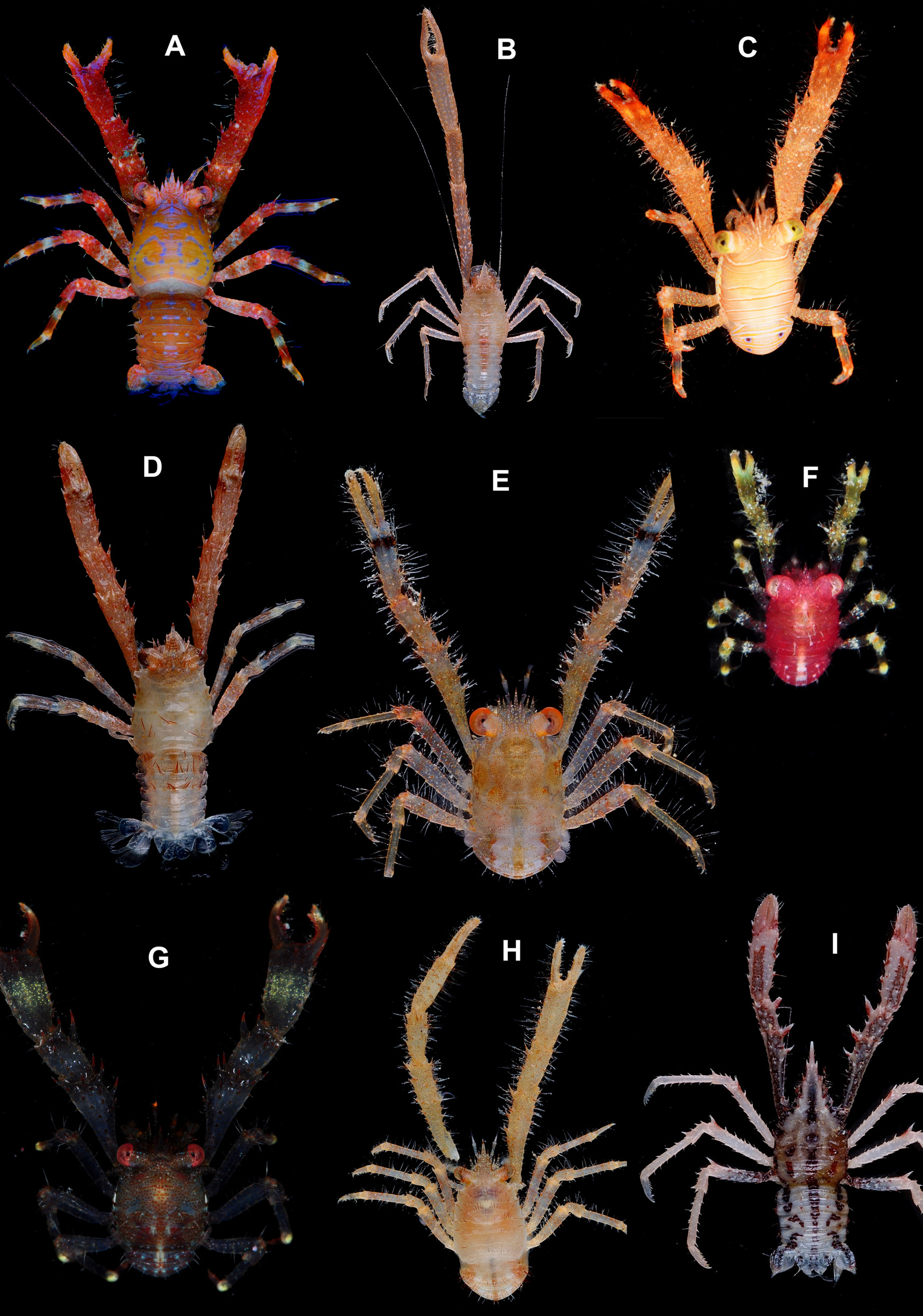
Galathea consobrina De Man , 1902
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3913.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:18D06EC6-A61D-4C45-9B5E-52435903556D |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3511641 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B3F979-FFA4-427C-FF6D-FD57001EEBA2 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Galathea consobrina De Man , 1902 |
| status |
|
Galathea consobrina De Man, 1902 View in CoL
( Figs 27 View FIGURE 27 , 116 View FIGURE 116 D)
Galathea consobrina De Man, 1902: 720 View in CoL , pl. 23, figs 41a–41f ( Ternate, Indonesia, Moluccas).— Baba, 1988: 73, fig. 30 (Sulu Archipelago, Davao Gulf off southeastern Mindanao, Sibuyan Sea, 37–68 m).—Baba et al., 2008: 67 (compilation).—Poore et al., 2008: 19 (SW Australia, 95–100 m).— Dong & Li, 2010: 7 View Cited Treatment , fig. 4 (South China Sea, 7–100 m).
Material examined. Holotype: Indonesia. Moluccas, Ternate: M 2.5 mm ( SMF 4556).
Philippines. MUSORSTOM 1, Stn 57, 13°53'N, 120°13'S, 96–107 m, 26 March 1976: 1 ov. F 3.0 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-13992). MUSORSTOM 2, Stn CP8, 13°55'N, 120°20'E, 85–90 m, 21 November 1980: 1 M 4.3 mm, 1 F 3.5 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-8384).— Stn CP28, 13°41'N, 120°50'E, 90–110 m, 23 November 1980: 1 ov. F 3.5 mm, 1 F 2.6 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-8389).— Stn CP47, 13°33'N, 122°10'E, 81–84 m, 26 November 1980: 1 F 4.4 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-13984). MUSORSTOM 3, Stn DR117, 12°31'N, 120°39'E, 92–97 m, 3 June 1985: 2 M 2.3–3.6 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-8399), 1 M 2.7 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-8398), 1 ov. F 2.7 mm (MNHN-IU-2013- 8397).—Stn DR137, 12°03'N, 122°06'E, 56 m, 6 June 1985: 1 M 4.0 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-8385).
Indonesia. Makassar Strait. CORINDON, Stn DR258, 01°56.8'S, 119°17.3'E, 30 m, 6 November 1980: 1 ov. F 2.8 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-8396). Kei Islands. KARUBAR, Stn DW22, 05°22'S, 133°01'E, 85–124 m, 25 October 1991: 1 F 2.8 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-13954).
Vanuatu. SANTO, Stn EP10, 15°38.0'S, 167°13.6'E, 45–101 m, 15 September 2006: 1 M 2.6 mm, 1 ov. F 2.8 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-8387).—Stn AT56, 15°36.1'S, 167°01.3'E, 98–105 m, 2 October 2006: 2 M 2.4–3.3 mm, 1 ov. F 3.4 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-8395).—Stn AT65, 15°40.3'S, 167°15.9'E, 160–167 m, 5 October 2006: 1 F 3.2 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-8386).— Stn AT75, 15°37.0–37.3'S, 167°09.2–09.6'E, 52–66 m, 10 October 2006: 1 ov. F 3.5 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-8390).—Stn AT80, 15°31.7'S, 167°10.8'E, 36–43 m, 12 October 2006: 1 ov. F 3.4 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-8400).— Stn AT84, 15°32.4'S, 167°14.3'E, 71–104 m, 12 October 2006: 1 M 2.4 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-8394).— Stn EP41, 15°37.7'S, 167°05.1'E, 112 m, 19 October 2006: 1 F 3.0 mm (MNHN- IU-2013-8391).
Australia. Western Australia. 34°53.10'S, 115°30.25'E, 95–100 m, 21 November 2005: 1 ov. F 2.8 mm ( J55124 View Materials ).
New Caledonia. Lagon East. Stn 656, 21°49.1'S, 166°32.5'E, 30–40 m, August 1986: 1 M 3.5 mm (MNHN- IU-2013-8392).— Stn 732, 21°18.9'S, 165°50.9'E, 43–50 m, August 1986: 1 M 4.3 mm (MNHN-IU-2013- 8388). Touho. 20°47'S, 165°13'E, September 1993: 1 M 2.7 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-8394), 1 ov. F 3.6 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-8383).
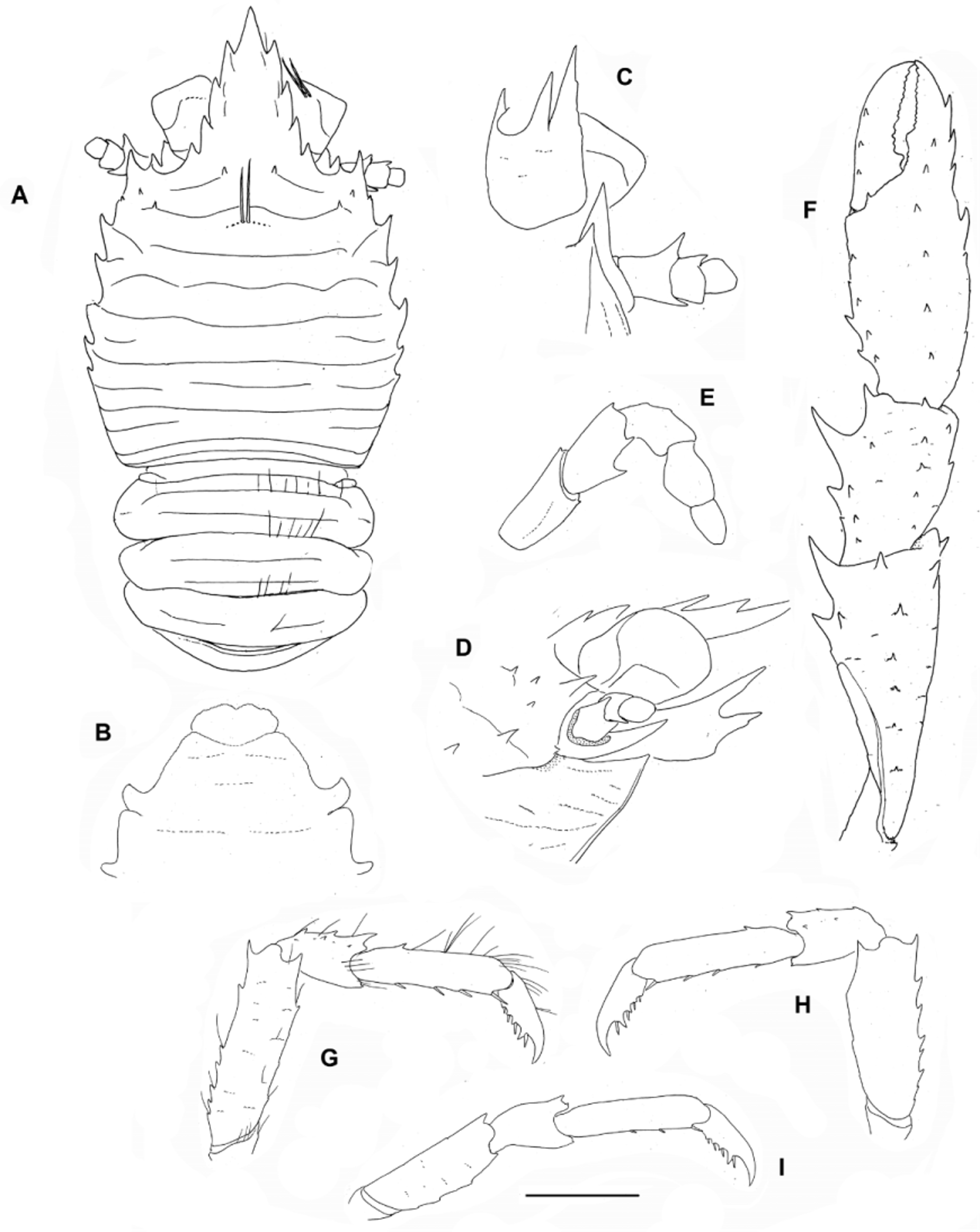
Description. Carapace: as long as broad; transverse ridges with dense short setae, and a few scattered long non-plumose setae; cervical groove distinct, laterally bifurcated. Gastric region with 6 transverse ridges: 1 epigastric ridge with 2 epigastric spines, medially interrupted; 2 protogastric ridges, anterior uninterrupted, convex medially, with 1 parahepatic spine on each side, posterior ridge short and median, sometimes with a few long setae; 1 mesogastric ridge uninterrupted but not extending laterally to anteriormost of branchial marginal spines; 2 metagastric ridges, anterior ridge usually uninterrupted extending laterally to anterior branchial ridges, posterior ridge short or absent. Anterior branchial region with distinct ridges. Mid-transverse ridge uninterrupted, preceded by shallow cervical groove, followed by 5 ridges. One small hepatic spine on each side, near first (anterolateral) marginal spine. Lateral margins well convex medially, with 7 spines: 2 spines in front of, and 5 spines behind, anterior cervical groove; first anterolateral, well-developed, at same level of lateral limit of orbit, second, small, at midlength between anterolateral spine and anteriormost spine of branchial margin, accompanying another spine ventral to between first and second; 2 spines on anterior branchial region, and 3 spines on posterior branchial margin, last small. Small spine on lateral limit of orbit; infraorbital margin with strong spine. Rostrum 1.5 as long as broad, length 0.6 postorbital carapace length and breadth 0.4 that of carapace; distance between distalmost lateral incisions 0.25 distance between proximalmost lateral incisions; dorsal surface nearly horizontal in lateral view, with some setose scales; lateral margin with 4 deeply incised sharp teeth.
Pterygostomian flap rugose, unarmed, ridges with short setae, anterior margin blunt.
Sternum: As long as broad, lateral extremities gently divergent posteriorly.
Abdomen: Somites 2–4 each with 2 uninterrupted transverse ridges on tergite, posterior ridge sometimes medially interrupted; somites 5 and 6 each with 2 medially interrupted ridges, sometimes absent. Males with G1 and G2.
Eyes: Ocular peduncles 1.3 times longer than broad, maximum corneal diameter 0.6 rostrum width.
Antennule: Article 1 with 3 well-developed distal spines, distodorsal larger, distomesial spine slightly smaller than others. Ultimate article with a few short fine setae not in tuft on distodorsal margin.
Antenna: Article 1 with ventral distomesial spine exceeding distal margin of article 2. Article 2 wider than or as wide as long, with 2 well-developed subequal distal spines, reaching midlength of article 3. Articles 3 and 4 unarmed.
Mxp3: Ischium with small spine on flexor and extensor distal margins; crista dentata with 23 or 24 denticles. Merus as long as ischium; flexor margin with 2 subequal spines; extensor margin with small distal spine. Carpus unarmed.
P1: 2.5 times carapace length, covered with finely setiferous scales, with scattered long setae. Merus as long as carapace, 4 times as long as carpus, with spines arranged roughly in rows, dorsomesial spines stronger; distal spines prominent. Carpus 0.4 length of palm, 2.1 times as long as broad; dorsal and lateral surfaces with some spines; mesial margin with 3 or 4 spines (distal second strong). Palm twice longer than broad, lateral and mesial margins slightly convex; spines arranged roughly in dorsolateral and dorsomesial rows, some small spines scattered on dorsal side. Fingers slightly shorter than palm, unarmed; each finger distally with two rows of teeth, spooned.
P2–4: moderately slender, with setose striae and sparse long plumose setae. P2 1.9 times carapace length. Meri successively shorter posteriorly (P3 merus 0.9 length of P3 merus, P4 merus 0.8 length of P3 merus); P2 merus 0.7 carapace length, 4.5 times as long as broad, 1.5 times longer than P2 propodus. Extensor margin with row of 7–9 proximally diminishing spines on P2–3, 6 spines on P4; ventral margins distally ending in strong spine followed proximally by 0 or 1 spines and several eminences, lateral sides unarmed. Carpi with 2 or 3 spines on extensor margin on P2–3, 1 spine on P4; lateral surface with 2 or 3 acute granules sub-paralleling extensor margin; flexor distal margin acute. Propodi 3.5–4.0 times as long as broad; extensor margin unarmed; flexor margin with 4–6 movable spines. Dactyli distally ending in well-curved strong spine, length 0.7–0.8 that of propodi; flexor margin with 5 or 6 proximally diminishing teeth, terminal one prominent.
Epipods absent on pereiopods.
Coloration. Translucent reddish brown or light brown overall. Long setae on carapace and abdomen reddish. P1 fingers distally whitish. P2–4 with brownish and whitish stripes.
Remarks. Galathea consobrina belongs to the group of species with non-scale-like gastric ridges, including a laterall interrupted mesogastric ridge carapace lateral margin with one small but distinct spine between anterolateral spine and anteriormost branchial marginal spine, antennular basal article with 3 well-developed terminal spines, two epigastric spines, P1 are distally spooned and pereiopods without epipods. The closest species are G. argus n. sp. from Western Australia, and G. t a g a ro n. sp. from Vanuatu and Solomon Islands. The species can be distinguished by the following aspects:
Galathea argus resembles G. tagaro and G. consobrina from which it can be differentiated by having the carapace dorsal surface without scale-like median ridge behind the protogastric transverse ridge, whereas this median ridge is always present in G. consobrina and G. tagaro .
Galathea consobrina is also very similar to G. tagaro n. sp. The two species can be distinguished by the length of the P2–4 propodi, being 3.5–4.0 times longer than broad in G. consobrina , whereas they are 4.5–4.8 times in G. tagaro . Furthermore, the ground color of G. consobrina is light brown, instead of green in G. t a g a ro.
No genetic data are available for G. a rg u s and G. tagaro .
Distribution. Philippines, Indonesia, Vanuatu, New Caledonia and Western Australia, 30– 167 m.
| SMF |
Forschungsinstitut und Natur-Museum Senckenberg |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Galathea consobrina De Man , 1902
| Macpherson, Enrique & Robainas-Barcia, Aymee 2015 |