Galathea leporis, Macpherson, Enrique & Robainas-Barcia, Aymee, 2015
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3913.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:18D06EC6-A61D-4C45-9B5E-52435903556D |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5136049 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B3F979-FF57-4280-FF6D-FF4F0021ED02 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Galathea leporis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Galathea leporis View in CoL n. sp.
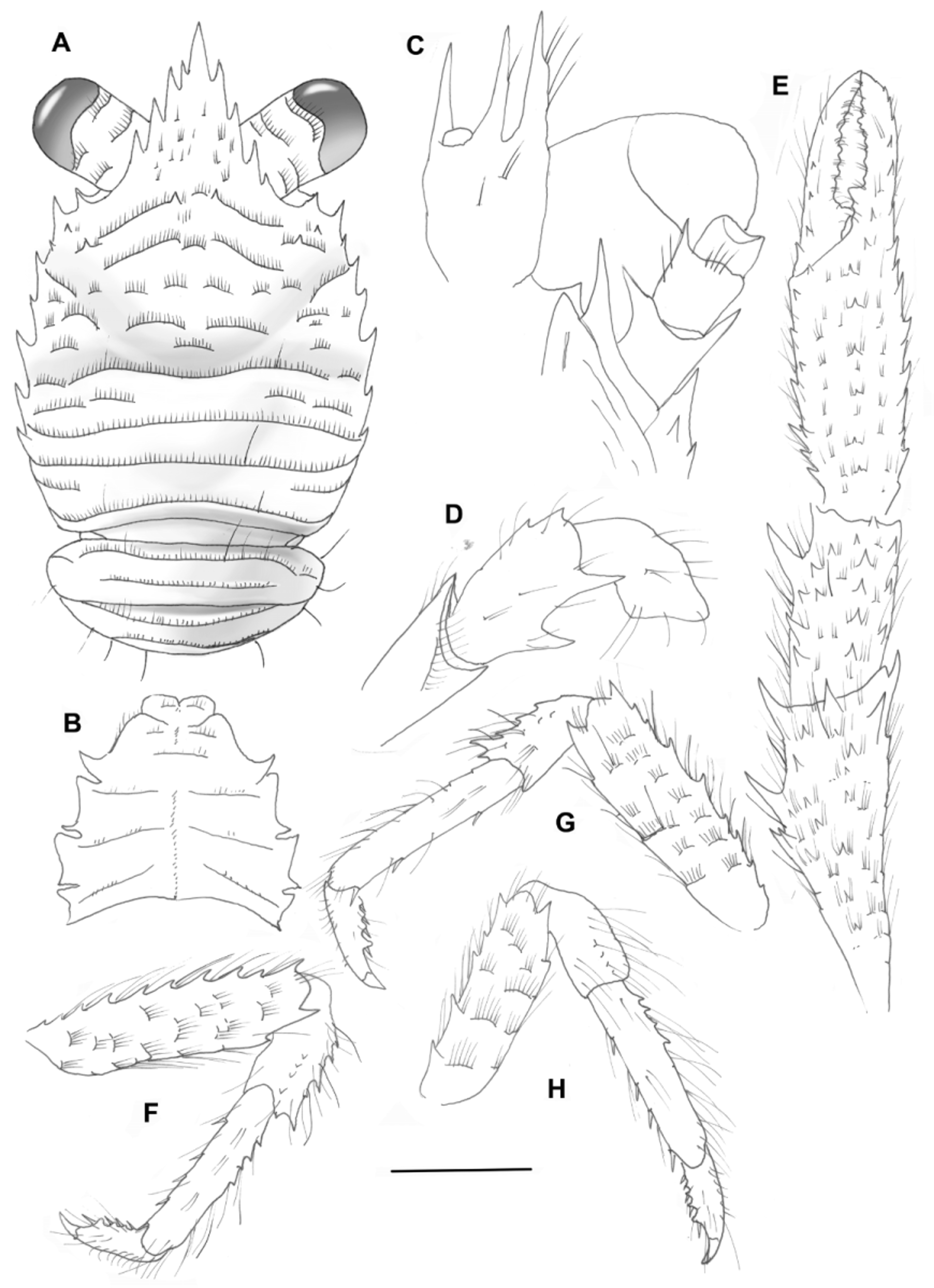
( Figs 58 View FIGURE 58 , 117 View FIGURE 117 H)
Galathea algae View in CoL .— Baba, 1979b: 646 (Gorong Island and Marsegu Island, Moluccas, subtidal) (not G. algae Baba, 1969 )
Material examined. Holotype: Vanuatu. SANTO, Stn FB92, 15°33.6'S, 167°16.6'E, 2–4 m, 14 October 2006: M 2.4 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-15985).
Paratypes: Indonesia. Gorong Island, 26 January 1975: 2 M 2.8–3.4 mm, 1 ov. F 3.8 mm, 1 F 3.5 mm (MNHN- Ga1146).
Papua New Guinea. PAPUA NIUGINI, Stn PR4, 05°10.1'S, 145°50.5'E, 30 m, 7 November 2012: 1 M 2.3 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-771).—Stn PB11, 05°17.9'S, 145°46.7'E, 10 m, 30 December 2012: 4 ov. F 2.9–3.2 mm, 1 F 2.1 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-15997); 1 ov. F 2.2 mm, 1 F 1.9 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-15995); 1 M 3.0 mm (MNHN-IU- 2013-370); 1 ov. F 2.3 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-371).—Stn PB16, 05°04.7'S, 145°48.8'E, 5 m, 30 December 2012: 1 M 3.2 mm, 1 ov. F 2.7 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-16000).—Stn PB21, 05°01.4'S, 145°48'E, 5 m, 30 December 2012: 1 ov. F 2.1 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-723); 8 M 1.8–3.0 mm, 2 ov. F 3.0– 3.3 mm, 1 F 1.6 mm (MNHN-IU-2013- 15998).—Stn PB28, 05°11.9'S, 145°49.6'E, 10 m, 30 December 2012: 7 M 2.3–3.3 mm, 1 ov. F 2.5 mm, 2 F 2.0– 2.4 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-15999).—Stn PB29, 05°18'S, 145°46.1'E, 17 m, 30 December 2012: 1 ov. F 2.9 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-9765).—Stn PD32, 05°08'S, 145°49.5'E, 31 m, 30 December 2012: 1 M 2.0 mm (MNHN-IU- 2013-15996).—Stn no number: 3 M 1.5–2.2 mm, 2 ov. F 2.3–2.5 mm, 6 F 1.4–2.0 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-774). Kranket Island, 5.2025°S, 145.8218°E, 17 m, 6 November 2102: 3 M 1.5–2.8 mm, 2 ov. F 2.7–2.9 mm (UF36157).
Vanuatu. SANTO. Stn EP1, 15°32.5'S, 167°09.0'E, 46–47 m, 10 September 2006: 2 juv. 1.0– 1.1 mm (MNHN- IU-2013-15983).—Stn DB29, 15°38.9'S, 167°05.1'E, 15 m, 17 September 2006: 2 ov. F 2.6–3.3 mm (MNHN-IU- 2013-15982).—Stn DB48, 15°38.7'S, 167°5.2'E, 10–17 m, 21 September 2006: 1 M 3.4 mm (MNHN-IU-2013- 15984).
New Caledonia. Chesterfield Islands. CORAIL 2, Stn DW88, 19°06'S, 158°56'E, 32 m, 26 July 1988: 2 F 2.4–2.5 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-15986).
New Caledonia. South Reef, Stn 327, 22°26'S, 167°04'E, 60 m, November 1984: 2 M 3.8–4.0 mm (MNHN- IU-2013-9762). Touho, 20°47'S, 165°13'E, 10 m, 6 September 1993: 1 ov. F 3.3 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-9761). Koumac, 12 m, 7 October 1993: 1 M 2.4 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-15987).
New Caledonia. Lifou Island. LIFOU, Stn 1454, 20°56.65’S, 167°02.0’E, 15–18 m, 4 November 2000: 1 M 3.2 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-15992).—Stn 1457, 20°46.8’S, 167°02.75’E, 5–10 m, 4 November 2000: 1 M 3.5 mm, 1 ov. F 3.3 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-13996).— Stn 1458, 20°46.7’S, 167°03.1’E, 17–24 m, 4 November 2000: 1 ov. F 3.6 mm, 1 F 2.5 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-15994).—Stn 1435, 20°55.2’S, 167°00.7’E, 5–30 m, 8 November 2000: 1 M 3.2 mm, 2 ov. F 2.3–2.4 mm, 1 F 2.0 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-15990).—Stn 1459, 20°47.0'S, 167°03.0'E, 55–80 m, 5 November 2000: 2 ov. F 3.0– 3.3 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-15989).—Stn 1465, 20°47.7’S, 167°07.0’E, 35–45 m, 16 November 2000: 6 M 2.3–3.2 mm, 4 ov. F 2.1–3.3 mm, 6 F 1.9–2.2 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-15991).—Stn 1448, 20°45.8’S, 167°01.65’E, 20 m, 17 November 2000: 1 M 2.4 mm, 1 ov. F 2.7 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-9764).—Stn 1451, 20°47.3’S, 167°06.8’E, 10–21 m, 19 November 2000: 2 M 3.0– 3.6 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-15993).—Stn 1455, 20°56.8’S, 167°02.7’E, 15-20 m, 25 November 2000: 1 M 2.0 mm, 1 F 1.8 mm (MNHN-IU-2013- 15988).—Stn 1410, 20°56.7’S, 167°03.1’E, 2–4 m, 25 November 2000: 2 M 1.6–1.7 mm, 1 ov. F 3.0 mm, 2 F 1.5–1.7 mm (MNHN-IU-2013-9763).
Etymology. From Lepus , the Hare, one of the Southern Hemisphere constellations.
Description. Carapace: slightly broader than long; transverse ridges with dense short setae, and a few moderately long simple setae; cervical groove distinct, laterally bifurcated. Gastric region with 5 transverse ridges: 1 epigastric ridge medially interrupted, with 2 spines; 2 mesogastric ridges, anterior one medially interrupted by 1 arcuate scale, posterior ridge scale-like; 2 metagastric scale-like ridges. One small parahepatic spine, and one hepatic spine, near anterolateral spine, on each side. Anterior branchial region with distinct scale-like ridges. Midtransverse ridge uninterrupted, preceded by shallow cervical groove. Posterior branchial region with 4 transverse ridges, 2 of them uninterrupted. Lateral margins slightly convex, with 7 spines: 2 spines in front of, and 5 spines behind, anterior cervical groove; first anterolateral, well-developed, at same level of lateral limit of orbit, second small, with spine ventral to between first and second spines; 2 spines on anterior branchial region, and 3 spines on posterior branchial margin, last small. Spine on lateral limit of orbit, 1 small spine between orbital and anterolateral spine in some specimens; infraorbital margin with strong spine. Rostrum 1.7 as long as broad, length 0.6 postorbital carapace length and breadth 0.4 that of carapace; distance between distalmost lateral incisions 0.25 distance between proximalmost lateral incisions; dorsal surface nearly horizontal in lateral view, with some short setae; lateral margin with 4 deeply incised sharp teeth.
Pterygostomian flap rugose, unarmed, ridges with short setae, anterior margin acute.
Sternum: 0.8 times as long as broad, lateral extremities gently divergent posteriorly.
Abdomen: Somites 2–3 with 2 transverse uninterrupted ridges; somites 4–6 smooth; somite 6 with posteriomedian margin straight. Males with G1 and G2.
Eyes: Ocular peduncles 1.4 times longer than broad, maximum corneal diameter 0.8 rostrum width.
Antennule: Article 1 with 3 well-developed distal spines, distodorsal larger, distomesial spine smaller. Ultimate article with a few short fine setae, not in tuft, on distodorsal margin.
Antenna: Article 1 with ventral distomesial spine exceeding distal margin of article 2. Article 2 with 2 subequal distal spines, barely reaching midlength of article 3. Article 3 with small distomesial spine. Article 4 unarmed.
Mxp3: Ischium with small spine on flexor and extensor distal margins; crista dentata with 21–24 denticles. Merus as long as ischium; flexor margin with 2 subequal well-developed spines; extensor margin with 2 spines. Carpus smooth or with 1 or 2 granules along extensor margin.
P1: 2.5–3.0 times carapace length, covered with finely setiferous scales, with numerous long simple setae. Merus as long as carapace, 1.7–1.8 times as long as carpus, with spines arranged roughly in rows, dorsomesial spines stronger; distal spines prominent. Carpus 0.9 length of palm, twice longer than broad; dorsal and lateral surfaces with some spines; mesial margin with 2 or 3 spines (distal second strong). Palm twice longer than broad, lateral and mesial margins subparallel; spines arranged roughly in dorsolateral and dorsomesial rows, continuing along fixed and movable fingers, respectively; a few small spines scattered on dorsal side. Fingers as long as palm, each finger with with 2 rows of teeth distally spooned.
P2–4: moderately slender, with setose striae and sparse long plumose setae. P2 2.1–2.2 carapace length. Meri successively shorter posteriorly (P3 merus 0.9 length of P3 merus, P4 merus 0.8 length of P2 merus); P2 merus as long as carapace, 4.0 times as long as broad, 1.7 times longer than P2 propodus; P3 merus 3.5 times as long as broad, 1.4 times longer than P3 propodus; P4 merus 3.1 times as long as broad, 1.2 times longer than P2 propodus. Extensor margin of P2–3 meri with row of 10 proximally diminishing spines, 5 spines on P4; ventral margins distally ending in strong spine followed proximally by 0–1 spines and several eminences; lateral sides unarmed. Carpi with 4–6 spines on extensor margin on P2–3, 0–2 spines on P4; lateral surface with 2–4 small spines or acute granules sub-paralleling extensor margin; flexor distal margin acute. P2–4 propodi 4.0–5.0 times as long as broad; extensor margin with 3–5 proximal spines on P2–4; flexor margin with 4 or 5 slender movable spines. Dactyli distally ending in well-curved strong spine, length 0.5 that of propodi; flexor margin with 4 or 5 proximally diminishing teeth, terminal one prominent.
Epipods present only on P1.
Coloration. Base color translucent white. Anterior part of carapace light orange. P1 whitish, with distal part of merus, carpus and palm orange or brownish, fingers brownish with whitish tips. P2–4 whitish, with brownish distal stripes on each merus, carpus and propodus.
Remarks. Galathea leporis n. sp. resembles G. tongi n. sp. from Mariana Islands, Kiribati and French Polynesia (see Remarks of this latter species).
Distribution. Indonesia (Gorong Island), Papua New Guinea, Vanuatu, and New Caledonia; 2– 80 m.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Galathea leporis
| Macpherson, Enrique & Robainas-Barcia, Aymee 2015 |
Galathea algae
| Baba 1979: 646 |