Microstonyx aff. major (GERVAIS, 1848)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.2478/if-2017-0021 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03AF8797-FFDC-FFA2-FF41-FE15B9F1FCCA |
|
treatment provided by |
Diego |
|
scientific name |
Microstonyx aff. major (GERVAIS, 1848) |
| status |
|
Microstonyx aff. major (GERVAIS, 1848)
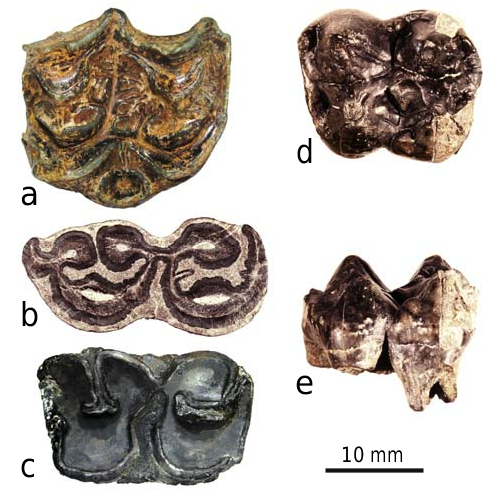
Text-fig. 15d, e View Text-fig
M a t e r i a l. dP4 sin, Volchaya Balka (bed 3).
C o m m e n t s. The deciduous premolar dP4 (19.5 × 17.3 mm) is generally larger than in Propotamochoerus , but similar to Microstonyx . The size and shape of the specimen coincide with those of Microstonyx major from Samos and Nikiti 1 ( Greece) ( Kostopoulos 1994). The widespread European species Microstonyx major is fairly widespread in the Late Miocene of Europe (MN 10 through MN 12) ( van der Made and Moya-Sola 1989, van der Made 1990).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |