Procloeon (Oculogaster), Kluge 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4820.3.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:44BD1E07-C9F3-4488-936E-819C2FCA18C8 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4397963 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03AF3A05-8D73-FFA9-FAA9-F90FA66AFCFD |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Procloeon (Oculogaster) |
| status |
|
( Figs 1–133 View FIGURES 1–7 View FIGURES 8–16 View FIGURES 17–18 View FIGURES 19–29 View FIGURES 30–33 View FIGURES 34–35 View FIGURES 36–42 View FIGURES 43–48 View FIGURES 49–56 View FIGURES 57–66 View FIGURES 67–70 View FIGURES 71–72 View FIGURES 73–77 View FIGURES 78–83 View FIGURES 84–89 View FIGURES 90–98 View FIGURES 99–102 View FIGURES 103–108 View FIGURES 109–112 View FIGURES 113–117 View FIGURES 118–126 View FIGURES 127–133 )
Subgenus Oculogaster Kluge 2016: 494 .
Type species: Procloeon cylindroculum Kimmins 1956 .
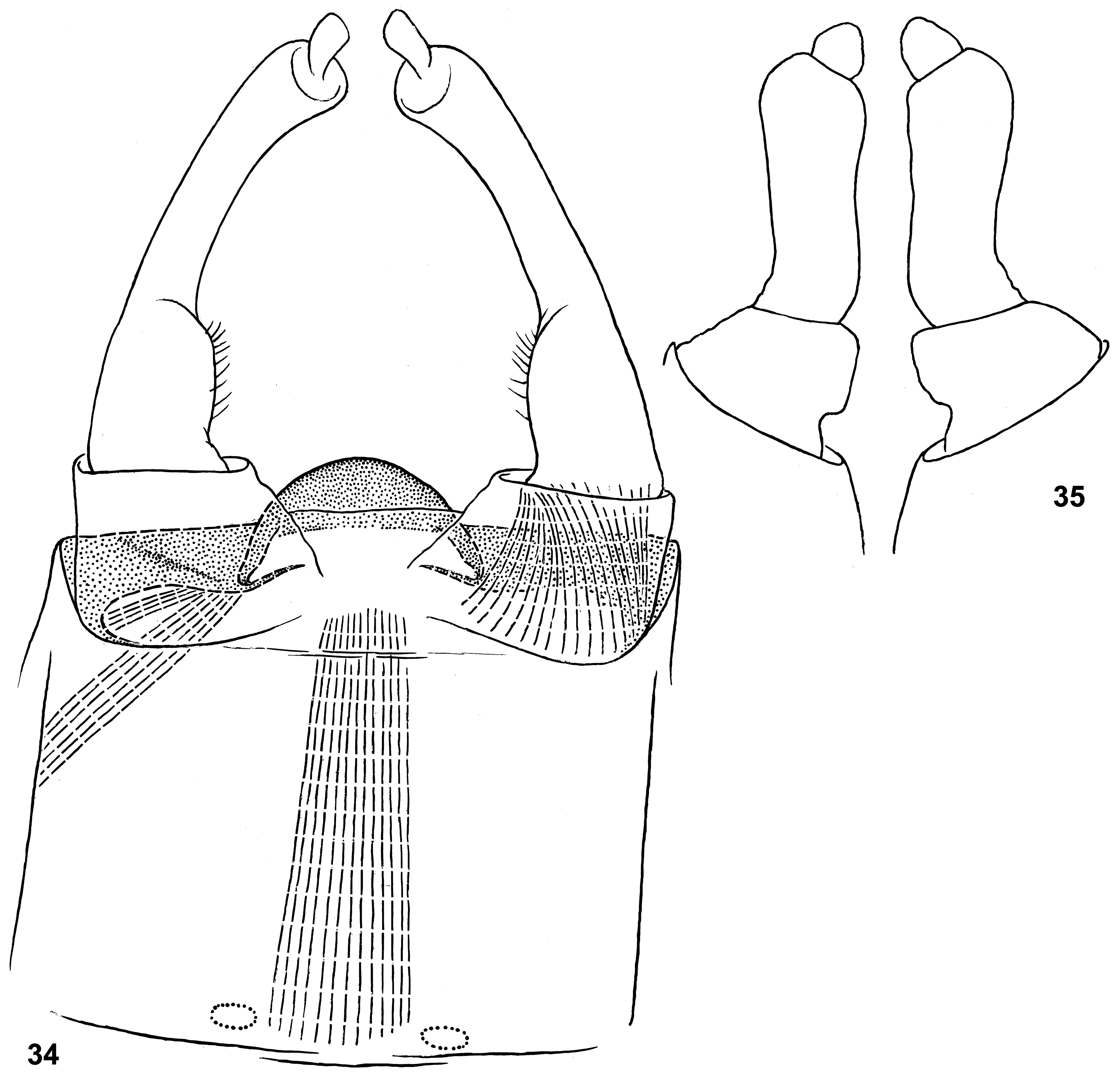
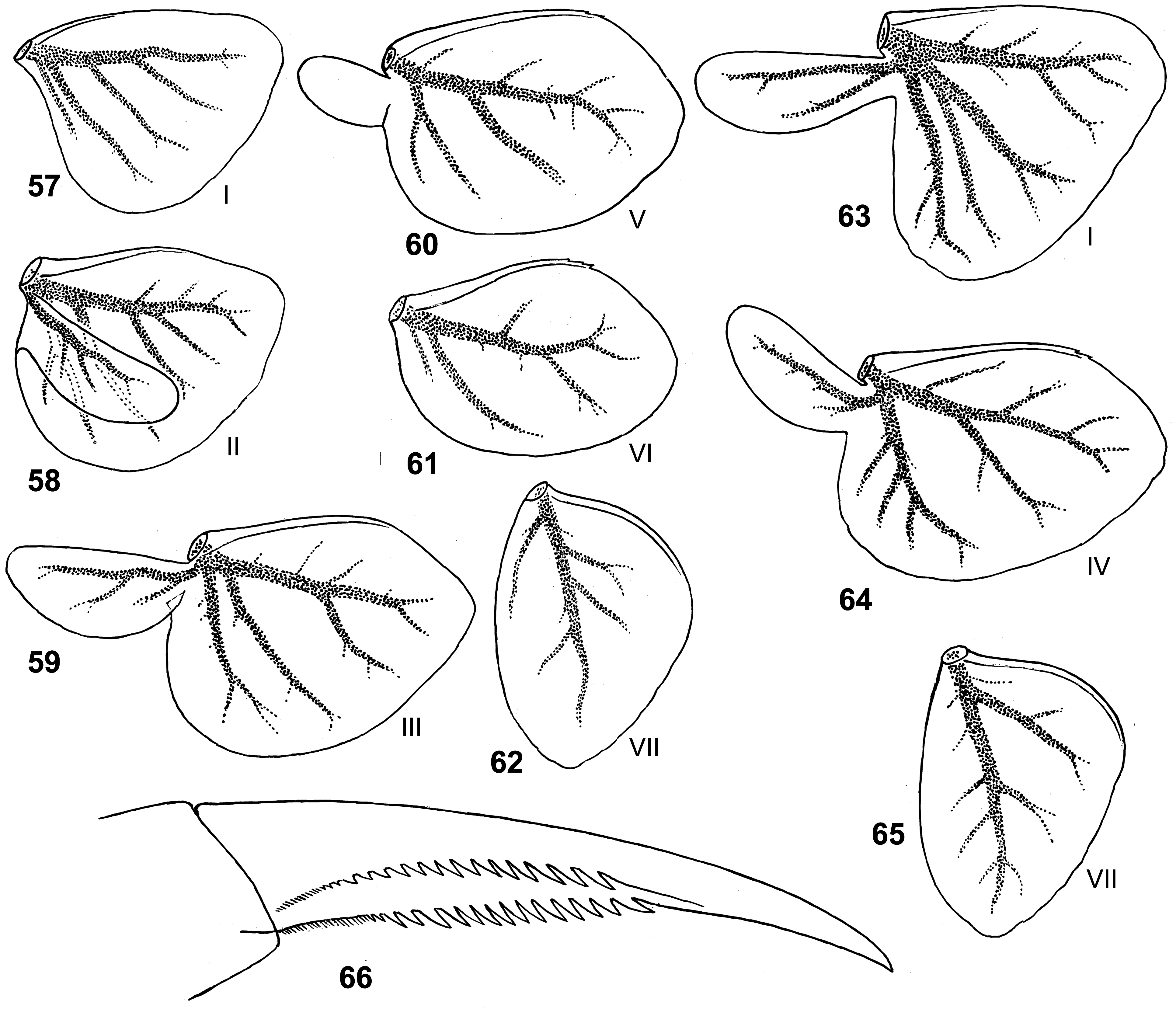
Diagnosis. (1) Viviparous ( Kluge 2016: figs 38–42, 76–79). The same in Cloeon s. str. and some other mayflies, but not in other Procloeon /g1. (2) Pterostigma normally either with 1 cross vein ( Fig. 40 View FIGURES 36–42 ), or with 2 cross veins ( Fig. 104 View FIGURES 103–108 ) (on individual wings this number varies from 1 to 3) ( Figs 40–41 View FIGURES 36–42 ). (3) Larval femur with two apical spine-like setae ( Figs 17 View FIGURES 17–18 , 81 View FIGURES 78–83 , 110 View FIGURES 109–112 ). The same in many other taxa of Baetidae , but not in other Procloeon /g1 and not in other Cloeon /fg1.
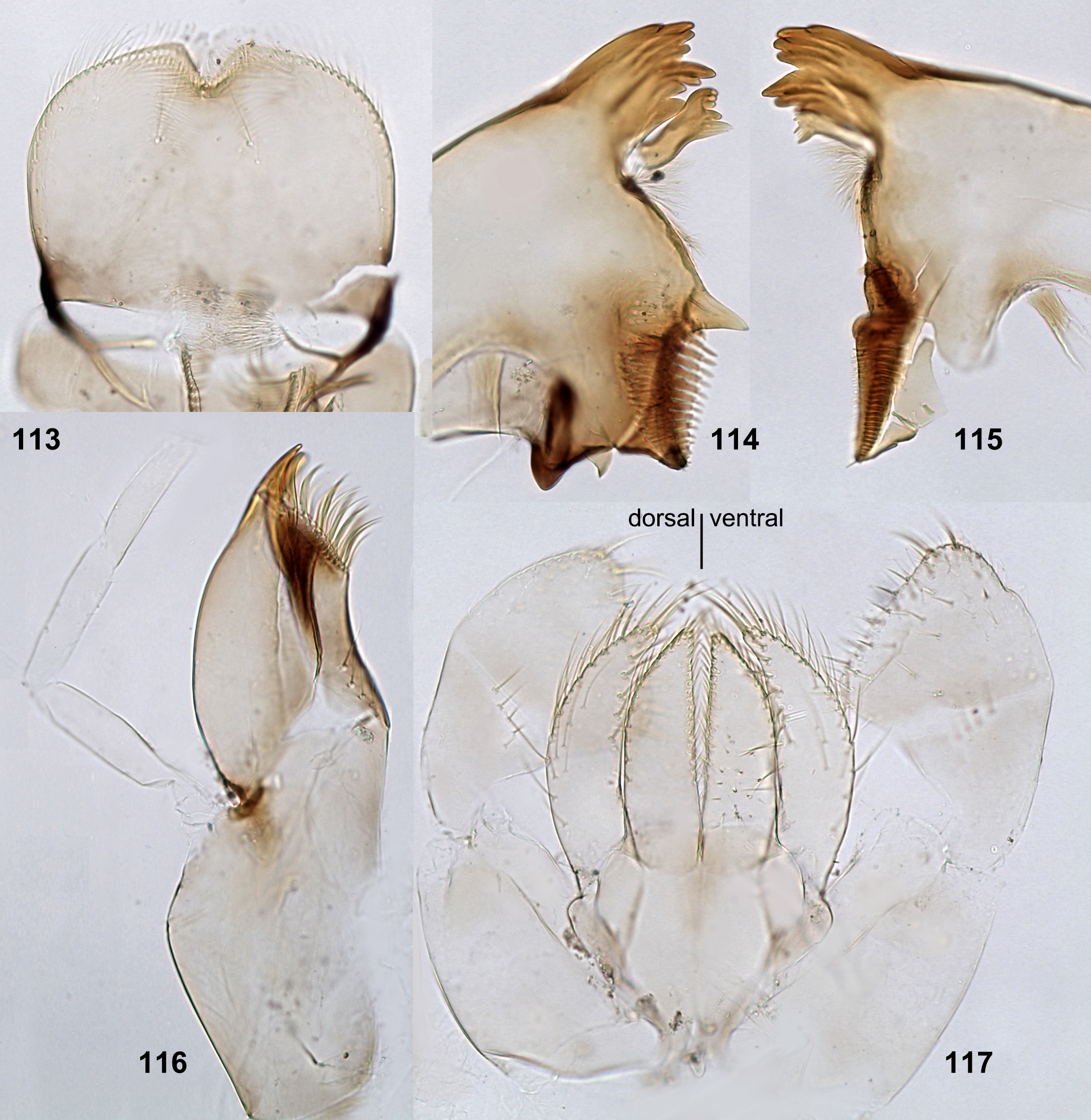
Larvae of all Oculogaster have a similar structure of the labium, with a pair of submedian setae distinguishable among other setae of dorsal surface ( Figs 50 View FIGURES 49–56 , 113 View FIGURES 113–117 ). Mandibles of the « Baetis - type » ( Kluge 2020a: table 1 and p. 578), i.e. with incisor and kinetodontium fused, left prostheca wide, and all denticles of incisor, kinetodontium, prostheca and mola visible in one view ( Figs 51–52 View FIGURES 49–56 , 114–115 View FIGURES 113–117 ). All species of Oculogaster lack hind wings, and larvae have no vestiges of hind protoptera ( Müller-Liebenau & Hubbard 1985: fig. 9h).
Distribution. Paleotropical (Afrotropical and Oriental Regions).
Discussion. In the previous diagnosis, the number of cross veins in pterostigma was reported as one, with individual variability; this diagnosis was based on P. (O.) cylindroculum and P. (O.) album , whose pterostigma normally has one cross vein. Examination of P. regularum reveals that it should be placed in Oculogaster , while its pterostigma normally has 2 cross veins; this fact expands the diagnosis of Oculogaster . While pterostigma with one cross vein is not found in any taxa other than Oculogaster , pterostigma with two veins occurs in some other taxa, particularly in some species of Cloeon s. str., which were confused with species belonging to Oculogaster .
Species composition and classification. Oculogaster can be divided into two species groups: the African group, which includes P. (O.) cylindroculum Kimmins 1956 , P. (O.) barnardi sp. n., P. (O.) niger sp. n., P. (O.) sp. «Wolfkloof» and presumably P. (O.) silvicola Gillies 1997 , and the Asian group, which includes P. (O.) album Kluge 2016 , P. (O.) regularum Müller-Liebenau & Hubbard 1985 , P. (O.) malabarensis sp. n., presumably P. julia ( Gillies 1949) comb. n. and unnamed P. sp. «Thailand-3», P. sp. «Sulawesi» and P. sp. « Philippines ».
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Procloeon (Oculogaster)
| Kluge, Nikita J. 2020 |
Oculogaster
| Kluge, N. J. 2016: 494 |