Barycnellus, Khalaim & Ward, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4425.1.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:BBAFBFC5-9A0B-4519-AB75-DF1EBB702D7C |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5978601 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03AD87D5-5263-364C-BBF7-CB05FA46F2A1 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Barycnellus |
| status |
gen. nov. |
Key to species of Barycnellus
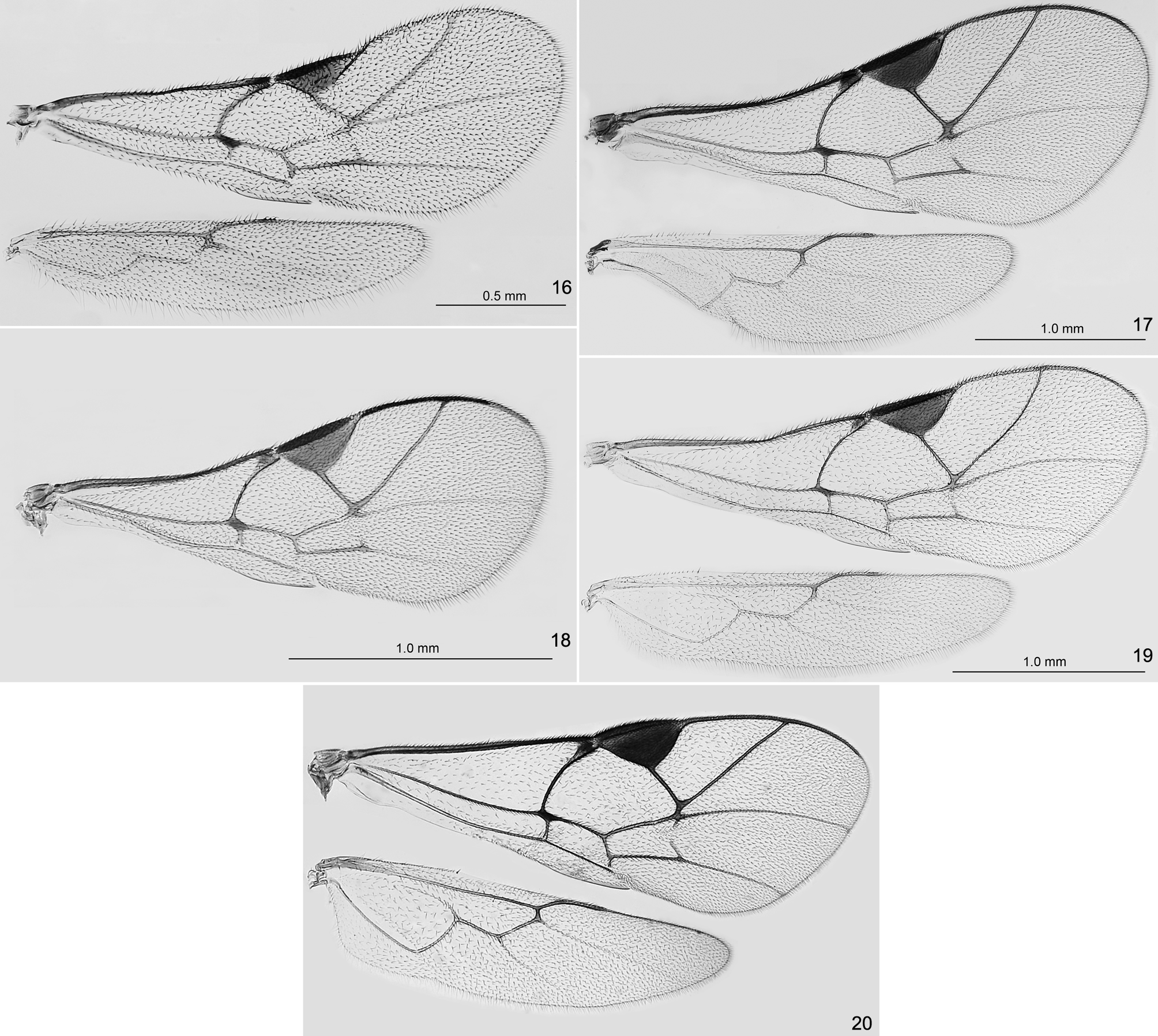
1. Fore wing with 2m-cu vein postfurcal ( Fig. 14 View FIGURES 10–15 ). Head, in dorsal view, weakly transverse ( Fig. 67 View FIGURES 65–71 ). Antennae entirely orangebrown or brown, with 21–23 flagellomeres ( Fig. 65 View FIGURES 65–71 ). Ovipositor very short, with apex very thin and strongly upcurved ( Fig. 68 View FIGURES 65–71 ), its sheath about 0.35× as long as hind tibia............................................. B. cuvierensis sp. nov.
- Fore wing with 2m-cu vein antefurcal or interstitial, sometimes vein is virtually absent ( Fig. 12, 13, 15 View FIGURES 10–15 , 16 View FIGURES 16–20 ). Head, in dorsal view, strongly transverse. Antennae dark brown or blackish, with 14–22 flagellomeres. Ovipositor weakly upcurved to almost straight ( Figs 64 View FIGURES 59–64 , 75 View FIGURES 72–79 , 81 View FIGURES 80–87 ), its sheath 1.5–1.6× longer than hind tibia.............................................. 2
2. Head, in lateral view, with antennae inserted well below level of centre of head, and eyes strongly displaced ventrally ( Figs 63 View FIGURES 59–64 , 78 View FIGURES 72–79 ). Flagellum short and thick, usually slightly clavate, with 14–18 flagellomeres ( Figs 61 View FIGURES 59–64 , 79 View FIGURES 72–79 ). Hind leg robust, with femur 2.7–3.2× as long as broad ( Fig. 80 View FIGURES 80–87 )........................................................................ 3
- Head, in lateral view, with antennae inserted at, or slightly below level of centre of head, and eyes less displaced ventrally ( Figs 60 View FIGURES 59–64 , 71 View FIGURES 65–71 ). Flagellum slender, more or less filiform, with 17–22 flagellomeres ( Figs 59 View FIGURES 59–64 , 69 View FIGURES 65–71 ). Hind leg slender, with femur 3.5–3.8× as long as broad ( Fig. 74 View FIGURES 72–79 )........................................................................ 4
3. Head, in lateral view, subrectangular, strongly flattened frontally, and 1.9× as high as broad (from lower margin of clypeus to top of head) ( Fig. 63 View FIGURES 59–64 ). Mesosoma very strongly compressed laterally, with mesoscutum, in dorsal view, 0.55× as broad as head ( Fig. 62 View FIGURES 59–64 ). Ovipositor weakly and evenly upcurved ( Fig. 64 View FIGURES 59–64 )..................................... B. conlisus sp. nov.
- Head, in lateral view, globose, rounded frontally, and 1.5× as high as broad (from lower margin of clypeus to top of head) ( Fig. 78 View FIGURES 72–79 ). Mesosoma less strongly compressed laterally, with mesoscutum, in dorsal view, 0.65× as broad as head ( Fig. 77 View FIGURES 72–79 ). Ovipositor almost straight and the apex strongly upcurved ( Fig. 81 View FIGURES 80–87 ).................................... B. robustus sp. nov. 71). Flagellum with 17–18 flagellomeres.................................................... B. globosus sp. nov. - Frons shagreened ( Fig. 59 View FIGURES 59–64 ). Head, in lateral view, with antennae inserted slightly below the level of the centre of head ( Fig. 60 View FIGURES 59–64 ). Flagellum usually with 20–22 flagellomeres, rarely with 19 flagellomeres.................. B. aucklandellus sp. nov.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |