Acanthagrion minutum Leonard, 1977
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3646.1.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:DBE8A8B1-56F3-4C46-98BF-069F99352D5B |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6160681 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03ACCC6A-FF9F-FFE9-FF46-872DE276FED9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Acanthagrion minutum Leonard, 1977 |
| status |
|
Acanthagrion minutum Leonard, 1977 View in CoL
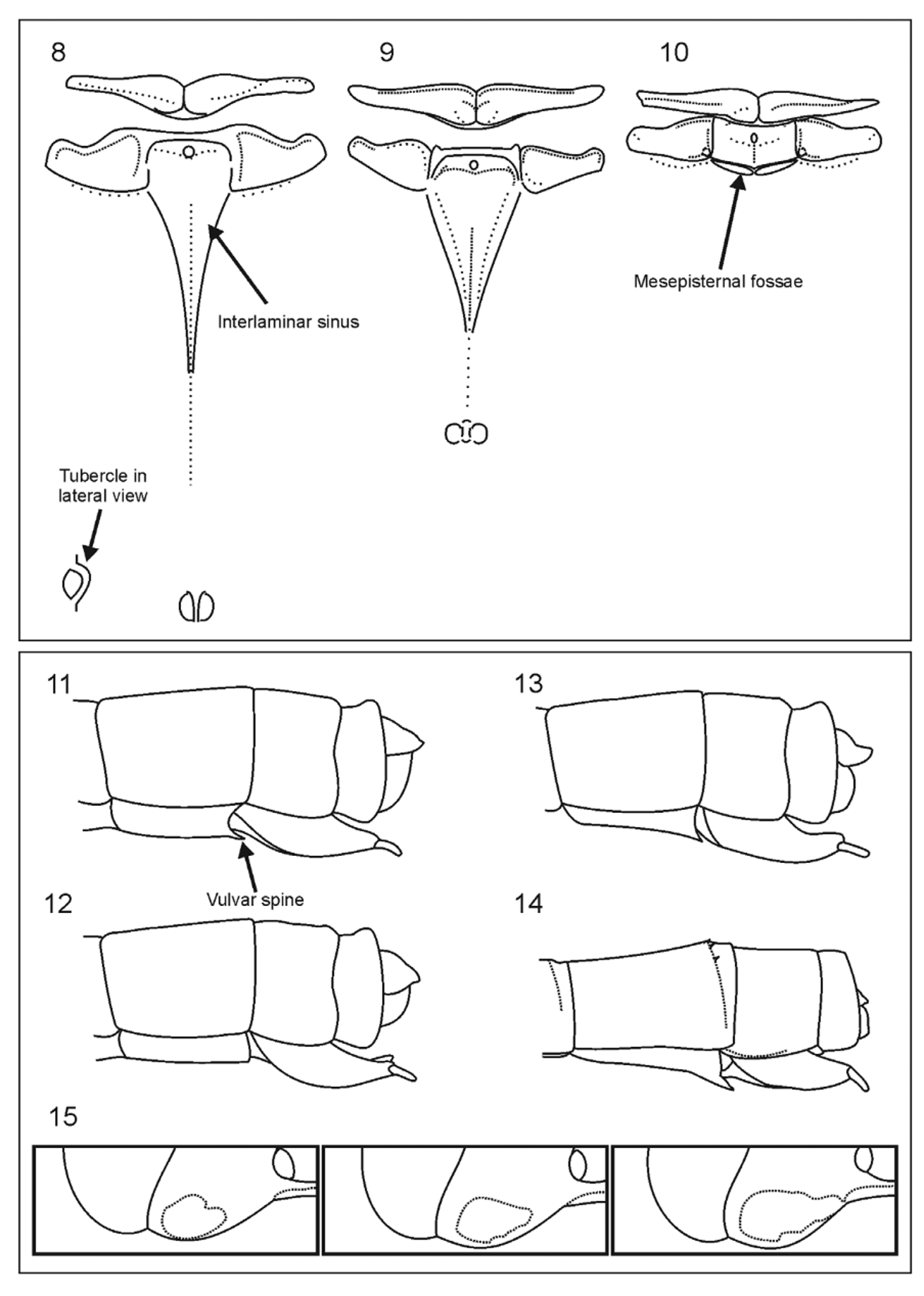
( Figs. 10, 14–16 View FIGURES 8 – 15 )
Acanthagrion minutum Leonard, 1977: 7 , 22, 24, 98, 119–122, 135, 159, 166, 173; pl. V: figs. 51–52, pl. XII: figs. 130, 135– 136, pl. XIX; Gloyd, 1977: 122, 148–149; De Marmels, 1983: 156; De Marmels, 1984: 25; Paulson, 1984: 12, table 1; De Marmels, 1989: 29; De Marmels, 1990: 336; Costa et al. 2000: 12; table 1; Ferreira-Perruquetti & Fonesca-Gessner, 2003: 221; table 1; Garrison et al. 2003: 35; Lencioni, 2005: 10; fig. A3A; Lencioni, 2006: 8–9, 65; fig. A3A, figs. 15 A–E; Muzón et al. 2008: 66; von Ellenrieder & Lozano, 2008: 97, 99, 101–102, 111; table 1; fig. 11; von Ellenrieder & Muzón, 2008: 59; Rojas-R. & Sánchez, 2009: 17–18; Garrison et al. 2010: 181–182.
Head: Labrum light blue with posteromedian spot and posterolateral margins black. Anteclypeus light blue; postclypeus mostly black with margins light blue. Antefrons light blue, in some cases with black median line. Genae light blue. Dorsum of head mostly black, with the following pale brown to light blue spots: two circular spots behind scapes, in some cases light blue color of genae extends posteriorly and contacts these spots either through thin line or band; circular or triangular spot anterior to median ocellus; two circular spots on each side of lateral ocelli; irregular spot between these latter spots and those behind scape that can be either small and subcircular or large and subtriangular reaching in some cases the antefrons. In many specimens dorsum of head shows different color patterns due to fusion of two or more spots described above. Occipital bar pale brown to light blue. Antennifers anteriorly pale brown and posteriorly black. Antennae: scape either black or with anterior half light blue and posterior half black; pedicel and flagellum dark brown to black. Postocular spots light blue or pale brown, generally with projections towards sagittal plane that reaches occipital bar ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 8 – 15 ). Most posterior point of head located behind compound eyes. Occipital area light blue or pale brown, except for two dark brown to black rounded spots on each side of occipital foramen.
Prothorax. Anterior lobe: Central spot light blue and subrectangular, occupying anterior half of lobe, rest of dorsum black; laterals from pale brown to light blue. Middle lobe generally with large trapezoidal or subrectangular geminate median spots, in a few cases very small or absent; dorsolateral spots light blue; propleuron light blue or pale brown. Posterior lobe ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 8 – 15 ): light blue with anterior margin black; lateral margins rounded; without median projection.
Pterothorax. Predominant color light blue. Middorsal black stripe usually interrupted at middorsal carina by thin pale brown to dark brown line. Antealar sinus black with margins pale brown to brown. Antehumeral stripe light blue and entire, not reaching antealar crest; antehumeral stripe widens to 1.5 its minimum width anterior to posterior limit of mesinfraepisternum. Humeral stripe black; posterior margin generally in contact with antealar crest, in some specimens separated from it. Interpleural suture black. Stripe of metapleural suture incomplete. Mesinfraepisternum with dorsal third black and remainder light blue; in some cases black coloration reaches ventral third. Metinfraepisternum pale brown, in some cases with anterior angle slightly darker. Venter of thorax pale brown, generally with two circular black spots. Mesostigmal plates ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 8 – 15 ) without diagonal carina, inner half black and outer half light blue, posterior angle with blunt tubercle. Interlaminar sinus ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 8 – 15 ) subrectangular, (width of interlaminar sinus/length of interlaminar sinus more than 1.0) and brown to black; anterior margin of sinus straight or slightly concave; lateral tips acute and projected anteriorly. Mesepisternal fossae ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 8 – 15 ) contiguous to interlaminar sinus, not elevated, separated from each other by middorsal carina, slightly elongated transversally.
Legs. Coxae and trochanters pale brown to light blue. Femora with external surface of extensor margin dark brown to black, internal surface slightly paler; flexor margin pale brown to light blue, slightly darker distally. Length of femur 1/width of head equal to 1 (5%) or slightly more than 1 (95%). Tibiae pale brown to brown; on extensor margin, just behind row of external spurs, a dark brown to black stripe. Tarsi dark brown with tips black. Leg spurs shorter than intervening spaces.
Wings. CuP reaching posterior margin of CuP&AA’ or slightly distal to it; arculus opposite to antenodal 2. FW: Px 7 (17.5%), 8 (67.5%) or 9 (15%); RP 2 beginning between Px3 and Px4 (52.5%), at Px4 (42.5%) or between Px4 and Px5 (5%); IR1 beginning at Px7 (52.5%), between Px7 and Px8 (30%), at Px8 (12.5%), between Px8 and Px9 (2.5%) or at PtP (2.5%); 2 (35%), 3 (57.5%) or 4 (5%) cells posterior to Pt (without data 2.5%). HW: Px 6 (42.5%) or 7 (57.5%); RP 2 beginning at Px3 (35%) or between Px3 and Px4 (65%); IR1 beginning between Px5 and Px6 (5%), at Px6 (40%), between Px6 and Px7 (27.5%), at px7 (2.5%), between LPx and PtP (12.5%) or at PtP (12.5%); 3 (72.5%) or 4 (25%) cells posterior to pt (without data 2.5%). pt pale brown.
S1. Tergum: posterior margin of anterior spot in contact with posterior stripe of S1. Posterior stripe complete, its central region separated from posterior margin of tergum; lateral margins visible as thin line widened distally, reaching ventral third or fourth of tergum in lateral view. Sternum pale brown, with triangular black spot on posterior margin that extends anteriad, reaching anterior third of the sternum.
S2. Tergum: dorsal spot subrectangular, slightly widened on posterior half or third; anterior margin in contact with anterior margin of tergum through stripe as wide as its minimum width; posterior margin in contact with posterior stripe of S2. Posterior stripe in contact with posterior margin of tergum; lateral margins reaching ventrolateral margins of tergum in lateral view. Sternum pale brown with black midventral stripe, in some cases occupying almost all of sternum.
S3 to S6. Terga: dorsal T-shaped spots reaching anterior margin through thin black line; anterior margins rounded or acute; lateral arms directed anteriad, reaching halfway down terga in lateral view. Posterior stripes visible, reaching ventral fourth or ventrolateral margin of terga in lateral view. Sterna: S3 black, rest generally brown with black midventral stripe.
S7. Tergum: with large T-shaped spot similar to those described for other terga; anterior margin blunt, in contact or not with anterior margin of tergum; lateral margins subparallel, reaching from halfway down to ventral third of tergum in lateral view; lateral arms reaching from ventral fourth to ventrolateral margin of tergum in lateral view; posterior margin reaching subapical row of spines, in some cases black coloration surpasses this line without reaching posterior margin. Subapical row of spines present. Sternum: pale brown with a black midventral stripe.
Terminalia ( Fig. 14 View FIGURES 8 – 15 ). S8 tergum with black subrectangular spot that extends posteriorly up to subapical row of spines and lateroventrally halfway up sides of tergum in lateral view; sternum pale brown with midventral line black; with well-developed vulvar spine that reaches anterior fourth of S9. S9 tergum with black subrectangular spot that occupies almost all of dorsum, lateral margins generally concave, in some cases spot reduced and restricted to posterior third; rest of tergum light blue. Anterior gonapophyses of ovipositor pale brown; posterior gonapophyses brown; valves reaching posterior margin of S10; ventral margin slightly concave and serrated. S10 light blue with anterior margin black, in some cases black triangular spot on anterior margin visible dorsally. Cerci slightly shorter than (75%), equal to (5%) or longer than (20%) half length of S10; in lateral view dorsal margin slightly concave or straight, ventral margin convex, tip directed posteriorly; in dorsal view external margin convex, inner margin slightly concave or straight, tips parallel. Paraprocts without modifications.
Measurements: (mean and standard deviation given; range in brackets; N=20 unless stated otherwise).
Head: max. length 0.9 ± 0.05 [0.8–1.0]; width between compound eyes along anterior margin 1.33 ± 0.05 [1.3–1.4]. Legs: femur 1 length 1.48 ± 0.06 [1.4–1.6]; femur 2 length 2.06 ± 0.09 [1.9–2.2]; femur 3 length 2.64 ± 0.09 [2.4–2.8]. Thorax: interlaminar sinus max. length 0.19 ± 0.04 [0.1–0.2]; interlaminar sinus width between anterior angle of mesostigmal plates 0.3 ± 0.02 [0.2–0.3]; distance between mesepisternal fossae and posterior margin of mesostigmal plates 0. Wings: FW length left (N=19) 13.61 ± 0.34 [12.9–14.3], right 13.65 ± 0.40 [12.6– 14.4]; HW length left 12.74 ± 0.34 [12.1–13.4], right (N=19) 12.8 ± 0.37 [11.8–13.3]. Abdomen: max. length 18.4 ± 0.46 [17.3–19.0]; S1 max. length 0.54 ± 0.05 [0.5–0.6]; S2 max. length 1.27 ± 0.05 [1.2–1.3]; S3 max. length 2.91 ± 0.08 [2.7–3.0]; S4 max. length 3.05 ± 0.08 [2.9–3.2]; S5 max. length 3.04 ± 0.09 [2.8–3.2]; S6 max. length 2.9 ± 0.09 [2.7–3.0]; S7 max. length 2.4 ± 0.09 [2.2–2.5]; S8 max. length 1.18 ± 0.05 [1.1–1.3]; S9 max. length 0.65 ± 0.05 [0.6–0.7]; S10 max. length 0.31 ± 0.03 [0.3–0.4]; S3 min. width 0.46 ± 0.07 [0.3–0.6]; S9 height 0.76 ± 0.06 [0.7–0.9]; S10 height 0.76 ± 0.06 [0.7–0.9]. Cerci: distance surpassing posterior margin of S 10 in lateral view 0.13 ± 0.04 [0.1–0.2]. Paraprocts: length in lateral view 0.08 ± 0.03 [0.05 – 0.1]. Total length 23.72 ± 0.57 [22.6– 24.5].
Females examined (N=39): BRAZIL: Roraima state: Surumu NW of Depósito, 04°14’00’’S - 60°55’00’’W, {141 m. a.s.l.}, leg. M. Alvarenaga, IX-1966, 39Ƥ, UMMZ.
Identification of females: Even though neither tandems nor copulas were examined, identification was possible because males and females were collected together in the same locality, and in many cases a male and a female were together in the same envelope. Besides, there were similarities between the color pattern of males and females (i.e. projection of postocular spots towards the occipital bar), and this species is the smallest in the genus.
Other material examined (N=29): ARGENTINA: Corrientes province: Reserva Natural Rincón de Santa María, artificial ponds, 27°28’23’’S - 56°34’38’’W, {83 m. a.s.l.}, leg P. Pessacq & J. Muzón, 30-IX-2003, 13, MLP. BRAZIL: Roraima state: Surumu NW of Depósito, 04°14’00’’S - 60°55’00’’W, {141 m. a.s.l.}, leg. M. Alvarenaga, IX-1966, 2833, UMMZ.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |