Nothotylenchus, Thorne, 1941
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4729.4.2 |
|
publication LSID |
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:642E0816-A99F-4F7E-9690-190C590F05E8 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3808667 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03ABB532-FFDD-FFE5-FF24-F8D859C53AE7 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Nothotylenchus |
| status |
|
Updated list, identification key and tabular compendium of Nothotylenchus characteristics
Lists of Nothotylenchus species were published by Siddiqi (1986, 2000) and Andrássy (2007). In this study, an upto-date species list of the genus Nothotylenchus includes 41 valid species; species that have been synonymized with other species, transferred to other genera, or considered as species inquirendae, species incertae sedis and nomina nuda are compiled in separate lists.
= Boleodoroides Mathur, Khan & Prasad, 1966
= Boleodorus ( Boleodoroides Mathur, Khan & Prasad, 1966 ) ( Khera, 1970)
Tail tip: D = dull, Fili = filiform, FR = finely rounded, m = mucronate, P = pointed, R = rounded;? = no information available; [] = obtained from measured drawing and not given in description;> = slightly more than; <= slightly less than.
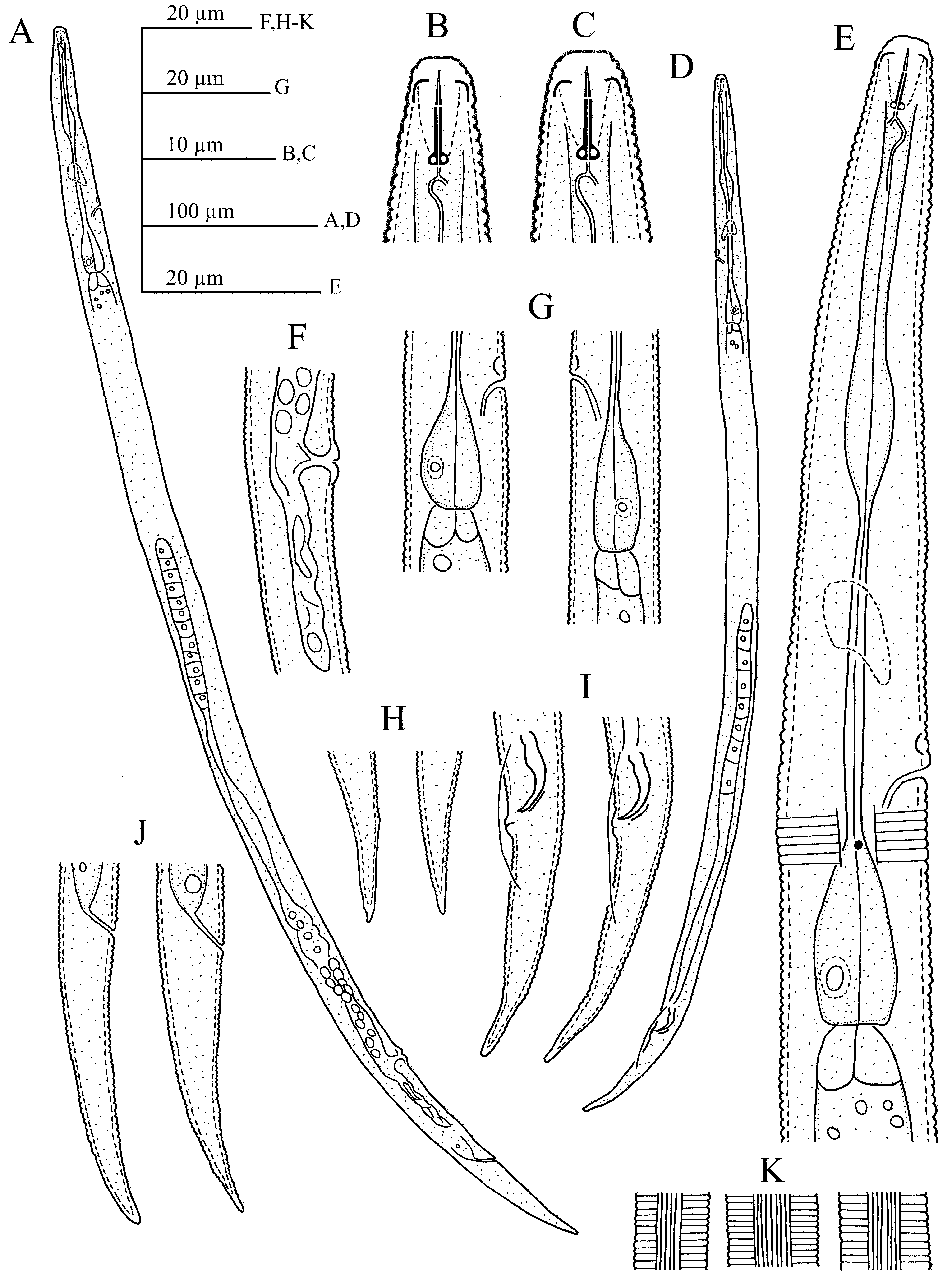
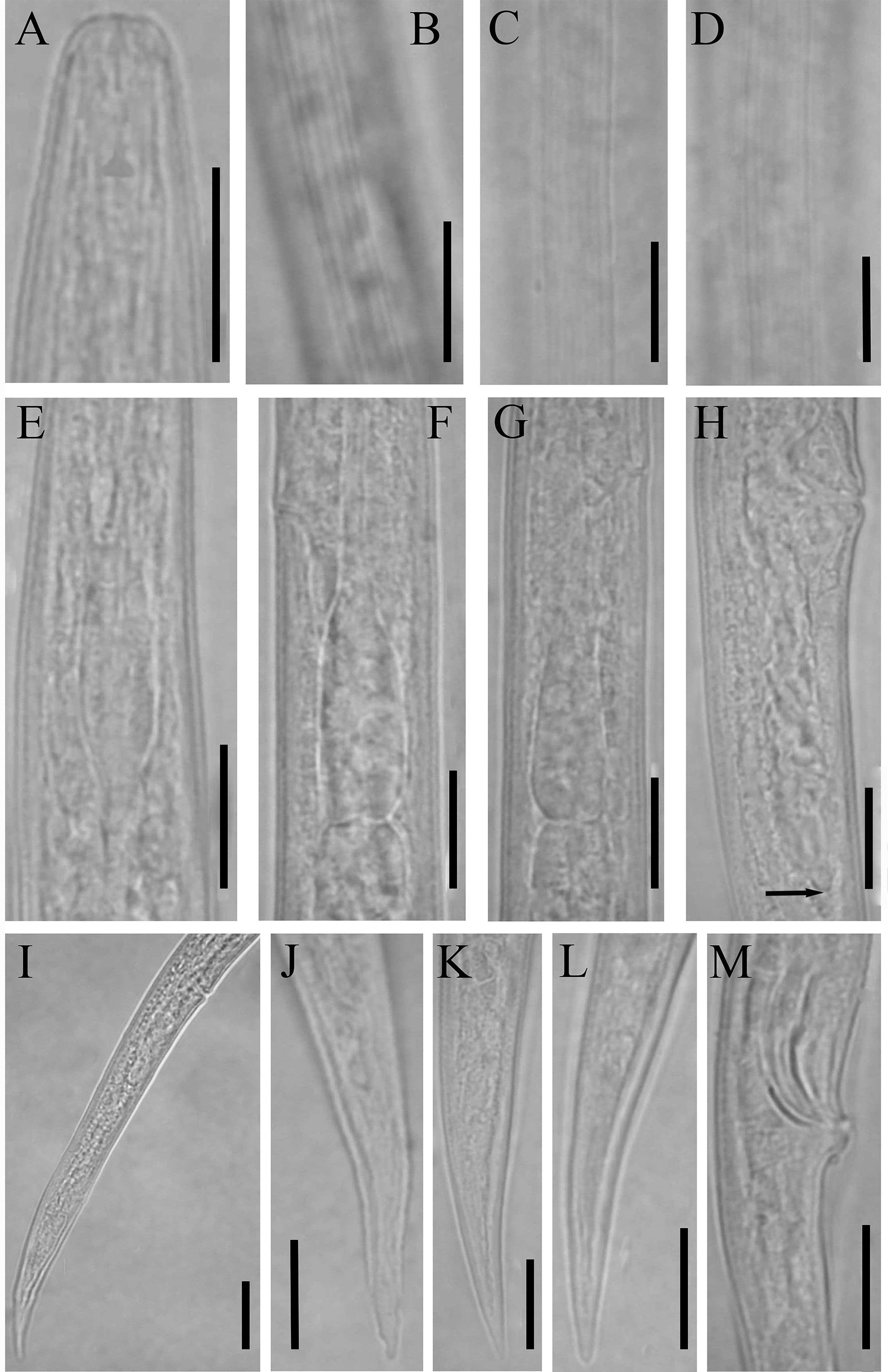
Remark: In this table, Bursa/tail% that has been used previously ( Brzeski, 1991, 1998; Sturhan & Brzeski, 1991), has been removed, because we observed that this feature is very variable even within a population and it can only be used in case of great differences between species (e.g., species with bursa reaching tail tip vs. adanal forms). Diagnosis (emended after Siddiqi, 2000). Anguinidae . Body vermiform, mature females not or slightly swollen. Body size between 0.4 and 1.2 mm. Cuticle finely striated. Lateral fields usually with four or six (occasionally two, five or more than six) incisures, which may be indistinct. Lip region usually low and flattened, continuous or slightly offset; cephalic framework of six equal sectors, not or slightly sclerotized. Stylet 5–14 µm long with conus less than half its total length, weak to moderately-developed, knobs rounded. Median pharyngeal bulb non-muscular, non-valvate; isthmus not separated from basal bulb by a constriction; pharyngeal glands enclosed in a basal bulb of variable shape and size, offset from intestine or overlapping it for a shorter or longer distance. Vulva at 57–86% of body length. Spermatheca elongate-axial. Post-vulval uterine sac one body width or more long. Tails of both sexes similar, elongate-conoid, rarely filiform, tip pointed to rounded, rarely mucronate or clavate. Deirids present. Phasmids absent. Bursa leptoderan, arising near head of spicules and generally extending to middle of tail, rarely adanal, exceptionally reaching tail end.
Type species
Nothotylenchus acris Thorne, 1941
Other species
Nothotylenchus acutus Khan, 1965
= N. allii Khan & Siddiqi, 1968
= N. srinagarensis Fotedar & Mahajan, 1974
= N. indicus Saxena, Chhabra & Joshi, 1973
N. andrassy Jalalinasab, Nassaj Hosseini & Heydari, 2018
N. brzeskii n. sp.
N. bhatnagari Tikyani & Khera, 1969
N. bhattii ( Das & Bajaj, 2005) comb. n.
= Ditylenchus bhattii Das & Bajaj, 2005
N. citri ( Varaprasad, Khan & Lal, 1981) Siddiqi, 1986
= Paurodontus citri Varaprasad, Khan & Lal, 1981
N. clavatus Dhanachand & Gambhir, 1991
N. cylindricollis Thorne, 1941
N. cylindricus Khan & Siddiqi, 1968
= N. elongatus Husain & Khan, 1974
N. hexaglyphus Khan & Siddiqi, 1968
N. medians Thorne & Malek, 1968
N. oryzae ( Mathur, Khan & Prasad, 1966) Siddiqi, 1986
= Boleodoroides oryzae Mathur, Khan & Prasad, 1966
N. persicus Esmaeili, Heydari, Castillo & Palomares-Rius, 2016
N. phoenixae Esmaeili, Heydari & Ye, 2017
N. siddiqii n. sp.
N. similis Thorne & Malek, 1968
N. singhi Das & Shivaswamy, 1980
N. solani ( Varaprasad, Khan & Lal, 1981) Siddiqi, 1986
= Paurodontus solani Varaprasad, Khan & Lal, 1981
N. taylori Husain & Khan, 1974
N. truncatus Eliashvili & Vacheishvili, 1980
N. turfus ( Yokoo, 1968) Siddiqi, 1986
= Neotylenchus turfus Yokoo, 1968
N. uniformis Truskova & Eroshenko, 1977
Species inquirendae
N. atypicus ( Khera & Chaturvedi, 1977) Siddiqi, 1986
= Boleodorus atypicus Khera & Chaturvedi, 1977
N. longistylus ( Khera & Chaturvedi, 1977) Siddiqi, 1986
= Boleodorus longistylus Khera & Chaturvedi, 1977
N. montanus Kiknadze & Eliashvilli, 1988
N. typicus ( Husain & Khan, 1968) Siddiqi, 1986
= Boleodorus typicus Husain & Khan, 1968
Ditylenchus robustus Das & Bajaj, 2005 (see remark 1)
Ditylenchus triticus Das & Bajaj, 2005 (see remark 2)
Species incertae sedis
Neotylenchus nitidus Massey, 1969
= N. nitidus ( Massey, 1969) Siddiqi, 1986
Nomina nuda
Species transferred to other genera
N. innuptus Andrássy, 1961 , to Boleodorus
Remarks on some species inquirendae
Remark 1: Ditylenchus robustus is described by lateral fields with indistinct incisures, fusiform non-valvate median bulb, elongated, narrow spermatheca, genital tract coiled before crustaformeria, and short PUS. But drawings ( Fig. 4A, C & D View FIGURE 4 ) show the spermatheca as not elongate and that it seems to be offset and pouch-like, considered by the authors as coiling of genital tract before crustaformeria ( Das & Bajaj 2005). Therefore, reexamination and redescription of the species is necessary to determine its taxonomic position.
Remark 2: D. triticus is characterised by indistinct lateral fields, fusiform and valveless median bulb, elongateoval spermatheca, filled with large sperms, looped genital tract near spermatheca, and short PUS. The elongated, bipartite and offset spermatheca, filled with small sperms shown in Fig. 3A & C View FIGURE 3 ( Das & Bajaj 2005) excludes this species from Ditylenchus or Nothotylenchus , and the disagreement between the description and drawings require it to be considered as species inquirenda.
Key for identification of species
1- Lateral fields with two incisures; stylet length = 7.5 µm; V = 76; spicule length = 14 µm ..................... N. petilus
- Lateral fields with four or more incisures.................................................................. 2
2- Lateral fields with four incisures......................................................................... 3
- Lateral fields with five or more incisures................................................................. 22
3- Average stylet length ˂ 10 µm ........................................................................... 4
- Average stylet length> 10 µm .......................................................................... 18
4- Basal pharyngeal bulb always long and cylindrical.......................................................... 5
- Basal pharyngeal bulb usually pyriform or short cylindrical................................................... 9
5- Tail terminus pointed.................................................................................. 6
- Tail terminus rounded; basal pharyngeal bulb cylindrical...................................................... 8
6- V = 90, vagina oblique; V-A about two times VBW; basal pharyngeal bulb cylindrical.................. N. cylindricollis
- V = 71–77; vagina perpendicular to body axis; V-A longer.................................................... 7
7- Stylet length = 6.5–7 µm; PUS/VBW = 0.3–0.4.................................................... N. antricolus
- Stylet length = 9–10 µm; PUS/VBW> 2........................................................ N. attenuatus
8- Basal pharyngeal bulb without projection; PUS/VBW = 0.8; spicule length = 17–19 µm ................... N. bhatnagari
- Basal pharyngeal bulb with a small cardiac projection; PUS/VBW = 1.5–2; spicule length = 14 µm .......... N. cylindricus
9- PUS/VBW = 3.4–5.7; tail terminus pointed; bursa covering 1/6 tail................................... N. danubialis
- PUS/VBW ≤ 3...................................................................................... 10
10- Spicule length = 20.5–23 µm; V = 83.3–84.4; PUS/VBW = 0.6–1.2; tail thick and usually with rounded tip.. N. brzeskii n. sp.
- Spicule length <20 µm ............................................................................... 11
11- V = 67%; PUS/VBW = 0.6; tail terminus rounded..................................................... N. loksai
- V ˃ 70% ........................................................................................... 12
12- PUS/VBW = 0.6; tail terminus mucronate.......................................................... N. thornei
- PUS/VBW = 1.3–3.0; tail terminus not mucronate.......................................................... 13
13- Body length ≥ 700 µm; tail terminus pointed.............................................................. 14
- Body length ≤ 650 µm; tail terminus variable, pointed, dull or rounded......................................... 15
14- Bursa nearly reaching tail terminus (~100%)......................................................... N. turfus
- Bursa extending slightly past middle of tail........................................................... N. acris
15- Spicule length = 11–13 µm; V = 80–82; tail terminus pointed.......................................... N. websteri
- Spicule length ≥ 13 µm; V <80......................................................................... 16
16- Spicule length = 14–20 µm; tail terminus pointed, dull or rounded........................................ N. acutus
- Spicule length = 13–15 µm; tail terminus rounded or dull.................................................... 17
17- Stylet length = 6–8 µm; L = 350–500 µm; basal pharyngeal bulb pyriform.................................. N. basiri
- Stylet length = 9 µm, L = 630 µm, basal pharyngeal bulb short cylindrical.................................. N. singhi
18- PUS/VBW <1; tail terminus clavate.............................................................. N. clavatus
- PUS/VBW> 1; tail terminus rounded, dull or pointed....................................................... 19
19- V = 57–66................................................................................. N. truncatus
- V = 68–83 ......................................................................................... 20
20- Spicule length = 13–15 µm; V = 75–79; basal pharyngeal bulb cylindrical................................ N. utschini
- Spicule length = 17–24 µm; basal pharyngeal bulb pyriform.................................................. 21
21- V = 68–76.8; spicule length = 21–24 µm ............................................................ N. adasi
- V = 80.2–83; spicule length = 17–21 µm ............................................................ N. bhattii
22- Lateral fields with five incisures; stylet length = 11–12 µm; V = 81–85%; spicule length = 18–21 µm ....... N. drymocolus
- Lateral fields with six (or more) incisures................................................................. 23
23- Stylet length = 11–12 µm; V = 82–83, PUS/VBW = 0.5–0.7; spicule length = 20–21 µm ..................... N. goldeni
- Stylet length ≤ 10 µm ................................................................................ 24
24- Basal pharyngeal bulb with extension.................................................................... 25
- Basal pharyngeal bulb without extension................................................................. 26
25- Stylet length = 6–8 µm; basal pharyngeal bulb extension short; tail terminus rounded......................... N. solani
- Stylet length = 8–10 µm; basal pharyngeal bulb extension long; tail terminus pointed.......................... N. citri
26- Tail terminus clavate; basal pharyngeal bulb cylindrical, set off from the intestine........................... N. oryzae
- Tail terminus pointed, dull or rounded................................................................... 27
27- Tail terminus always pointed........................................................................... 28
- Tail terminus rounded, dull or rarely pointed.............................................................. 32
28- Tail terminus filiform; spicule length = 13–14 µm; V = 71–76............................................ N. tenuis
- Tail terminus pointed; spicule length ≥ 18 µm; V> 76 µm .................................................... 29
29- Stylet length = 5–7 µm; basal pharyngeal bulb pyriform; PUS/VBW ≤ 1......................................... 30
- Stylet length = 8–9 µm; basal pharyngeal bulb cylindrical; PUS/VBW> 1.2 (two similar species, probably synonymous)... .................................................................................................. 31
30- S-E pore located posterior to basal pharyngeal bulb.................................................. N. persicus
- S-E pore located at the level of anterior third part of basal pharyngeal bulb.............................. N. phoenixae
31- PUS/VBW = 1.2–1.4; male unknown............................................................ N. uniformis
- PUS/VBW = 1.4–2.4; male known............................................................... N. andrassy
32- Stylet length = 10 µm; basal pharyngeal bulb always cylindrical.......................................... N. similis
- Stylet length ≤ 9 µm; basal pharyngeal bulb mostly pyriform................................................. 33
33- Maximum spicule length> 19 µm ...................................................................... 34
- Maximum spicule length <19 µm ...................................................................... 35
34- V = 75–80; PUS/VBW = 1.8–3; spicule length = 16.5–20 µm ........................................... N. taylori
- V = 81.6–86.0; PUS/VBW = 0.5–1.3; spicule length = 19–22 µm .................................... N. hexaglyphus
35- Lateral fields with six to nine incisures; V = 79.3–81.0; PUS/VBW = 1.9–2.4; spicule length = 14.5–16.5 µm .................................................................................................... N. siddiqii n. sp.
- Lateral fields with six incisures......................................................................... 36
36- V = 84–86; PUS/VBW <1; basal bulb always short cylindrical......................................... N. fotedari
- V usually ≤ 84...................................................................................... 37
37- Basal bulb always cylindrical; PUS/VBW = 1.1–1.8; tail terminus finely rounded............................ N. boroki
- Basal bulb mostly pyriform or slightly overlapping (four similar species)........................................ 38
38- Uterus length/VBW = 3–4, basal bulb slightly overlapping........................................... N. tuberosus
- Uterus length/VBW usually ˂ 3; basal bulb mostly pyriform and offset......................................... 39
39- Head high, stylet knobs sloping posteriorly........................................................ N. geraerti
- Head low, stylet knobs rounded......................................................................... 40
40- Stylet length = 8–9 µm, PUS/VBW = 1.1–1.3, tail not thick............................................. N. affinis
- Stylet length = 6.5–8 µm, PUS/VBW = 1.3–2.6, tail thick............................................. N. medians
TABLE 3. Some diagnostic features of Nothotylenchus species (all measurements are for females except spicules)
| Species | Lateral incisures | Stylet | V | V′ | PUS/VBW | PUS/V-A% | Tail tip | c | c′ | Spicules |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N. acris | 4 | 5.5–10 | 76–82 | - | 2–3 | - | P | 9.6–17.8 | 3.5–5.2 | 12.5–19.5 |
| N. acutus | 4 | 7.5–10 | 70–79 | 80–87 | 1.3–3.0 | 25–51 | P,D,R | 8.1–12.1 | 4.5–9.2 | 14–20 |
| N. adasi | 4 | 10.5–13 | 68.0–76.8 | 79.0–85.4 | 1.2–2.3 | 16.0–37.7 | R,D,P | 8.8–10.8 | 4.9–7.5 | 22–24 |
| N. affinis | 6 | 8–9 | 76–80 | - | 1.1–1.3 | - | R | 9.2–11.7 | 4.7–7.3 | 15–17 |
| N. andrassy | 6 | 8–9 | 77.1–82.4 | - | 2.0–2.4 | 49.1–62.0 | P | 8.9–13.2 | 4.4–6.0 | 18–19 |
| N. antricolus | 4 | 6.5–7 | 70.7–72.4 | - | 0.3–0.4 | - | P | 6.7–6.9 | 9.6–10.0 | - |
| N. attenuatus | 4 | 9–10 | 74–77 | - | >2 | 36 | P | 13–16 | [7.5] | - |
| N. basiri | 4 | 6–8 | 73.0–79.6 | 82.1–87.7 | 1.1–2.3 | 19.3–35.8 | R,D | 8.8–11.3 | 5.0–6.9 | 13–15 |
| N. bhatnagari | 4 | 9–10 | 80–82 | - | ˂1 | [20] | FR | 11.2–17.5 | [4.2] | 17–19 |
| N. bhattii | 4 | 10–12 | 80.2–83.0 | - | 1.0–1.3 | 33–36 | D,P | 7.5–13.0 | 4.0–5.7 | 17–21 |
| N. boroki | 6 | 7–9 | 74.9–78.8 | - | 1.1–1.8 | - | FR | 9.2–10.8 | 3.6–5.4 | 14–15 |
| N. brzeskii n. sp. | 4 | 7–8 | 83.4–84.4 | 90.1–90.8 | 0.6–1.2 | 20.2–35.3 | R,D | 13.3–15 | 3.2–4.0 | 20.5–23 |
| N. citri | 6 | 8–10 | 78–80 | - | 2 | - | P | 12–15 | 4–6 | 20–22 |
| N. clavatus | 4 | 11–14 | 69–72 | - | 0.5 | - | Clavate | 8 | 7–8 | - |
| N. cylindricollis | 4 | 7 | 90 | - | 1 | - | P | 17.0 | [4.1] | 20 |
| N. cylindricus | 4 | 6–9 | 75–82 | - | 1.5–2.0 | 30–50 | R | 7.0–11.4 | 4.8–6 | 14 |
| N. danubialis | 4 | 7.5 | 72.2–73.3 | - | 3.4–5.7 | - | P | 9.3–10.4 | 6–8 | 15–16 |
| N. drymocolus | 5 | 11–12 | 81–85 | - | <1 | - | P | 9.7–11.8 | [4.9] | 18–21 |
| N. fotedari | 6 | 9 | 84–86 | - | <1 | - | P,?D,?R | 14–16 | 4 | 17 |
| N. geraerti | 6 | 6.5–9 | 74.8–84.6 | 82.0–95.8 | 0.6–3.0 | 14–77.0 | R,D,P | 8.4–15.6 | 3.4–6.7 | 14–18.5 |
| N. goldeni | 6 | 11–12 | 82–83 | - | 0.5–[0.7] | [20] | P,D,R | 12–14 | 3.3–3.8 | 20–21 |
| N. hexaglyphus | 6 | 7–8.5 | 81.6–86 | 89.2–91 | 0.5–1.3 | 18–36.3 | R,D | 11.2–15.5 | 3.4–5.1 | 19–22 |
| N. loksai | 4 | 8 | 66.7 | 79 | >0.5 | - | R | 6.3 | 8 | 14 |
....Continued next page
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |