Schleiferilactobacillus, Zheng & Wittouck & Salvetti & Franz & Harris & Mattarelli & O’Toole & Pot & Vandamme & Walter & Watanabe & Wuyts & Felis & Gänzle & Lebeer, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004107 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4728473 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A8D903-D213-025D-FFD0-F95754B9319A |
|
treatment provided by |
Valdenar (2021-04-29 20:05:09, last updated by Guilherme 2025-02-06 14:43:30) |
|
scientific name |
Schleiferilactobacillus |
| status |
gen. nov. |
DESCRIPTIONOF SCHLEIFERILACTOBACILLUS GEN. NOV.
Schleiferilactobacillus (Schlei.fer.i.lac.to.ba.cil’lus. L. masc. noun Schleiferi, of (Karl-Heinz) Schleifer, a German microbiologist and taxonomist who made seminal contributions to bacterial taxonomy. N.L.masc. n. Lactobacillus a bacterial genus; N.L. masc. n. Schleiferilactobacillus , a lactobacillus named after Karl-Heinz Schleifer).
Gram-positive, rod-shaped, catalase-negative, homofermentative and aerotolerant. Strains of the genus were isolated from spoiled beverages including beer and fermented dairy beverages, fermented vegetables, andfermented cereals. Growth is observed in the range of 15–42 °C; a wide range of carbohydrates including pentoses, hexoses and oligosaccharides are fermented. The genome size ranges from 3.14 to 3.32 Mbp; the mol% G+C content of DNA ranges from 49.1 to 56.3.
Aphylogenetic tree on the basis of 16S rRNA genes of all species in thegenus Schleiferilactobacillus is provided in Fig. S6E View Fig .
Thetype species of thegenus is S. perolens comb. nov.; Schleiferilactobacillus was previouslyreferred to as L. perolens group.
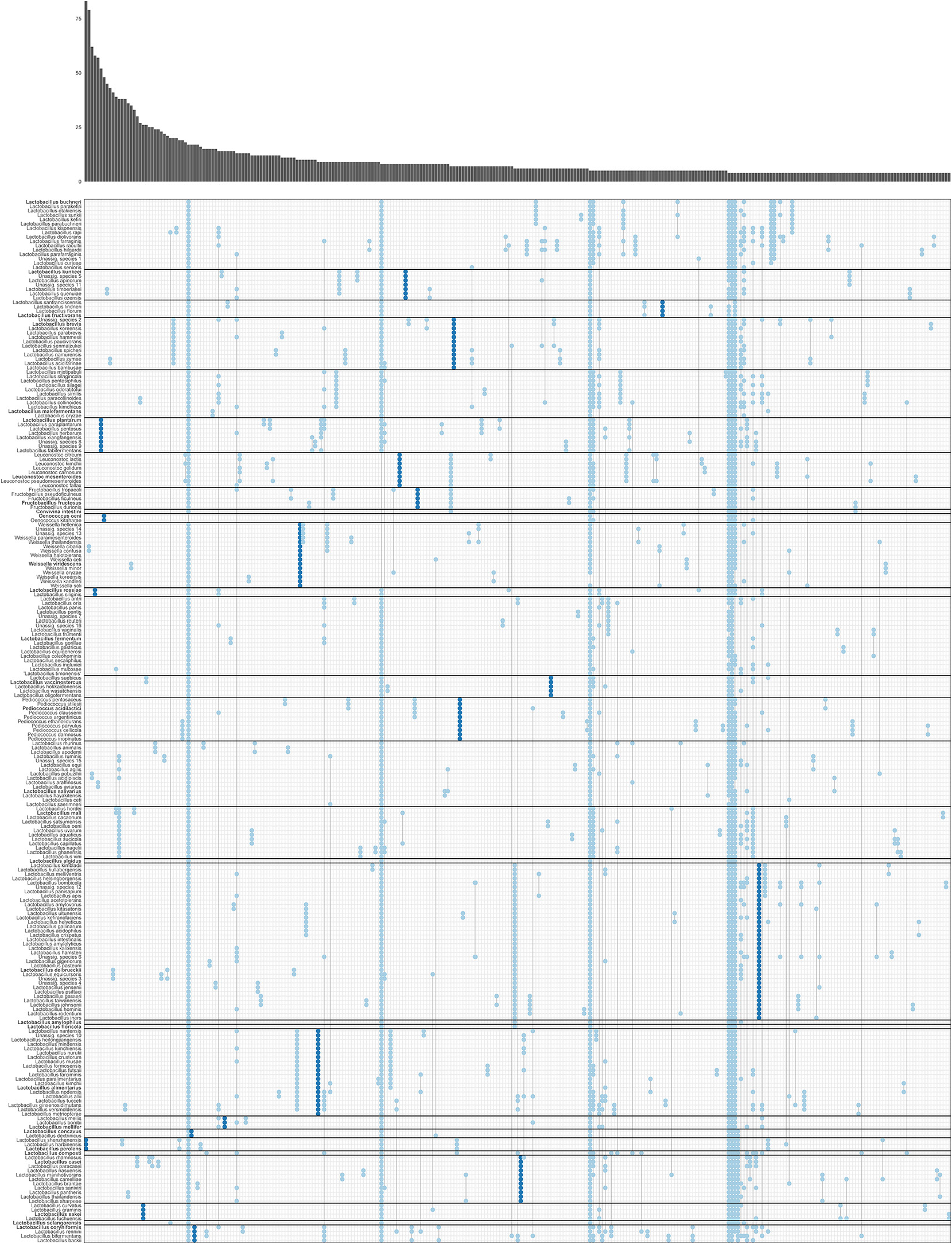
Fig. 6. Gene family presence/absence patterns in Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Each column represents a gene family presence/absence pattern in species of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostoaceae, where presence is indicated with a dot. The absolute number of gene families that conform to each pattern is visualized in the marginal bar plot at the top. Separations between phylogroups are indicated with horizontal black lines. We defined genes that were present in all genomes of a clade and in none of the genomes outside of that clade as ‘signature genes’ (dark blue); other genes are shown in light blue. Only presence/absence patterns followed by four or more gene families are shown. Patterns of presence in a single species or all species are not shown. Unassigned species are clusters of closely related genomes which could not be assigned to a known species due to low whole-genome similarity to a type strain and/or low 16S rRNA similarity to a type strain.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
1 (by valdenar, 2021-04-29 20:05:09)
2 (by ExternalLinkService, 2021-04-29 21:47:49)
3 (by valdenar, 2021-04-30 14:27:18)
4 (by valdenar, 2021-04-30 14:46:18)
5 (by ExternalLinkService, 2021-04-30 19:06:52)
6 (by valdenar, 2021-04-30 19:23:20)
7 (by ExternalLinkService, 2022-01-29 07:26:42)
8 (by valdenar, 2022-06-14 18:02:19)
9 (by plazi, 2023-11-02 08:01:04)