Aceria banatica, Vidović, Biljana, 2011
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.205738 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5683208 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A4DA7C-FFA1-F76A-FF5F-DD10FB6F8846 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Aceria banatica |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Aceria banatica n. sp.
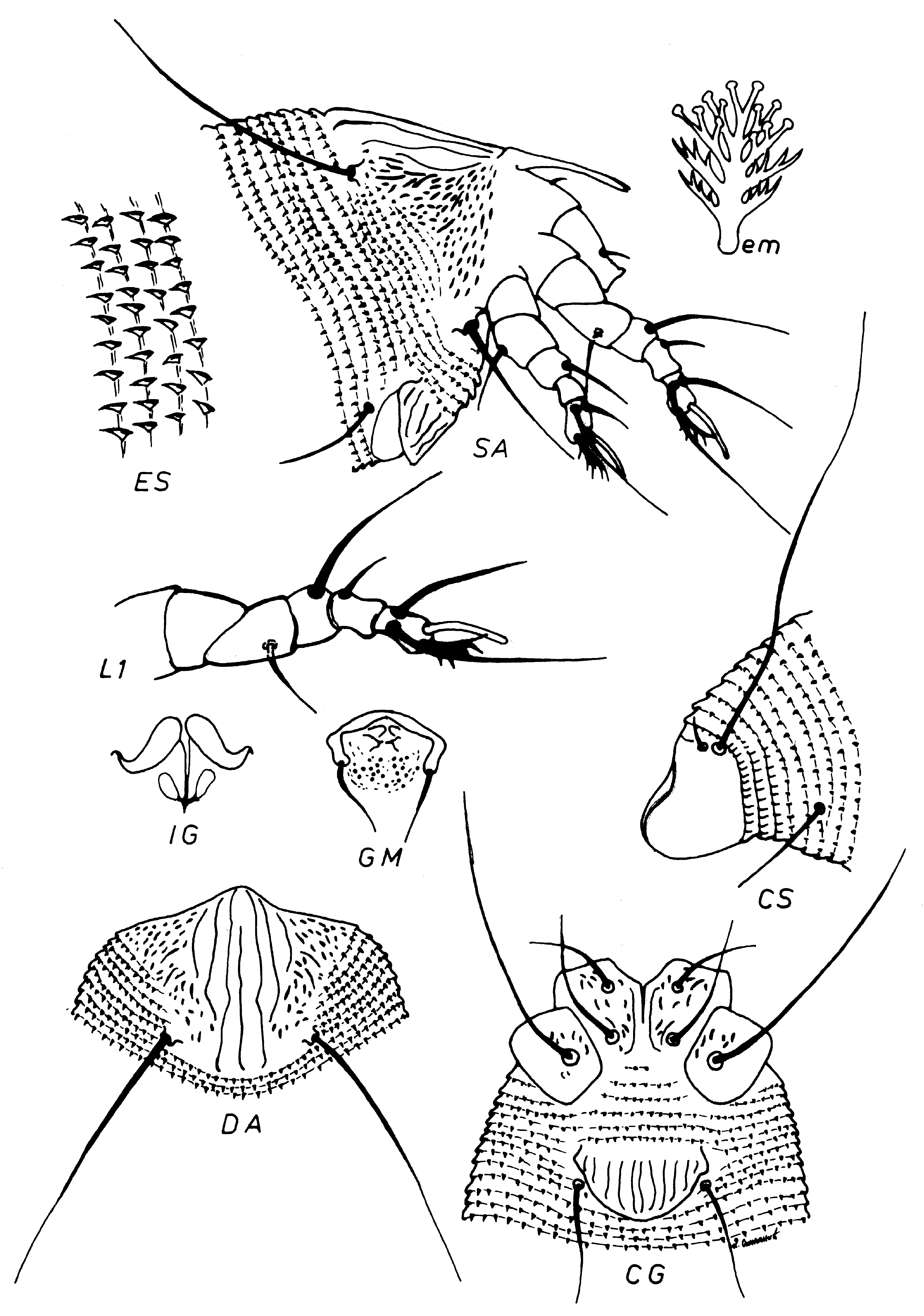
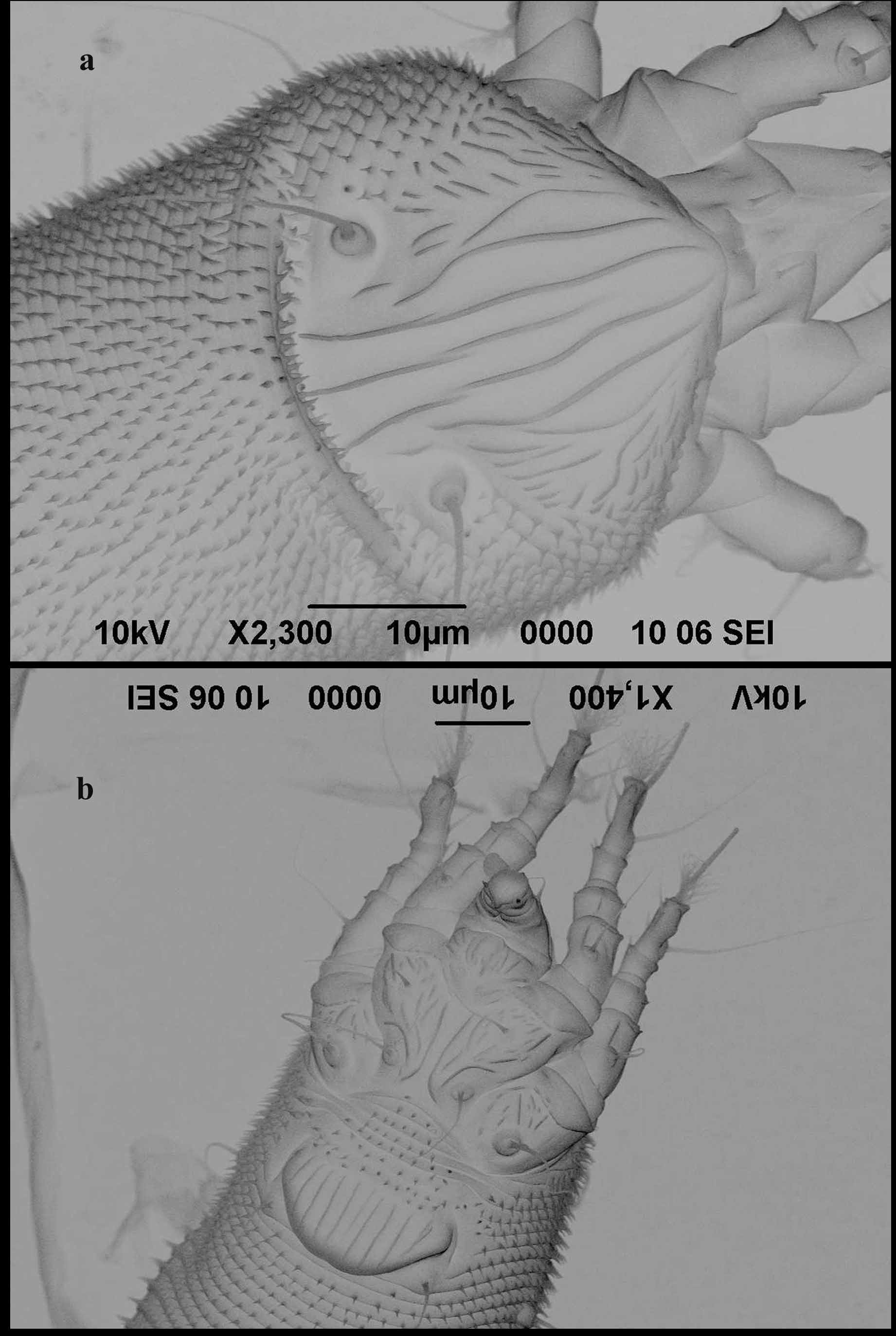
( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 & 2 View FIGURE 2 )
Female: (n=10). Body wormlike 173 (160–176), 49 (46–53) wide, white in colour. Gnathosoma 18 (16–18), downcurved, dorsal genual setae (d) 3 (3–5), cheliceral stylets 16 (14–16). Prodorsal shield 26 (25–27), 27 (24– 28) wide. Anterior half triangular, posterior part semi-elliptical without lobe over gnathosoma. Prodorsal shield tubercles on the rear margin of the shield 16 (15–17) apart, scapular setae (sc) 32 (29–38), projecting posteriorly. Shield design composed of one median line on rear ¾ of shield; two complete admedian lines; I submedian lines extending from anterior margin and ending on rear ¼ of shield; II submedian lines slightly mesally curved, ending almost in the middle of shield; there are numerous dashes between II submedian line and lateral margin of shield. Legs with all usual segments and setae. Leg I 25 (25–27); femur 5 (5–6), femoral setae (bv) 10 (9–11); genu 4 (4– 5), genual setae (l") 21 (19–22); tibia 5 (4–6), tibial setae (l') 5 (5–7); tarsus 5 (5–7), inner fastigial setae (ft') 16 (15–18), outer fastigial setae (ft") 24 (20–25); solenidion (ω) 9 (8–10), distally rounded; empodium 5 (5–6) and 5 rayed. Leg II 21 (20–23); femur 5 (5–6), femoral setae (bv) 11 (10–12); genu 3 (3–4), genual setae (l") 9 (9–11); tibia 4; tarsus 5, inner fastigial setae (ft') 6 (4–7), outer fastigial setae (ft") 23 (21–24); solenidion (ω) 9 (9–11), distally rounded; empodium 5 (4–6) and 5 rayed. Coxigenital area with a pattern of numerous dashes; sternal line 6 (6–7) long; coxal setae (1b) 10 (10–13), 10 (8–10) apart; coxal setae (1a) 16 (15–18), 6 (5–7) apart; coxal setae (2a) 27 (26–34), 18 (16–18) apart. Genitalia 11 (9–11), 17 (17–20) wide, genital coverflap with 11 (10–11) longitudinal striae in one row; coxal setae (3a) 14 (13–15), 15 (13–15) apart. Opisthosoma with subequal annuli: 75 (70–78) dorsal and 73 (67–73) ventral annuli; 5 (5–6) coxogenital annuli. Annuli with thornlike microtubercles, posterior ventral annuli with elongated microtubercles. Setae c2 12 (12–17), 44 (39–47) apart, on annulus 11 (10– 13); setae d 36 (30–51), 35 (31–35) apart, on annulus 24 (22–25); setae e 8 (8–10), 18 (17–19) apart, on annulus 41 (37–41); setae f 20 (17–20), 16 (16–19) apart, on annulus 68 (63–68); setae h2 62 (55–72), 10 (10–11) apart; setae h1 6 (5–6), 7 (6–7) apart.
Male: (n=4). Body wormlike 152 (145–156), 45 (41–45) wide. Gnathosoma 17 (16–17), dorsal genual setae (d) 4 (3–4), cheliceral stylets 15 (13–15). Prodorsal shield shape and design similar to that of females, 26 (23–26), 24 (23–24) wide. Tubercles of scapular setae (sc) located on rear margin of shield, 17 (15–17) apart, sc 35 (32–40), projecting posteriorly.
Leg I 26 (24–27); femur 7 (6–7), femoral setae (bv) 11 (10–11); genu 4, genual setae (l") 13 (13–17); tibia 5 (4–5), tibial setae (l’) 5 (5–6); tarsus 6 (5–6), inner fastigial setae (ft') 15 (13–16), outer fastigial setae (ft") 23 (20– 23); solenidion (ω) 9 (9–10), distally rounded; empodium 5 and 5 rayed. Leg II 23 (20–23); femur 6 (5–6), bv 9 (9– 10); genu 4 (3–4), l" 9 (9–11); tibia 3 (3–4); tarsus 5, ft' 7, ft" 22 (21–22); solenidion (ω) 10, distally rounded; empodium 5 and 5 rayed. Coxigenital area similar to female. Coxal setae (1b) 9 (9–13), 9 (8–9) apart; coxal setae (1a) 10 (10–11), 5 apart; coxal setae (2a) 32 (21–32), 15 (14–16) apart. Genitalia 15 wide, coxal setae (3a) 11 (10– 12), 12 (11–13) apart. Opisthosoma with subequal annuli: 76 (72–76) dorsal annuli, 67 (63–67) ventral annuli, 5 (5–6) coxogenital annuli. Annuli with microtubercles similar to female. Setae c2 15 (13–15), 41 (34–41) apart, on annulus 11 (10–11); setae d 36 (31–47), 30 (28–31) apart, on annulus 25 (20–25); setae e 8 (8–10), 16 (15–16) apart, on annulus 38 (34–38); setae f 17 (16–19), 16 (14–16) apart, on annulus 62 (58–62); setae h2 57 (48–62), 10 (9–10) apart; setae h1 5 (4–5), 6 (5–6) apart.
Nymph: (n=1). Body wormlike 130, 32 wide. Gnathosoma 13 long downcurved, dorsal genual setae (d) 2, cheliceral stylets 14. Prodorsal shield shape and design similar to that of females, 22, 18 wide. Scapular setae (sc) 30, 16 apart directed on the rear divergently. Leg I 18; femur 5, femoral setae (bv) 5; genu 3, genual setae (l") 17; tibia 3, tibial setae (l') 4; tarsus 4, inner fastigial setae (ft') 13, outer fastigial setae (ft") 17; solenidion (ω) 7, distally rounded, empodium 5 and 5 rayed. Leg II 18; femur 5, femoral setae (bv) 6; genu 3, genual setae (l") 8; tibia 2; tarsus 3, inner fastigial setae (ft') 3, outer fastigial setae (ft") 16; solenidion (ω) 7, distally rounded; empodium 5 and 5 rayed. Coxigenital area. Coxal setae (1b) 7, 9 apart; coxal setae (1a) 8, 3 apart; coxal setae (2a) 29, 14 apart. Opisthosoma with 69 dorsal annuli, 60 ventral annuli, 9 coxogenital annuli. Setae c 2 12, 35 apart, on annulus 11; setae d 30, 26 apart, on annulus 20; setae e 7, 14 apart, on annulus 30; setae f 11, 12 apart, on annulus 55; setae h 2 43, 7 apart; setae h1 4, 5 apart.
Larva. Not found
Type material. Female holotype (slide # 158/2). Male paratype (slide # 158/40) and 12 female paratypes (slides ## 158/1, 158/3, 158/4, 158/5, 158/6, 158/7, 158/9, 158/11, 158/13, 158/41, 158/42, 158/43); nymph (slide # 158/34). All collected from Echinops ruthenicus (Fisch.) (Asteraceae) , Serbia, Deliblato Sands (Deliblatska peščara, Široka torina, 44o51.179’N, 21o06.119’E), 10 June 2007, coll. R. Petanoviċ.
Additional material. 23 females (slides ## 158/8, 158/10, 158/12, 158/14–33), 3 males (slides ## 158/44–46) and 2 nymphs (slide # 158/35 and 158/36). Same collection details as the holotype and paratypes; 27 females (slides ## 290/1–27), 9 males (slides ## 290/28–36), 2 nymphs (slide # 291/37 and 291/38) from the same host and locality but different date, 22 June 2008.
Etymology. The species name is derived from the name of the geographic region in which the host plant was found.
Host plant. Echinops ritro L. subspec. ruthenicus (M.Bieb.) Nyman (Asteraceae) .
Relation to the host. The mites are vagrants on the lower leaf surfaces. No visible damage was observed.
Differential diagnosis and remarks. Aceria banatica n. sp. is close to Aceria echinopsi Boczek and Nuzzaci 1988 , but it can be distinguished by the following meristic and qualitative characters: Number of rays on the tarsal empodium ( A. echinopsi = 6; A. banatica = 5); number of striae on the female genital coverflap ( A. echinopsi has 18 to 20; A. banatica has 10 to 11); prodorsal shield design ( A. echinopsi has three pairs of submedian lines, while A. banatica has two pairs of submedian lines). Aceria banatica is generally smaller, with shorter setae. Differing morphometric characters between A. echinopsi and the new species are presented in Table 1 View TABLE 1 . Besides these characters, both species have different life-styles: A. echinopsi forms sub-spherical galls with cells inside along the margins of leaves, whereas A. banatica is a vagrant on the lower leaf surface. The apparent common feature of both eriophyoid species is the presence of thornlike microtubercles on the dorsal and ventral annuli.
TABLE 1. Comparison of disposed key morphological characters between Aceria echinopsi Boczek and Nuzzaci 1988 and Aceria banatica n. sp.
| Morphometric Characters | Aceria echinopsi Boczek & Nuzzaci 1988 | Aceria banatica n. sp. |
|---|---|---|
| Length of body | 225 (182–230) | 173 (160–176) |
| Width of body | 40 | 49 (46–53) |
| Length of gnathosoma | 18 | 18 (16–18) |
| Length of dorsal genual setae (d) | 5 | 3 (3–5) |
| Length of cheliceral stylets | 13 | 16 (14–16) |
| Length of prodorsal shield | 30 (28–32) | 26 (25–27) |
| Tubercles of sc apart | 26 | 16 (15–17) |
| Length of setae sc | 38 | 32 (29–38) |
| Length of leg I | 26 | 25 (25–27) |
| Length of tibia | 4 | 5 (4–6) |
| Length of setae l ʹ | 10 | 5 (5–7) |
| Length of tarsus | 8 | 5 (5–7) |
| Length of solenidion | 10 | 9 (8–10) |
| Length of empodium | 8 | 5 |
| Number of rays on tarsal empodium | 6 | 5 |
| Length of leg II | 24 | 23 (20–23) |
| Length of tibia | 4 | 4 |
| Length of tarsus | 7 | 5 |
| Length of solenidion | 10 | 9 (9–11) |
| Length of empodium | 8 | 5 (4–6) |
| Length of setae 1b | 18 | 10 (10–13) |
| Apart of tubercules 1b | 15 | 10 (8–10) |
| Length of setae 1a | 38 | 16 (15–18) |
| Apart of tubercules 1a | 10 | 6 (5–7) |
| Length of setae 2a | 55 | 27 (26–34) |
| Apart of tubercules 2a | 28 | 18 (16–18) |
| Number of opisthosomal annuli | 95 (79–97) | 75 (70–78) dorsal 73 (67–73) ventral |
| Length of seta c2 | 20 | 15 (13–15) |
| On annulus | 16 | 11 (10–13) |
| Length of setae d | 45 | 36 (30–51) |
| On annulus | 35 | 24 (22–25) |
| Length of setae e | 21 | 8 (8–10) |
| On annulus | 54 | 41 (37–41) |
| Length of setae f | 25 | 20 (17–20) |
| On annulus | 89 | 68 (63–68) |
| Length of setae h1 | 4 | 6 (5–6) |
| Length of female genitalia | 13 | 11 (9–11) |
| Width of female genitalia | 25 | 17 (17–20) |
| Number of ridges | 18–20 | 11 (10–11) |
| Length of setae 3a | 20 | 14 (13–15) |
| Apart of setae 3a | 20 | 15 (13–15) |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SuperFamily |
Eriophyoidea |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |