Larsia hamadae, Oliveira, Caroline Silva Neubern De & Silva, Fabio Laurindo Da, 2011
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.205586 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5682142 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A0B021-7E06-8251-FF26-F963FE15FA96 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Larsia hamadae |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Larsia hamadae View in CoL sp. n.
( Figs 14–26 View FIGURES 14 – 17 View FIGURES 18 – 22 View FIGURES 23 – 26 )
Type material. Holotype male with larval and pupal exuviae, BRAZIL: Amazonas State, Manaus, Igarapé Cabeça Branca, 15/vii/2008, C. S. N. Oliveira & L. M. Fusari. Paratypes: 3 males with larval and pupal exuviae, same data as holotype.
Etymology. Named in honour of Dr. Neusa Hamada, entomologist of the Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas da Amazônia.
Diagnostic characters. Larsia hamadae differs from other Larsia species by combination of the following characters. Male: abdomen yellowish with brown spots; tergite IX with three dorsal setae; anal point bilobed. Pupa: respiratory atrium with distinct central duct. Abdomen pale brown without spots. Tergite IV with pores located lateral to D1. Anal lobe without shagreenation. Larva: head capsule with caudal maculation; second antennal segment and maxillary palp yellow; paraligula pectinate.
Description. Adult male (n = 4 unless otherwise stated)
Dimensions. Total length [1.88] 1.88–2.03 (3) mm. Wing length [1.18] 1.16–1.30 (3) mm. Total length/wing length [1.59]1.51–1.74 (3). Wing length/length of profemur [1.99] 1.99–2.18 (3).
Coloration. Head pale with dark brown occipital margin; pedicel and antenna pale brown; maxillary palp pale brown. Thorax pale with pale brown vittae; antepronotum pale; supraalar callus brown. Wing membrane transparent without spots, veins pale brown and macrotrichia on veins. Legs pale brown. Abdomen yellowish with brown spots. Hypopygium pale brown.
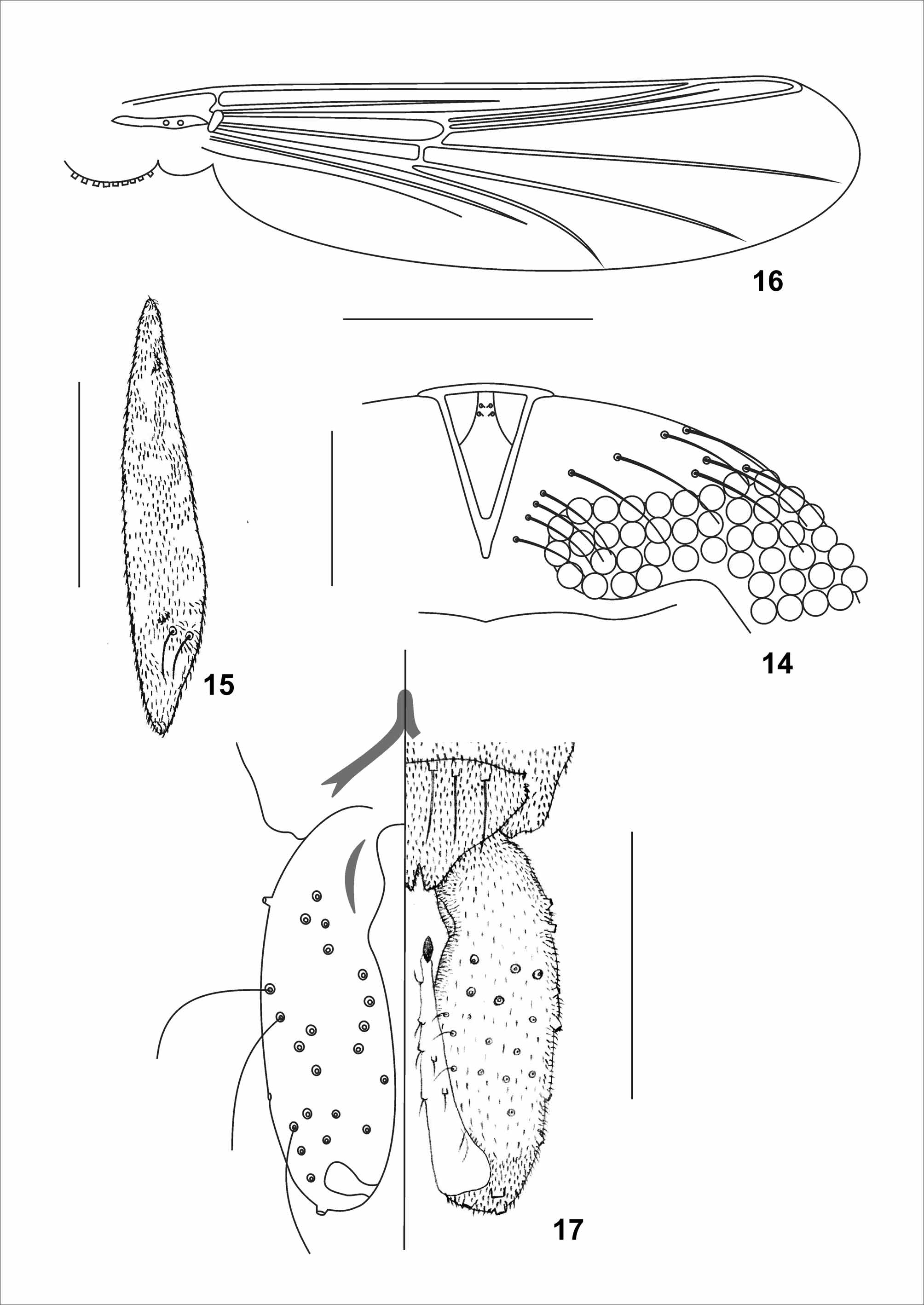
Head ( Fig. 14 View FIGURES 14 – 17 ). Antenna with 14 flagellomeres, AR [1.53] 1.40–1.65, flagellum [931] 884–994 μm long, apical seta single, [37] 25–50 long μm. Temporal setae [13] 13–16 (3), uniserial ( Fig. 14 View FIGURES 14 – 17 ). Eyes bare, with dorsomedian extension containing [5] 5 (3) terminal facets. Tentorium [151] 138–151 μm long, stipes not measurable. Clypeus [89] 80–89 (3) μm long, [69] 68–69 μm wide at largest part, bearing [12] 12–13 (3) setae. Cibarial pump with anterior margin concave, [211] 186–211 (3) μm long and with orifice [58] 57–58 (3) from apex. Labrum [45] 40– 45 (3) μm wide, with two setae. Palpomere lengths 1–5 (in μm): [39] 39–46; [75] 66–75; [108] 100–117; 130–142 (3); 200–225 (3).
Thorax ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 14 – 17 ). Antepronotum with [2] 2 (2) lateral setae ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 14 – 17 ). Acrostichals [17] 17 (1), biserials; dorsocentrals [23] 23–19 (2), irregularly biserials; prealars [12] 7–14 (3); supraalar 1 (3). Scutellum with [10] 10–15 (3) setae. Anepisternals, preepisternals and postnotals absent.
Wing ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 14 – 17 ). Width [0.30] 0.28–0.31mm. Costa [1.15] 1.00– 1.20 mm long, not produced beyond R4+5, ending very slightly beyond tip of M3+4. R2+3 present. VR [0.90] 0.88–0.93. WW [0.25] 0.22–0.26. Brachiolum with 3 setae. Squama with [12] 9–12 (3) setae.
Legs. Fore leg: tibia with single preapical seta [92] 77–100 (3) μm long and one apical and pectinate spur, teeth unobserved. Mid leg: tibia with single preapical seta [132] 132–136 μm long; two apical and pectinate spurs 19 (2) and 24–32 (2) μm long, with 19–21 (2) and 15–17 teeth respectively. Hind leg: tibia with single preapical seta [111] 85–115 μm long; two apical and pectinate spurs [23] 23–25 and [21] 21–25 μm long, with 10 (1) and 9 (1) teeth respectively. All legs with slender, hook-shaped claws. Pulvilli absent. Lengths and proportion of leg segments in Table 3.
fe ti ta1 ta2 ta3
p1 [594] 531–594 (3) [700] 600–700 (3) [613] 513–613 (3) [294] 275–294 (3) [207] 200–207 (3) p2 [625] 550–625 [588] 500–625 [469] 398–469 (3) [194] 194–200 (3) [131] 130–131 (3) p3 [588] 544–594 [744] 638–813 [619] 563–682 [288] 288–331 [200] 200–210 (3)
ta4 ta5 LR BV SV
p1 [138] 138 (3) [88] 88–94 (3) [0.88] 0.85–0.88 (3) [2.63] 2.33–2.63 (3) [2.11] 2.08–2.21(3) p2 [94] 94 (3) [69] 69–75 (3) [0.80] 0.77–0.80 (3) [3.45] 2.93–3.45(3) [2.59] 2.59–2.74 (3) p3 [131] 131–138 (3) [81] 81–83 (3) [0.83] 0.83–0.88 [2.79] 2.47–2.79 (3) [2.15] 2.06–2.17 Hypopygium ( Fig. 17 View FIGURES 14 – 17 ). TIX arched, with three dorsal setae. Anal point bilobed. Phallapodeme 37–38 (2) μm long. Sternapodeme pointed anteriorly. Gonocoxite elongate, [154] 143–154 μm long, with slightly concave inner margin; inferior volsella absent. Gonostylus simple, [100] 95–112 μm long; megaseta [11] 8–11 μm long. HR [1.54] 1.32–1.54. HV [1.88] 1.75–1.88.
Pupa (n = 3 unless otherwise stated)
Dimensions. Male abdomen [2.20] 2.00– 2.35 mm long.
Coloration. Exuviae and most of thoracic horn pale brown.
Cephalothorax ( Figs 18–20 View FIGURES 18 – 22 ). Frontal apotome dome-shaped. Wing sheath smooth [831] 763–875 mm long and [281] 263–294 mm wide ( Fig. 18 View FIGURES 18 – 22 ). Thoracic horn as in figures 19–20, [189] 169–206 μm long and [48] 35–48 μm wide; plastron plate [35] 23–35 μm long. Horn sac alveolar, filling most of the respiratory atrium. Basal lobe wedge-shaped. Thoracic comb with [13] 13–15 conical teeth.
Abdomen ( Figs 21–22 View FIGURES 18 – 22 ). Tergites I–VIII with shagreen composed of groups of 3–8 small spinules, serially arranged in transverse arched rows. T I with scar, [138] 138–162 (2) μm long. Chaetotaxy on segment IV as in figure 21. T VII with 4 lateral filaments. T VIII with 5 lateral filaments. Anal lobe as in figures 21–22, [340] 331–358 μm long and [175] 166–185 μm wide, with two anal macrosetae, outer margins spinulate, inner margins without spinules. Genital sac smaller than anal lobe, [222] 215–243 long, shagreen present. GS/AL [0.65] 0.65– 0.68.
4th instar larva (n = 3 unless otherwise stated)
Coloration. Head pale yellow, with caudal maculation; postoccipital margin brown. Second antennal segment and maxillary palp yellowish; distal tooth of mandible and apex of ligula brown. Abdomen pale yellow; procercus and anal setae pale brown. Posterior parapod claws pale yellow.
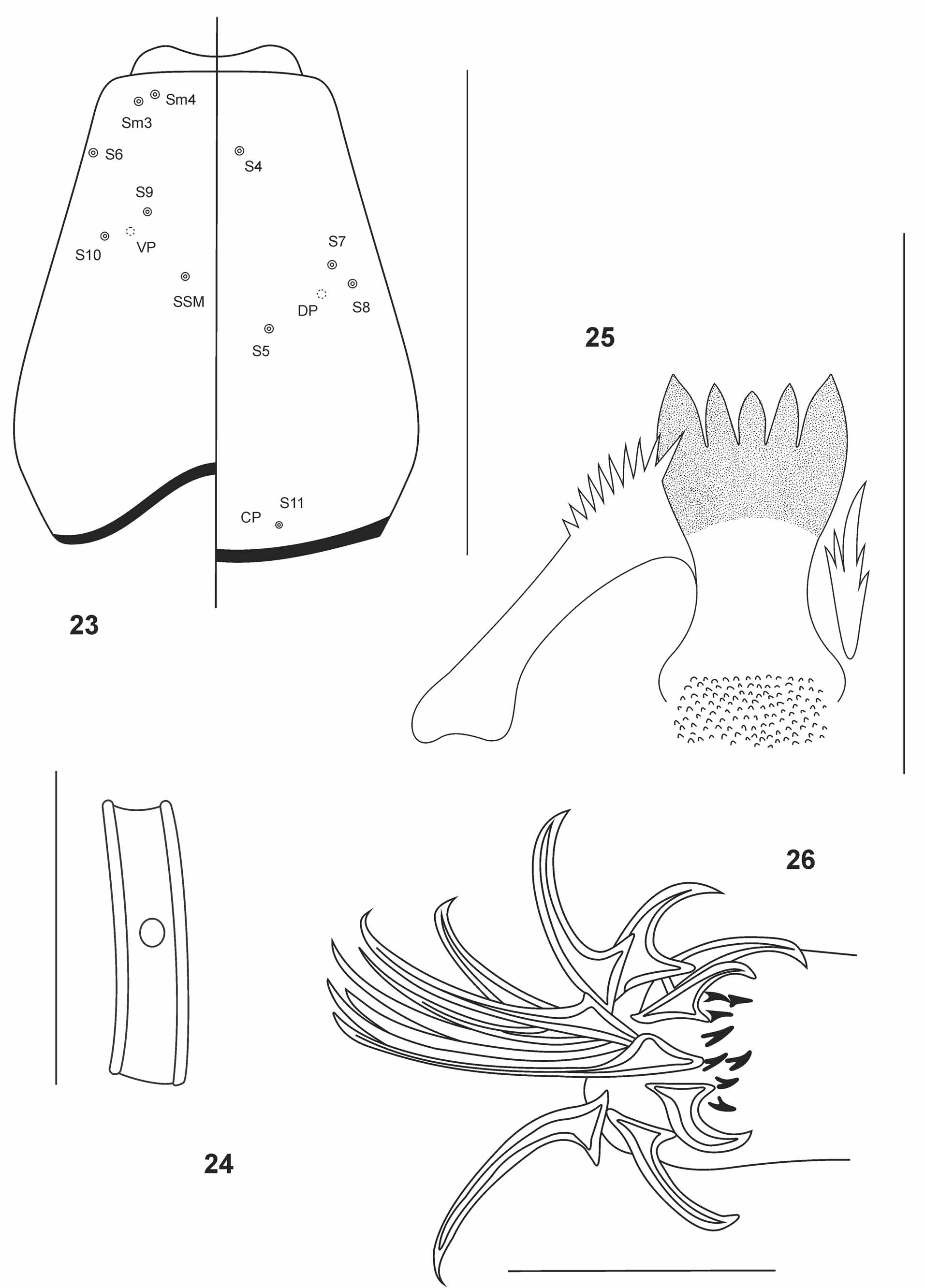
Head ( Fig. 23 View FIGURES 23 – 26 ). Length [425] 419–431 μm, [400] 375–405 μm wide; IC [0.94] 0.89–0.94. Chaetotaxy as in figures 21.
Antenna. Length [286] 286–298 μm long, A1 [228] 228–238 μm long, with ring organ placed [135] 92–137 μm from base, A2 [49] 49, 49 μm long. AR [3.89] 3.89–3.97.
Maxilla ( Fig. 24 View FIGURES 23 – 26 ). Basal palp segment [48] 40–48 μm long and [9] 7–9 μm wide, with ring organ [22] 22–23 μm from base, A1/P1 [5] 5–6, A2/P1 [1.03] 1.03–1.23.
Mandible. Length [83] 62–83 μm, with 3 lateral setae and 1 sensillum campaniformium. A1/MD [2.74] 2.74– 3.88.
Mentum and M appendage. Dorsomental teeth [15] 15–16 μm long; pseudoradula uniformly granulate.
Hypopharyngeal complex ( Fig. 25 View FIGURES 23 – 26 ). Ligula [68] 65–69 μm long, maximum width [34] 32–34 μm, anterior toothed margin concave. It/O [1.00] 1.00–1.05. Mt/O [0.78] 0.78–0.84. It/Li [0.13] 0.13–0.14. Muscle attachment [9] 9 (2) long. Paraligula pectinate. Pecten hypopharyngis with 10 teeth.
Body ( Fig. 26 View FIGURES 23 – 26 ). Without lateral fringe. Anterior parapods with simple claws. Procercus [111] 109–118 μm long, [23] 20–25 μm wide, with 7 anal setae [391] 391–406 μm long. L/W [4.80] 4.44–5.92. Supraanal seta [323] 308– 445 μm long. Anal tubules not measurable. Posterior parapod apex with hooklets and numerous simple claws.
Remarks. The male of L. hamadae resembles L. fittkaui Sublette & Sasa and L. planensis Johannsen , but can be separated based on abdominal coloration with brown spots, on higher number of teeth on tibial spurs of legs II and III, and on bilobed anal point. The pupa of L. hamadae is similar to pupa of L. reissi Sublette & Sasa distinguishing by the thoracic horn morphology, presence of shagreen on genital sac and chaetotaxy of tergite IV. The larva of L. hamadae seems to be closely related to L. gelhausi except for pectinate paraligula and coloration pattern of cephalic capsule.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |