Stolephorus tamilensis, Pavan-Kumar & Jahageerdar & Jaiswar, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4743.4.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:03C03264-B7BD-4B88-8946-F23E99BD8A78 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3691435 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A087F8-DB65-1265-9DF7-F962FBED4B5E |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Stolephorus tamilensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Stolephorus tamilensis sp. nov.
Proposed common name: Tamil anchovy ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 )
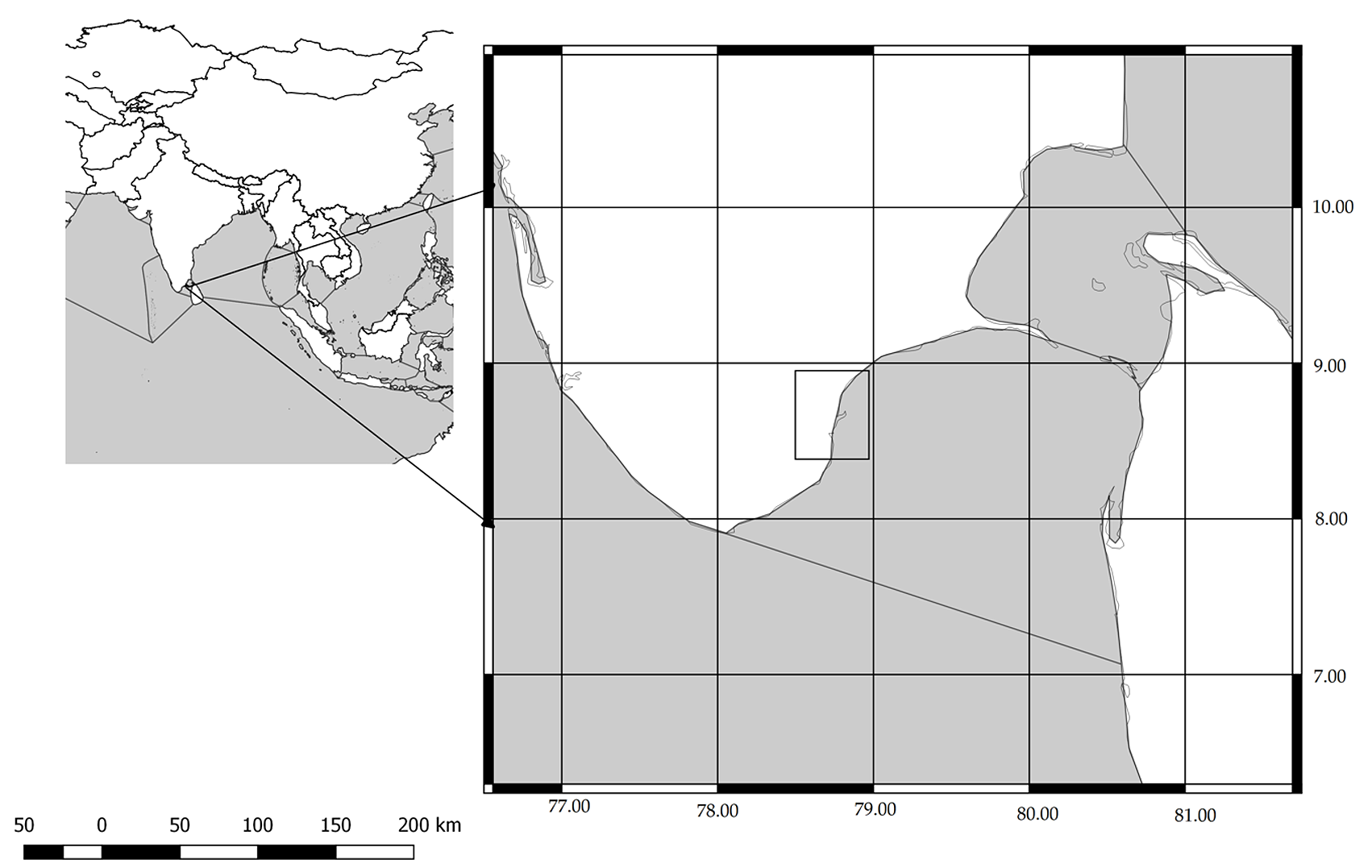
Holotype: ZSI F12077/2 (50.85 mm SL), Thoothukudi fish landing centre, Tamil Nadu, India (8.7642° N, 78.1348° E), 18 February 2015. GoogleMaps
Paratypes: All paratypes from Thoothukudi fish landing centre, Tamil Nadu, India, (8.7642° N, 78.1348° E), ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ) 18 February 2015 GoogleMaps : BNHS MF 10-12 View Materials (3 specimens, 48.48–51.16 mm SL), CIFE-FRM 945–971 (27 specimens, 47.37–53.64 mm SL) collected by Shardul S. Gangan on 18 February 2015 .
Diagnosis. A species of Stolephorus with the following combination of characters: relatively deep-bodied fish, 19.87–23.37% SL (mean 21.2%); eye relatively large, eye diameter 29.28–35.85% HL (mean 32.09%); posterior margin of preopercle indented; gill rakers 15–19 in upper series on first gill arch, 25–28 on in lower series, 40–47 in total; posterior tip of longest pectoral-fin ray not reaching pelvic-fin origin, pelvic-fin relatively short, 5.81–8.15% SL (mean 7.39%); no pre-dorsal spines and post-pelvic scutes, pre-pelvic scutes 5–6; dorsal-fin base length 13.85– 15.54% in SL (mean 14.57%); dorsal-fin origin is closer to base of caudal fin than to tip of snout; length from dorsal-fin origin to anal-fin origin 20.91–22.57 % in SL (mean 21.87%); anal-fin rays 17–19; numerous melanophores on dorsum and suborbital area.
Description. Body cylindrical, laterally compressed. Dorsal profile of head and body slightly convex from snout tip to dorsal fin origin, somewhat straight from the last point to caudal peduncle. Ventral profile of head and body is convex from anterior lower jaw tip to base of pelvic-fin, slightly concave from post pelvic fin to anal-fin origin. Posterior margin of pre- opercule concave, indented. Numerous melanophores on dorsum and suborbital area. Somewhat straight from posterior end of anal-fin to origin of lower caudal-fin lobe. Caudal peduncle slightly deep than longer. Vertebrae 39–40 (two specimens examined). Belly covered with 5–6 sharp needle-like scutes anterior to pelvic-fin insertion. Pelvic-fin without spine. Pre-dorsal and post-pelvic scutes absent.
Snout long, rounded, its length less than eye diameter. Mouth sub-terminal, extending backward beyond posterior margin of eye. Posterior end of the upper jaw rounded reaching to border of operculum. Lower jaw slender, extending beyond vertical through posterior margin of eye. Teeth pointed, small, slender, arranged in a single row in the pre maxilla, maxilla and lower jaw. Eye large, round, covered with adipose eye lid, positioned laterally on head dorsal to horizontal through pectoral-fin insertion, visible in dorsal view. Orbit elliptical. Nostrils close to each other, anterior to orbit. Inter orbital width less than eye diameter.
Dorsal-fin rays ii–iii + 15, origin closer to base of caudal-fin than to tip of snout. Pair of pigment line in front of dorsal-fin as well as between caudal-fin and dorsal-fin is absent. Anal-fin rays iii + 17–19, its origin at vertical through middle of the dorsal-fin. Pectoral-fin rays I + 13, posterior tip of longest pectoral-fin ray not reaching pelvic-fin origin, pectoral-fin axillary scale found in some specimens but in the remained it was absent, may be lost during collection. Pelvic-fin rays i–ii + 7, longest pectoral-fin rays not reaching vertical through to base of dorsal-fin. Caudal-fin forked, upper and lower lobes of caudal-fin well-developed. Gill rakers long and thin on first branchial arch, 15 –19 on the upper arch, 25–28 on lower arch ( Table 4 View TABLE 4 ).
Colour. Colour of thirty specimens of Stolephorus tamilensis sp. nov. in fresh condition silvery whitish, very faint silvery stripe running along the lateral side; small dark pigment line running along upper border of anal fin.
Distribution. Based on the collection of voucher specimens from present study, the type locality of Stolephorus tamilensis sp. nov. is Thoothukudi, Tamil Nadu State of India 8.7642° N, 78.1348° E. Probably this species is distributed in Gulf of Mannar and along the Tamil Nadu State coast.
Etymology. The species is named as “ tamilensis ” with reference to the Tamil Nadu, a state of India, the type locality of the species.
Comparisons. Stolephorus tamilensis differs from congeners except S. dubiosus , S. baganensis , S. bengalensis , S. carpenteriae , S. tri , S. ronquilloi , S. holodon , and S. andhraensis by the hind boarder of the pre-operculm concave (vs. rounded in S. indicus , S. commersonnii , S. waitei , S. chinensis , S. multibranchus , S. brachycephalus , S. advenus , S. nelsoni , S. apiensis , S. pacificus , S. continentalis , S. insignus and S. oceanicus ). The new species also distinguishes from S. dubiosus , S. tri and S. baganensis by the absence of pre-dorsal spine (vs. presence). Furthermore, S. tamilensis can be distinguished from S. andhraensis by the absence of scattered pigments between dorsal-fin and caudal peduncle (vs. presence). In addition, Stolephorus tamilensis is also distinct from S. andhraensis , S. ronquilloi , S. tri , S. multibranchus , S. brachycephalus , S. apiensis , S. pacificus , S. insignus , S. continentalis , S. teguhi , S. baganensis , S. waitei , S. chinensis , S. bataviensis , S. baweanensis , S. bengalensis and S. oceanicus by 25–28 gill rakers on the lower limb of the first gill arch (vs. 20–21 in S. andhraensis , 28–30 in S. ronquilloi , 18–22 in S. tri , 32–35 in S. multibranchus , 20–22 in S. brachycephalus , 30–31 in S. apiensis , 35–38 in S. pacificus , 26–28 in S. insignus & S. continentalis , 41–46 in S. teguhi , 20–23 in S. baganensis , 23–25 in S. waitei , 20–25 in S. chinensis , 19–22 in S. bataviensis & S. baweanensis , 22–27 in S. bengalensis and 24–28 in S. oceanicus ). The new species also differs from S. commersonnii , S. multibranchus , S. brachycephalus , S. advenus , S. pacificus , S. teguhi , S. chinensis , S. insignus , S. bataviensis and S. bengalensis by 5–6 needle like pre-pelvic scutes (vs. 1–4 in S. commersonnii , 2–4 in S. multibranchus , 4–5 in S. brachycephalus , 7 in S. advenus , 1–4 in S. pacificus , 2–5 in S. teguhi , 4–7 in S. chinensis , S. insignus & S. bataviensis , and 5–8 in S. bengalensis ). Stolephorus tamilensis is distinguishable from S. multibranchus , S. brachycephalus , S. carpentariae , S. advenus , S. teguhi , S. chinensis , S. bengalensis and S. insignus by 17–19 anal fin rays (vs. 18–20 in S. multibranchus , 19–22 in S. brachycephalus , 19–20 in S. carpenteriae , 16 in S. advenus , 19–21 in S. teguhi , 18–20 in S. chinensis , 16–19 in S. bengalensis and 18–19 in S. insignus ).
Furthermore, S. tamilensis differs from S. commersonnii , S. indicus , S. waitei ( S. baweanensis sensu Hata et al. 2019 ), S. insularis ( S. bengalensis sensu Hata et al. 2019 ), S. baganensis , S. dubiosus in eye diameter, dorsal fin base length, pelvic fin length, length between dorsal and anal-fin origins and maximum body depth ( Table 3 View TABLE 3 ).
Note: standard length or SL, snout length SNL (1), head length HL (2), postorbital head length POHL (3), interorbital width IOW (4), eye diameter ED (5), upper jaw length UJL (6), lower jaw length LJL (7), dorsal-fin base length DFBL (8), anal-fin base length AFBL (9), pelvic-fin base length PFBL (10), pelvic-fin length PLFL (11), pectoral-fin base length PTBL (12), pectoral fin long filament length PTFL (13), length from tip of snout to origin of dorsal fin TSDF (14), length from tip of snout to origin of anal fin TSAF (15), length from tip of snout to origin of pelvic fin TSPF (16), length from tip of snout to origin of pectoral fin TSPTF (17), length from origin of dorsal fin to origin of anal fin AFDL (18), maximum body depth MBD (19), length from base of pectoral fin to origin of pelvic fin BPTFPL (20), length from base of pectoral fin to origin of anal fin BPTFAL (21), length from base of pelvic fin to origin of anal fin BPLFAF (22)
Statistical analysis of morphometric variables. Higher F-ratio of more than 200 for ED/HL, DFBL/SL, PLFL/SL, AFDL/SL and MBD/SL reveal their better discrimination power than the other characters ( Table 3 View TABLE 3 ). Herein, a higher F-value of 3309.651 and 2471.632 for ED/HL and MBD/SL, respectively, showed the importance of insertion point in species differentiation. However, comparative analysis showed overlapping meristic characters between S. insularis ( S. bengalensis sensu Hata et al. 2019 ) and S. tamilensis ( Table 4 View TABLE 4 ).
TABLE 3. The comparative ANOVA of transformed morphometric ratios of species of Stolephorus genus.
| S. commersonnii | S. indicus | S. waitei * | S. insularis * | S. baganensis | S. dubiosus | S tamilensis | F-ratio | p value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNL/HL | Mean SD | 0.046190 ± 0.002246 | 0.058081 ± 0.003454 | 0.049800 ± 0.003447 | 0.037766 ± 0.004337 | 0.042993 ± 0.002949 | 0.040417 ± 0.002177 | 0.042775 ± 0.001798 | 191.450 | 0.000 |
| HL/SL | Mean SD | 0.242627 ± 0.004271 | 0.238745 ± 0.004729 | 0.253694 ± 0.005347 | 0.228759 ± 0.006581 | 0.227187 ± 0.006413 | 0.225029 ± 0.004740 | 0.225805 ± 0.005853 | 118.396 | 0.000 |
| POHL/HL | Mean SD | 0.131308 ± 0.003227 | 0.120148 ± 0.002786 | 0.128798 ± 0.003238 | 0.119573 ± 0.006617 | 0.123317 ± 0.007327 | 0.125276 ± 0.005056 | 0.105508 ± 0.004004 | 104.754 | 0.000 |
| Mean | 0.067905 | 0.062456 | 0.063794 | 0.065279 | 0.059727 | 0.064029 | 0.060471 | 24.958 | 0.000 | |
| IOW/HL | SD | ± 0.002954 | ± 0.002316 | ± 0.002730 | ± 0.003435 | ± 0.002793 | ± 0.003063 | ± 0.003086 | ||
| ED/HL | Mean SD | 0.068823 ± 0.002317 | 0.064285 ± 0.002030 | 0.075894 ± 0.003867 | 0.069402 ± 0.003081 | 0.150193 ± 0.006462 | 0.061898 ± 0.002579 | 0.145680 ± 0.004360 | 3309.651 | 0.000 |
| Mean | 0.168160 | 0.174433 | 0.196056 | 0.154415 | 0.169613 | 0.173783 | 0.162275 | 132.015 | 0.000 | |
| UJL/HL | SD | ± 0.005092 | ± 0.004715 | ± 0.006350 | ± 0.008832 | ± 0.009174 | ± 0.005717 | ± 0.004225 | ||
| Mean | 0.139017 | 0.134973 | 0.155936 | 0.130781 | 0.140920 | 0.140366 | 0.138614 | 56.789 | 0.000 | |
| LJL/HL | SD | ± 0.003881 | ± 0.005516 | ± 0.004402 | ± 0.008468 | ± 0.007459 | ± 0.006323 | ± 0.004147 |
...Continued next page
TABLE 3. (Continued)
| S. commersonnii | S. indicus | S. waitei * | S. insularis * | S. baganensis | S. dubiosus | S tamilensis | F-ratio | p value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 0.151532 | 0.142881 | 0.154491 | 0.142806 | 0.241402 | 0.144190 | 0.219116 | 1121.405 | 0.000 | |
| DFBL/SL | SD | ± 0.005939 | ± 0.005463 | ± 0.004583 | ± 0.004759 | ± 0.010471 | ± 0.007646 | ± 0.003913 | ||
| Mean | 0.199283 | 0.179706 | 0.204569 | 0.190184 | 0.216204 | 0.220501 | 0.187256 | 138.340 | 0.000 | |
| AFBL/SL | SD | ± 0.005452 | ± 0.008258 | ± 0.006973 | ± 0.006174 | ± 0.008219 | ± 0.007920 | ± 0.006286 | ||
| Mean | 0.0154 | 0.0135 | 0.0130 | 0.0205 | 0.0193 | 0.0267 | 0.0194 | 130.719 | 0.000 | |
| PFBL/SL | SD | ± 0.00121 | ± 0.00077 | ± 0.00165 | ± 0.00212 | ± 0.00196 | ± 0.00542 | ± 0.00079 | ||
| Mean | 0.0998 | 0.0764 | 0.0669 | 0.0868 | 0.1049 | 0.1029 | 0.0745 | 288.548 | 0.000 | |
| PLFL/SL | SD | ± 0.00460 | ± 0.00265 | ± 0.00220 | ± 0.00443 | ± 0.00830 | ± 0.00634 | ± 0.00545 | ||
| Mean | 0.1438 | 0.1332 | 0.1452 | 0.1279 | 0.1592 | 0.1680 | 0.1404 | 77.926 | 0.000 | |
| PTFL/SL | SD | ± 0.00680 | ± 0.00544 | ± 0.00898 | ± 0.01058 | ± 0.01438 | ± 0.01047 | ± 0.00411 | ||
| Mean | 0.0375 | 0.0402 | 0.0385 | 0.0349 | 0.0356 | 0.0388 | 0.0254 | 98.446 | 0.000 | |
| PTBL/SL | SD | ± 0.00474 | ± 0.00073 | ± 0.00188 | ± 0.00346 | ± 0.00390 | ± 0.00265 | ± 0.00208 | ||
| Mean | 0.5278 | 0.5340 | 0.5341 | 0.5295 | 0.5208 | 0.5236 | 0.5328 | 10.515 | 0.000 | |
| TSDF/SL | SD | ± 0.00656 | ± 0.00787 | ± 0.00635 | ± 0.00987 | ± 0.01229 | ± 0.00884 | ± 0.00634 | ||
| Mean | 0.6298 | 0.6130 | 0.6120 | 0.6252 | 0.6209 | 0.6247 | 0.6099 | 15.457 | 0.000 | |
| TSAF/SL | SD | ± 0.00851 | ± 0.00879 | ± 0.01108 | ± 0.01236 | ± 0.01392 | ± 0.01591 | ± 0.00724 | ||
| Mean | 0.4441 | 0.4303 | 0.4411 | 0.4477 | 0.4235 | 0.4285 | 0.4264 | 22.968 | 0.000 | |
| TSPF/SL | SD | ± 0.00547 | ± 0.01167 | ± 0.01448 | ± 0.00643 | ± 0.01355 | ± 0.01240 | ± 0.00589 | ||
| TSPTF/ | Mean | 0.2483 | 0.2466 | 0.2588 | 0.2446 | 0.2352 | 0.2316 | 0.2298 | 86.864 | 0.000 |
| SL | SD | ± 0.00511 | ± 0.00593 | ± 0.00537 | ± 0.00437 | ± 0.00966 | ± 0.00753 | ± 0.00490 | ||
| Mean | 0.2319 | 0.2014 | 0.2188 | 0.2320 | 0.2268 | 0.2616 | 0.2116 | 231.403 | 0.000 | |
| AFDL/SL | SD | ± 0.00396 | ± 0.00417 | ± 0.00518 | ± 0.00638 | ± 0.01190 | ± 0.01342 | ± 0.00536 | ||
| Mean | 0.2149 | 0.1921 | 0.2049 | 0.2276 | 0.0675 | 0.2468 | 0.0729 | 2471.632 | 0.000 | |
| MBD/SL | SD | ± 0.00503 | ± 0.00576 | ± 0.006740 | ±0.00687 | ± 0.00367 | ± 0.01456 | ± 0.00255 | ||
| BPTFPL/ | Mean | 0.2075 | 0.1906 | 0.1919 | 0.2162 | 0.2043 | 0.2049 | 0.2099 | 26.516 | 0.000 |
| SL | SD | ± 0.00510 | ± 0.01001 | ± 0.01428 | ± 0.01054 | ± 0.01424 | ± 0.01406 | ± 0.00631 | ||
| BPTFAF/ | Mean | 0.3970 | 0.3786 | 0.3658 | 0.4039 | 0.4039 | 0.4042 | 0.3943 | 38.602 | 0.000 |
| SL | SD | ± 0.00922 | ± 0.00693 | ± 0.01496 | ± 0.01303 | ± 0.02193 | ± 0.01860 | ± 0.01091 | ||
| BPLFAF/ | Mean | 0.1937 | 0.1854 | 0.1798 | 0.1898 | 0.2021 | 0.2046 | 0.1889 | 20.902 | 0.000 |
| SL | SD | ± 0.00535 | ± 0.00886 | ± 0.01686 | ± 0.00952 | ± 0.00919 | ± 0.01049 | ± 0.00704 |
| BNHS |
Bombay Natural History Society |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |