Thrichomys inermis
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.277069 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6189814 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039A87FE-FFCE-FFDE-7C8F-75E5FE79FCF9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Thrichomys inermis |
| status |
|
Thrichomys inermis View in CoL
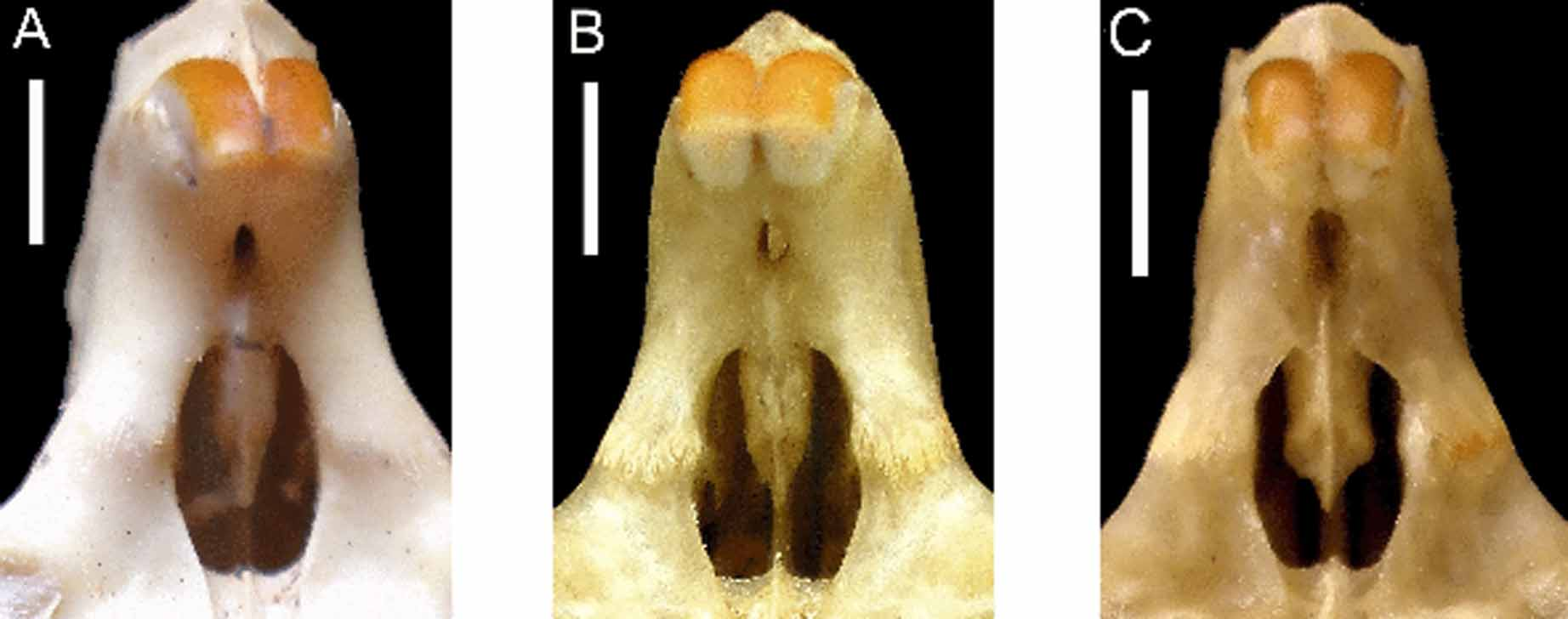
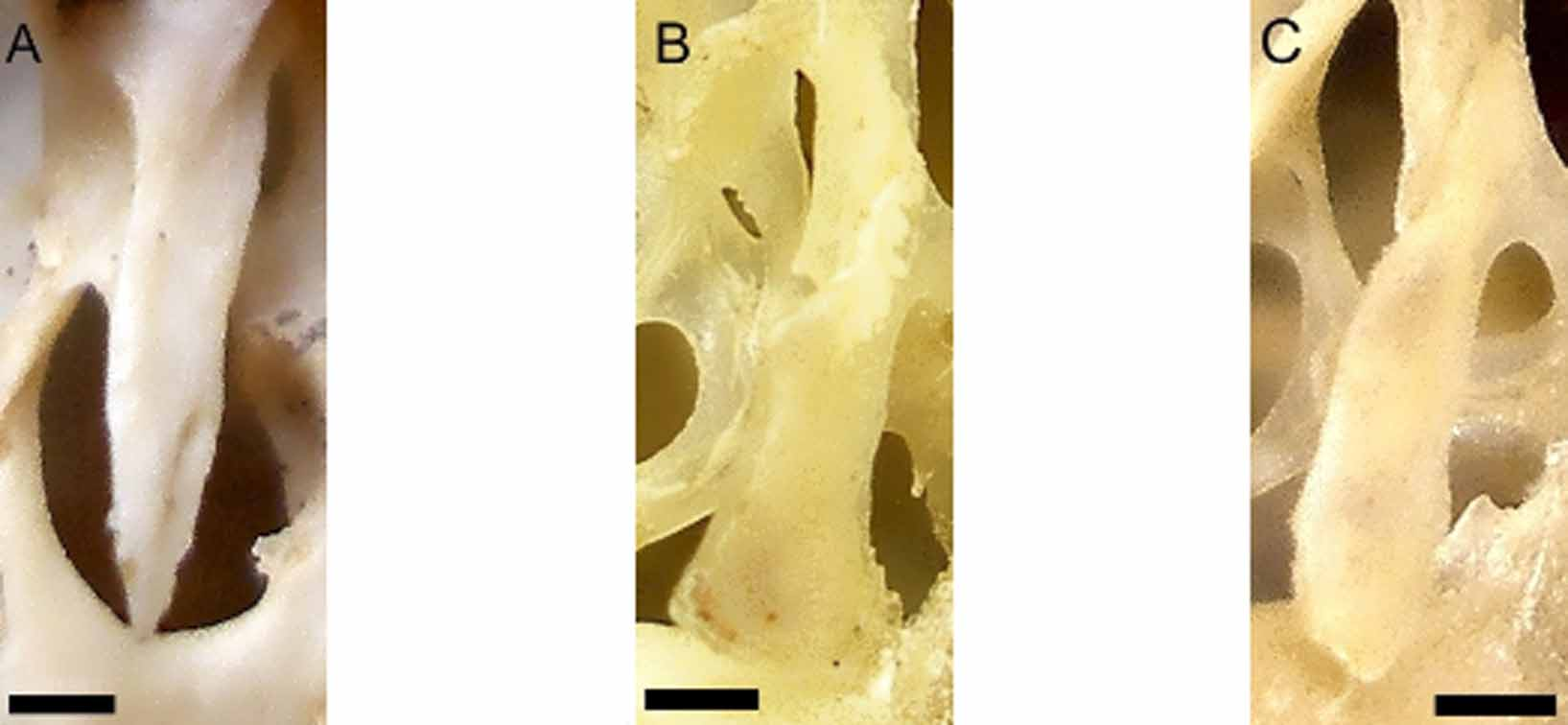
Nine ages were described for the sample from Morro do Chapéu, identified as T. inermis ( Fig 3 View FIGURE 3 .A–I). As expected, the wear of the occlusal surface of cheekteeth varies considerably during ontogeny. Juveniles (ags 1, 2 and 3) show premolar, first and second molar erupted ( Fig 3 View FIGURE 3 .A). Sub-adults (ages 4 and 5) have already erupted the third molar. The first flexus of first and second molars look like islands. The first flexus of second and third molar are connected to hypoflexi ( Fig 3 View FIGURE 3 .E). Adults, ages 6 and 7, which show the suture between basisphenoid and basiocciptal obliterated, present signals of wear of occlusal surface of cheekteeth. Both flexi of premolar and first molar are enamel islands ( Fig 3 View FIGURE 3 .G). Seniles (ages 8 and 9) show all cheekteeth severely worn, with all flexi isolated from labial surface. The hypoflexi of pre-molar, first and second molars are enamel islands ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 .I). Some aspects of skull did not vary through ontogeny, as the extension of supra-orbital ridge, which always reaches the suture between frontal and squamosal; interpremaxilar foramen is broad and rounded; the incisive foramen has a contrition in the suture between the maxilla and pre-maxilla ( Fig 4 View FIGURE 4 .C); anterior palatal foramen are located at anterior margin of pre-molar; the hamular processes of pterygoid bones are rectangular, but narrow in tip ( Fig 5 View FIGURE 5 .C); and mesopterygoid fossa has a "V"-shape. Dorsally, nasal bones reach the limit of pre-maxilla only at age 2. The supraorbital crest does not extend to suture between frontal and squamosal bones only at age 1. The ventral crest of infra-orbital foramen, poorly developed, is located after the edge of foramen infra-orbital at ages 1 and 2. At ages 3, 4 and 5 the ventral crest is partially located before the edge of foramen infra-orbital. At other ages the ventral crest is located before the edge of foramen infra-orbital. The post-orbital process of zygomatic arch is formed mainly by squamosal in juveniles, adults and seniles. Sub-adults at age 4, jugal and squamosal have equal participation in formation of this process and at age 5 only jugal form the process. The pre-maxillary portion of septum of incisive foramen, in juveniles, exceeds half of length of foramen. From sub-adults, the pre-maxillary portion is half of length of foramen. The palate reaches the posterior limit of the last molar erupted. The median crest of palate, well developed, separates the anterior palatine foramens which are located before the pre-molar, near to incisive foramen. The posterior palatine foramen is located at posterior margin of palate. Juveniles and sub-adults have the mesopterygoid fossa extending to medial portion of second molar. From adults, the mesopterygoid fossa extends up to half of third molar.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |