Axonchium noreasum, Naz, Tabbasam & Ahmad, Wasim, 2012
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.215075 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6169981 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03994F22-FFD3-E65F-21C1-D899FAC8F960 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Axonchium noreasum |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Axonchium noreasum n. sp.
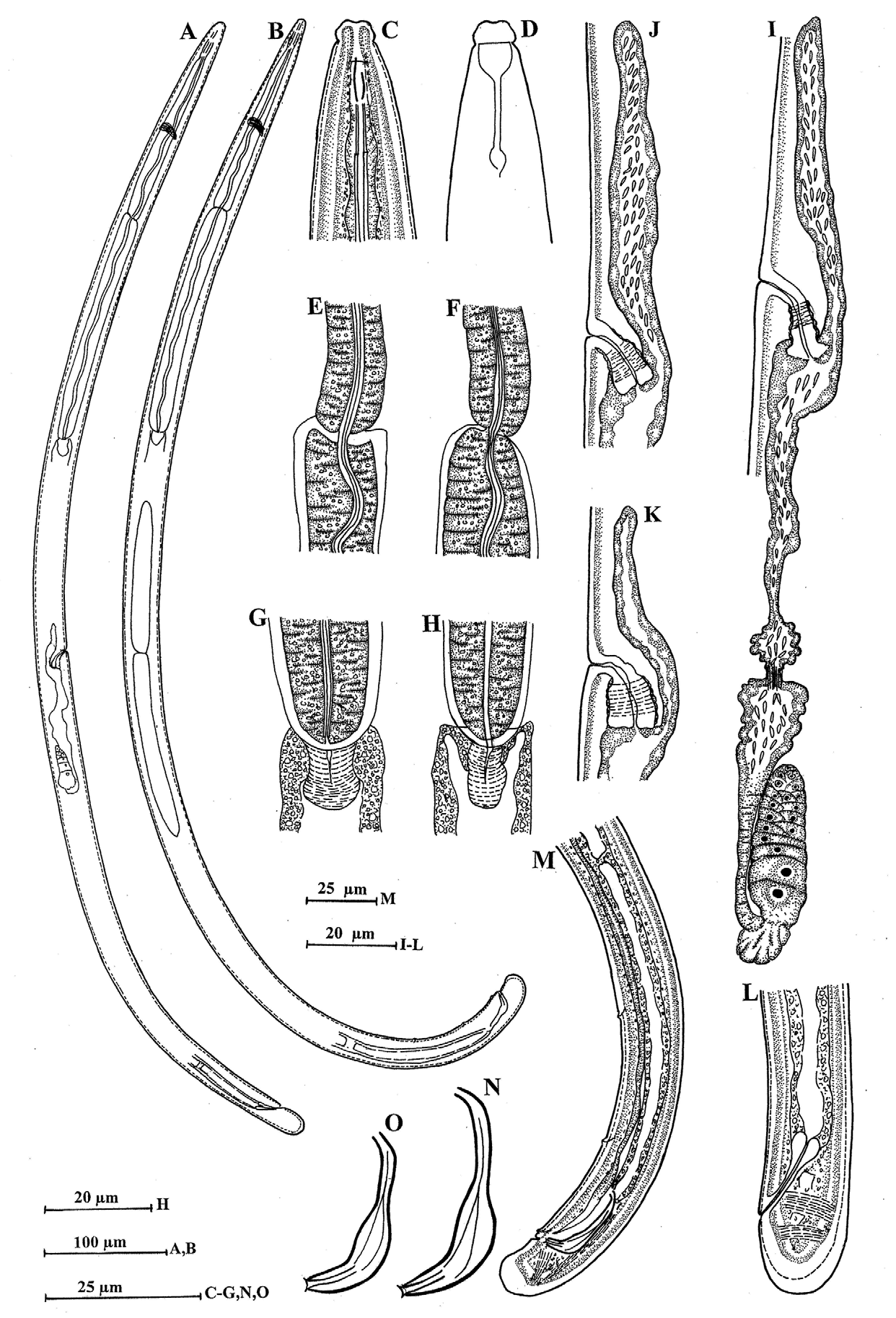
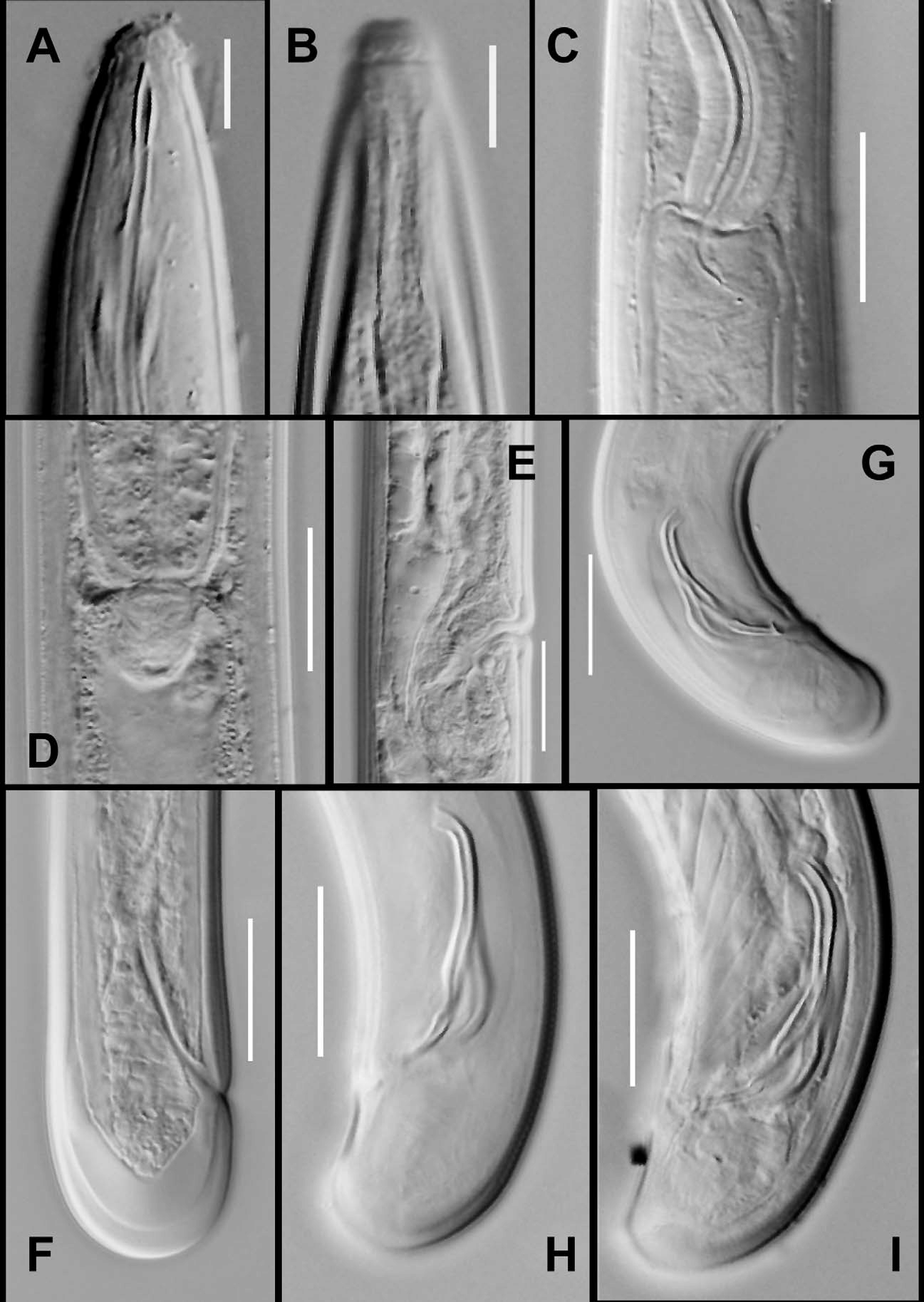
( Figs. 13–14 View FIGURE 13 View FIGURE 14 )
Measurements. Table 7.
Description. Female: Body curved ventrad upon fixation, tapering towards both extremities. Cuticle with fine transverse striations, 2–4 µm thick at mid body and 6–8 µm on tail. Lateral chords without distinct glandular bodies, about one-fifth to one-fourth of body width at mid body. Lateral, dorsal and ventral body pores indistinct.
Lip region offset, about one-fifth to one-fourth of body width at neck base; lips separated. Amphids cupshaped, their aperture 0.8 times the lip region width. Odontostyle fusiform, 1.1–1.3 times the lip region width long, its aperture about one-third of its length. Guiding ring single, at about one lip region width from anterior end. Odontophore linear, 1.1–1.3 times the odontostyle length. Nerve ring at 21–25% of neck length from anterior end. Anterior muscular part of pharynx separated from the posterior expanded part by a deep constriction the latter occupying about 52–64% of the neck length and enclosed in muscle sheath with straight bundles. Cardia, tonguelike, about one-third to one-half of the corresponding body width long.
Genital system mono-opisthodelphic. Anterior branch represented by a simple sac, 1.7–3.9 times the corresponding body width long and in most of the specimens filled with sperms. Posterior branch well developed; ovary reflexed, not reaching the oviduct-uterus junction, measuring 40–145 µm with oocytes arranged in a single row except near tip. Oviduct joining ovary subterminally, measuring 45–80 µm, consisting of a long slender part with prismatic cells and a slightly wider pars dilatata with clear lumen. Sphincter present at oviduct-uterus junction. Uterus measuring 80–100 µm, differentiated into three parts, distal expanded part with wide lumen, intermediate tubular part with narrow lumen and proximal wider part with wide lumen. Vulva transverse. Vagina bent posteriad, about two-thirds of the corresponding body width deep; pars proximalis vaginae 16–20 µm with almost straight walls; pars refringens vaginae absent; pars distalis vaginae 7–8 µm with rounded walls. Prerectum 3.5–6.5 times anal body width long. Rectum 1.2 –1.5 times anal body width long. Tail short rounded, hemispheroid to almost clavate, 0.9–1.2 times anal body width long; hyaline part about half of tail length. Caudal pores two on each side.
Male: similar to female in general morphology, except for posterior region being more curved because of the presence of copulatory muscles. Spicules slender, 1.5–1.8 times the cloacal body width in length, the proximal deviation (range).
Characters Bhalokpong population Shillong population
Holotype female Paratype females Paratype males Females Males
n 1 9 7 3 2
L (mm) 1.2 1.2±0.05 (1.1–1.3) 1.2±0.04 (1.2–1.3) 1.05±0.05 1.10, 1.14
(1.03–1.06)
a 46.5 45.9±1.36 41.6±2.01 39.7±1.2 36.7, 40.7
(44.1–48.4) (39.9–43.2) (38–41.4)
b 2.5 2.6±0.14 (2.5–2.7) 2.7±0.12 (2.7–2.8) 2.8±0.2 (2.7–3.3) 2.7, 3.1 Odontophore length 10 10.4±0.4 (10–11) 11±1.60 (10–13) 9.3±0.47 (9–10) 9, 9 continued.
Characters Umiam Shillong population Digboi(Assam) Population
Females Males Females Males
n 5 3 6 2 L (mm) 1.34±0.10 (1.2–1.5) 1.2±0.04 (1.2–1.3) 1.2±0.12 (1.0–1.4) 1.2, 1.2 a 39.6±3.01 (35.1–43.2) 42.6±2.16 (39.9–45.2) 44.4±4.29 (39.6–50.5) 45.1, 47.1 b 2.9±.0.21 (2.7–3.2) 3.3±0.24 (3.1–3.7) 2.9±0.28 (2.7–3.4) 2.8, 3.2
c 59.8±2.9 (57.7–64.9) 55.2±0.47 (54.6–55.7) 61.1±6.37 (51–68.3) 53.3, 57.5 c`0.9±.06 (0.9–1.04) 1.02±0.01 (1.0–1.04) 0.9±0.06 (0.9–1.05) 1.1, 1.2 V 52 ±1.7 (49–53) - 51.7±1.73 (49.1–54.6) -
G1 8.4±1.36 (6.3±10.1) - 5.1±0.79 (4.1–6.6) -
G2 17.1±2.05 (13.7–18.7) - 12.8±1.2 (6–7) -
Lip region width 6.6±0.47 (6–7) 7 5.8±0.63 (6–7) 5, 6 Lip region height 3.6±0.48 (3–4) 3.6±0.47 (3–4) 3.3±0.47 (3–4) 4, 4 Amphid aperture 5.3±0.47 (5–6) 5 5.8±0.68 (5–6) 5, 6 Odontostyle length 8.5±0.86 (8–10) 8.6±0.47 (8–9) 7.5±0.49 (7–8) 7, 8 Odontophore length 10.0 10.5±0.5 (10–11) 10±0 9, 10 Guiding ring from anterior end 9.0 9 6.8±0.37 (6–7) 7, 8 Nerve ring from anterior end 96.2±6.4 (90–105) 130±0 115±4.47 (110–120) 110, 110 Neck length 401±33.5 (350–450) 383±25.7 (350–413) 409±41.65 (375–500) 375, 440 Expanded part of pharynx 267±33.6 (215–275) 207±5.3 (208–213) 214±40.66 (175–300) 182, 265 Cardia length 12.8±1.16 (12–15) 13±0 12.5±2.32 (10–17) 12, 15 Body width at mid body 33.2±2.22 (30–35) 30.3±1.24 (29–32) 27.5±0.5 (26–28) 26, 28 Body width at neck base 32.2±2.2 (30–36) 31±0.81 (30–32) 28.1±1.21 (27–30) 27, 27 Body width at anus/cloaca 22.8±0.74 (22–24) 22.6±0.47 (22–23) 20.3±0.47 (20–21) 18, 20 Anterior genital branch 111±18.60 (85–138) - 63.6±10.2 (45–77) -
Posterior genital branch 216±43.5 (152–270) - 156±5.38 (150–165) -
Vaginal depth 20±1.4 (20–25) - 19.13±1.4 (18–22) -
Vulva from anterior end 732±75.43 (658–875) - 621±75.7 (545–765) -
Prerectum length 133±20.8 (100–165) 138±6.23 (130–145) 148±28.3 (120–200) 195, 220 Rectum length 27.4±2.72 (24–30) 30 24.8±1.57 (23–28) 30
Tail length 22.2±1.6 (21–25) 23.3±0.47 (23–24) 20±0.81 (19–21) 22,23 Spicules length - 39± 1.41 (37–401) - 30,32 Lateral guiding pieces - 10.6±1.6 (9–13) - 9,10 Ventromedian supplements - 2 - 2 slender part about two-fifths of the total spicule length with curved ends, distal part comparatively robust and slightly arcuate. Lateral guiding pieces with bifid end, about one-fourth of the spicules length. Supplements consisting of an adcloacal pair and two spaced ventromedians, starting above the range of spicules. Prerectum 5.5–8.5 times cloacal body width long. Rectum 1.2–1.6 cloacal body width long. Tail short, conoid, broadly rounded with slight concavity on ventral side, 0.9–1.2 times cloacal body width long. Caudal pores two on each side.
Type habitat and locality. From soil around the roots of teak tree ( Tectona grandis ), from reserve forest area near Bhalukpong check post, Bomdilla, Arunachal Pradesh, India. GPS coordinate 27.26684/92.43484; latitude 26o56'N, longitude 92o36'E.
Other habitats and localities. From soil around the roots of: i) unidentified grasses and herbs from Seven Miles, Shillong, Meghalaya; ii) unidentified grasses and herbs from Umiam, Shillong, Meghalaya and, iii) forest area from Digboi, district Tinsukia, Assam, India.
Type specimens. Holotype female on slide Axonchium noreasum n. sp. / 1; paratype females and males on slides Axonchium noreasum n. sp. / 2–15; deposited with the nematode collection of the Department of Zoology, Aligarh Muslim University, India. A paratype female and a male deposited with the nematode collection of the Universidad de Jaén, Spain.
Etymology. The species name " noreasum " stands for "north–east", because all the populations were collected from north-eastern India.
Diagnosis and relationships. Body 1.0– 1.3 mm long; lip region offset, lips separate; odontostyle 8–10 µm long; two parts of the pharynx separated from each other by deep constriction; vagina directed posteriorly; anterior uterine branch 46–95 µm in length; spicules slender, 30–36 µm or 1.5–1.8 times cloacal body width long, with proximal slender part about two-fifths of the total spicule length, with curved ends, and the distal part comparatively robust and slightly arcuate; lateral guiding pieces with bifid ends, about one-fourth of the spicule length, and two spaced ventromedian supplements.
The new species is most closely related to A. siddiqii Coomans & Nair, 1975 in having a posteriorly directed vagina in females, and only two ventromedian supplements in males. It differs mainly in spicule shape (vs simple arcuate, with proximal slender part about one-third or less of spicule length, lacking curved ends [see fig. 11D,G of Coomans & Nair, 1975). Although the new species is very similar to A. siddiqii but the shape of its spicules which so characteristic for species delimitation in the genus Axonchium , is distinctly different in the two species.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |