Steatomys parvus, Rhoads, 1896
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6600357 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6600335 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03993828-FFE6-0F42-FFF2-FDEACEA9F8EB |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Steatomys parvus |
| status |
|
Tiny Fat Mouse
French: Petit Rat-adipeux / German: Zwergfettmaus / Spanish: Raton grueso diminuto
Other common names: Tiny African Fat Mouse
Taxonomy. Steatomys parvus Rhoads, 1896 View in CoL ,
“ Rusia , Lake Rudolf [= on the shore of Lake Turkana, Ethiopia], Africa.”
This species is monotypic.
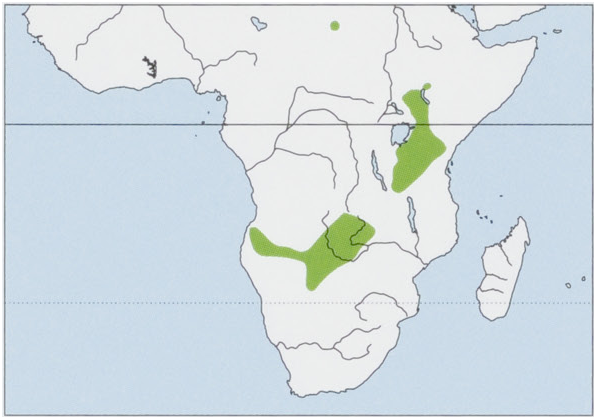
Distribution. Broadly distributed in at least two widely separated populations: one in E Africa (E Uganda, extreme SW Ethiopia, W & S Kenya, and N & W Tanzania), the other in S Africa (S Angola, NE Namibia, N Botswana, W Zambia, and extreme W Zimbabwe); isolated population in Jebel Marra, W Sudan. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body 55-83 mm, tail 34-51 mm, ear 11-15 mm, hindfoot 12-16 mm; weight 8-15 g. The Tiny Fat Mouse is very small—the smallest species of Steatomys . Tail is short and sparsely haired, white above and below. Furis soft and pale orange-brown dorsally, clearly demarcated from pure white or off-white belly. Chin, throat, and upper chest are white. Ears are relatively large and rounded. Limbs are white, with four digits on forefoot and five digits on hindfoot. It has eight nipples.
Habitat. Arid savannas and woodlands, particularly those on sandy soils.
Food and Feeding. Poorly known, but the Tiny Fat Mouse is presumed to be granivorous.
Breeding. Poorly known. A single lactating Tiny Fat Mouse was captured at the end of the dry season in November in Botswana.
Activity patterns. Poorly known. The Tiny Fat Mouse is nocturnal and terrestrial. It excavates a burrow in which food might be hoarded.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. No information.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Least Concern on The IUCN Red List.
Bibliography. Byrom et al. (2015), Coetzee (1977), Monadjem (2013c), Monadjem et al. (2015), Smithers (1971), Stanley et al. (2007), Swanepoel & Schlitter (1978).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.