Fidicinoides pronoe (Walker)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1590/s1519-566x2011000400006 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8248729 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039887E9-FFCE-4010-6D6A-9D2705BEDF55 |
|
treatment provided by |
Tatiana |
|
scientific name |
Fidicinoides pronoe (Walker) |
| status |
|
Fidicinoides pronoe (Walker) View in CoL View at ENA
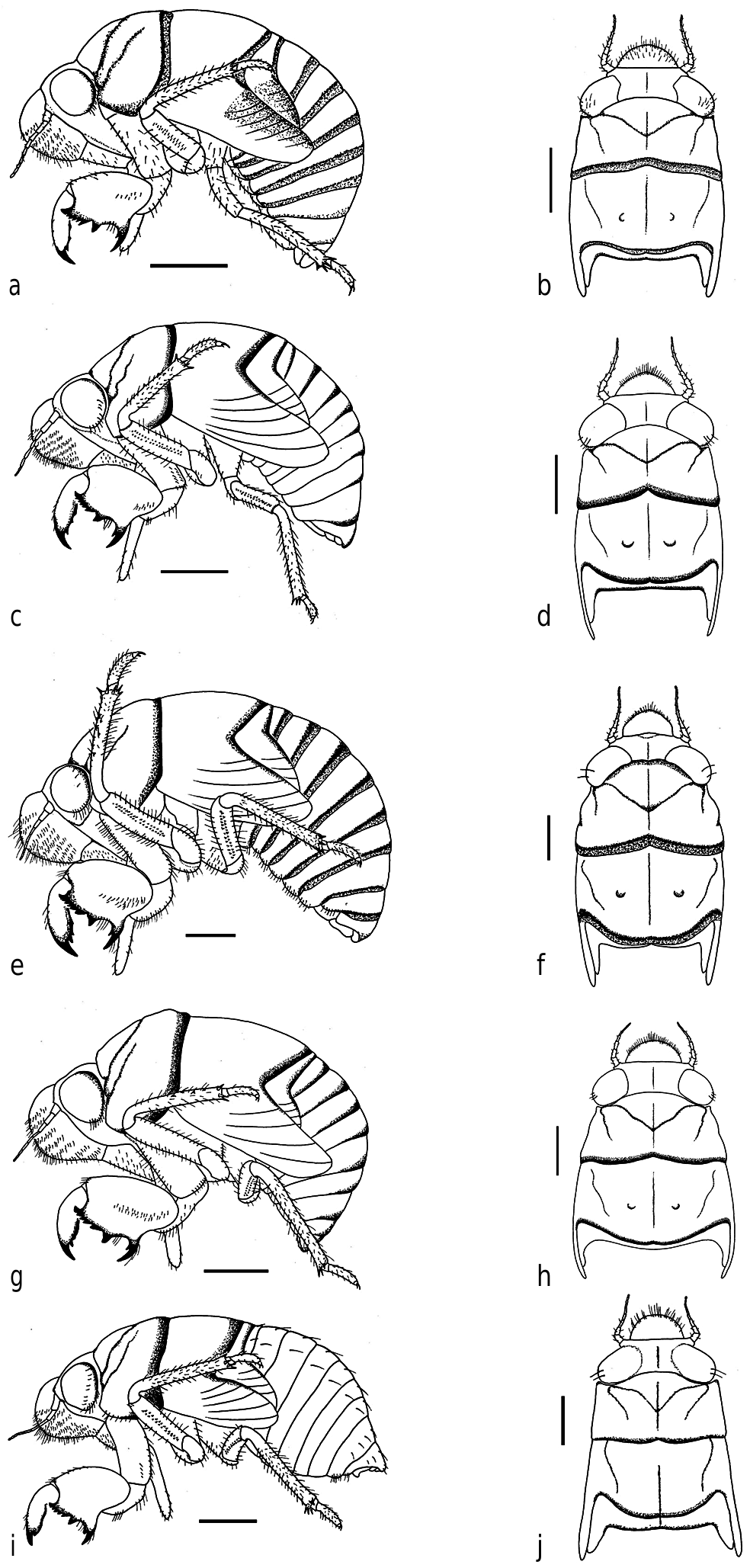
Body brownish in coloration, well curved in lateral view, covered with bristles scattered mainly in the ventral region ( Fig 1g View Fig 1 ).
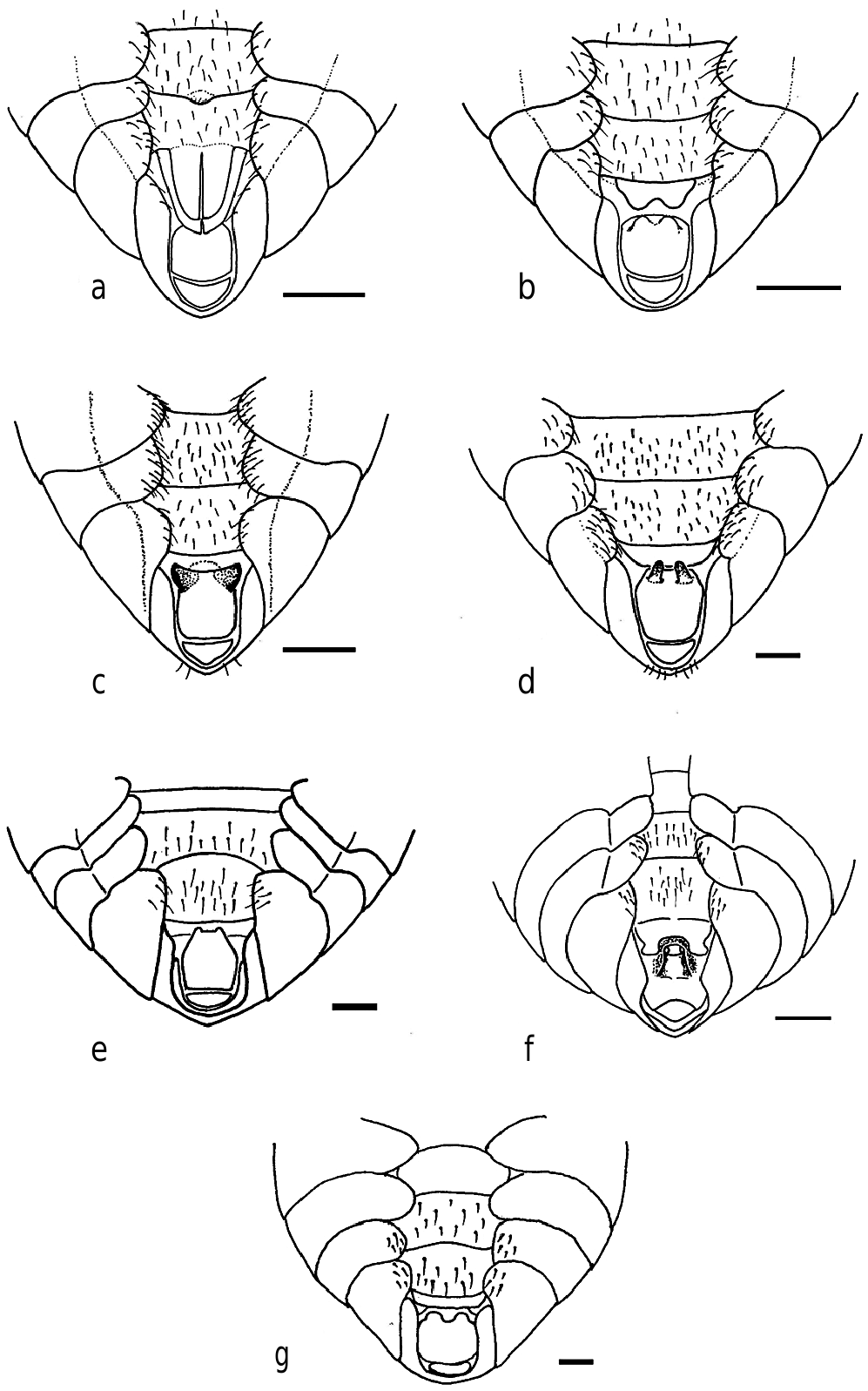
Head. In dorsal view, crown including eyes, about four times wider than long, slightly wider than the anterior margin of the pronotum ( Fig 1h View Fig 1 ). In ventral view, rostrum reaching posterior coxa.
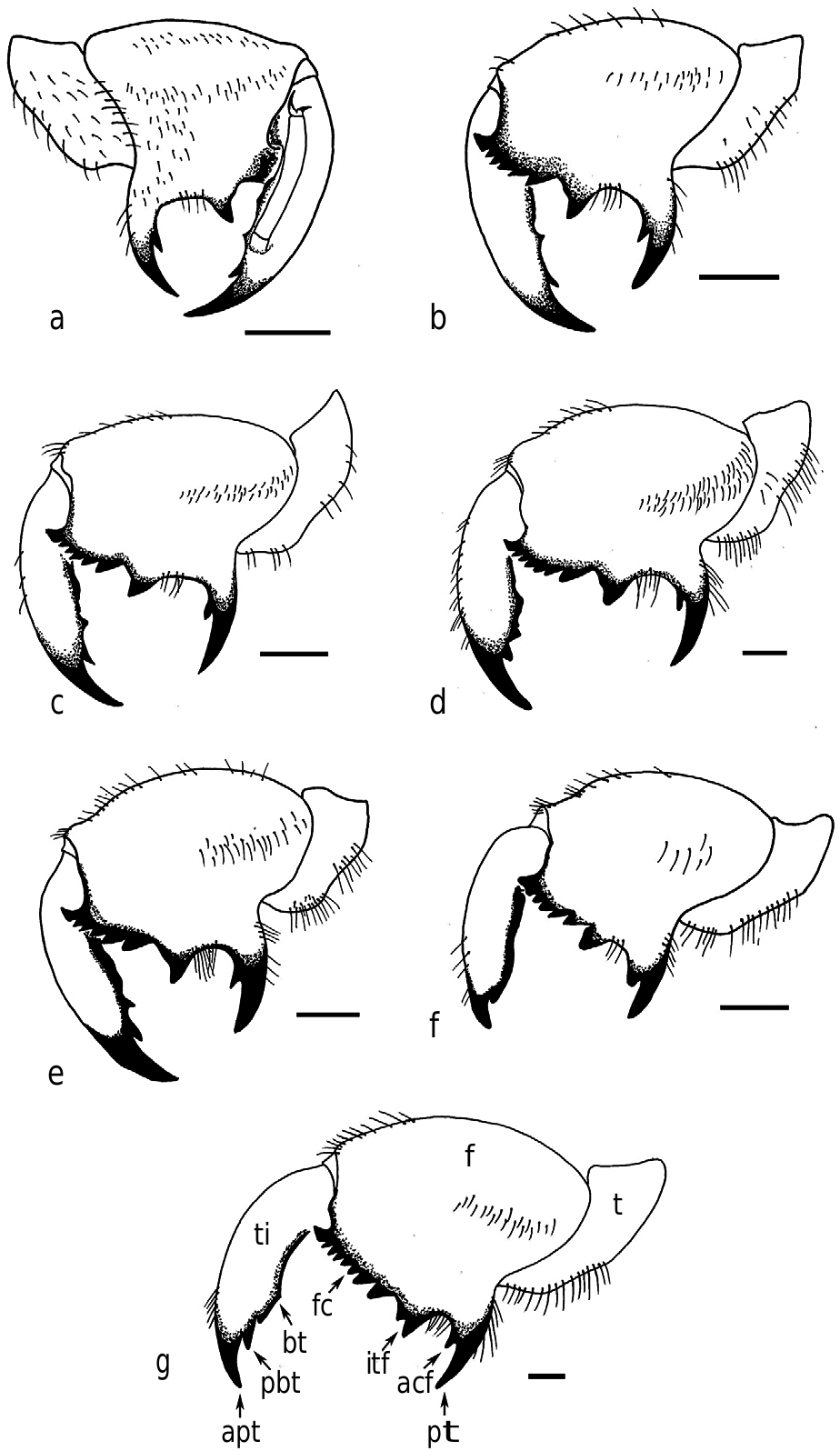
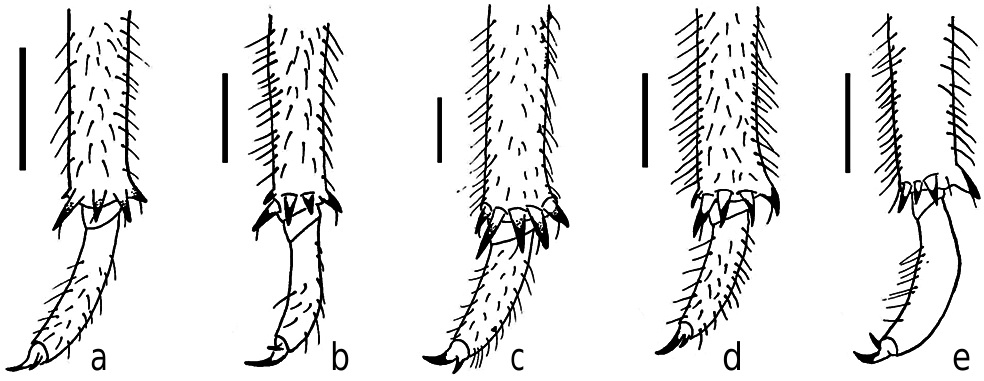
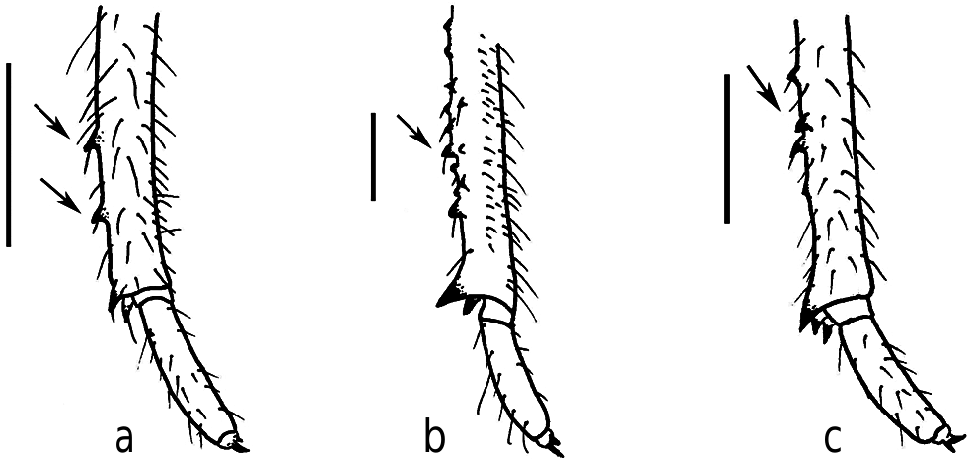
Thorax. In dorsal view, wider posteriorly, pronotum with a smaller surface than the mesonotum; metanotum very small when compared with pronotum and mesonotum ( Fig 1h View Fig 1 ). Wing cases developed, reaching abdominal segments ( Fig 1g View Fig 1 ). In the foreleg, femur with long and sharp posterior tooth, slightly bent forward, about two times longer than the width of its base, small and sharp accessory tooth, a strong intermediate tooth; femoral comb usually with six teeth, the first tooth wider and projected forward (femoral formula 2-1-6) ( Fig 2e View Fig 2 ). Tibia arched, flattened laterally, apical tooth long, blade of the tibia with a distinct tooth; tip of blade of tibia developed and separated from the apical tooth by a strong incision ( Fig 2e View Fig 2 ). Tarsi developed, folded over the inner surface of the tibia, two segmented, and the apical much longer and fitted with a pair of claws of unequal sizes. In the mid leg, tibia with at least three protrusions along its length. The distance between these protrusions is less than the distance between the distal one to the apex of tibia ( Fig 5c View Fig 5 ). In the hind legs, tibia with four spines, the outer one robust, in some cases there is a very small spine internally ( Fig 4d View Fig 4 ). Tarsi two segmented, the apical one much longer and fitted with a pair of claws of unequal sizes.
Abdomen. The size varies according to the development of the nymph, sometimes reduced, with the distal margin of the hind wing almost reaching the apex of abdomen, or elongated, with the distal margin of hind wing reaching the middle of abdomen. Female: 8th and 9th sternites with two sharp protrusions in the posterior margin.Male:10th sternite with two soft processes in the anterior margin ( Fig 3e View Fig 3 ).
Measurements (mm)
Male (n = 9): body length: 17.6 (16.2-20.0); postclypeus: length 4.4 (4.0-4.7), width 3.5 (3.3-3.8); crown: length 2.0 (1.9-2.2), width 8.4 (8.0-9.0); pronotum: length 4.9 (4.5- 5.3), width 9.0 (8.0-9.8); fore femur length 4.2 (3.8-4.5).
Female (n = 6): body length: 17.9 (15.7-19.8); postclypeus: length 4.4 (4.1-4.5), width 3.7 (3.6-3.8); crown: length 1.9 (1.7-2.1), width 8.4 (8.2-9.0); pronotum: length 4.9 (4.8- 5.1), width 9.5 (9.0-10.2); fore femur length 4.2 (4.0-4.5).
Material studied. BRAZIL. Minas Gerais: Coromandel, ix/ x – 1996 (R.C.Rangel), 8♂ and 5♀. São Paulo: Lençóis Paulista, Farm L. Wart , xi – 1984 (S. Zambon), 1 ♂ and 1 ♀.
Comment: A femoral comb with five teeth occurred in 6.7% of the specimens studied.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |