Mononchus altiplanicus, Andrássy, 2011
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1080/00222933.2010.524947 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039887CF-133B-BD3B-FE32-FC1BF0BC6FF8 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Mononchus altiplanicus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Mononchus altiplanicus sp. nov.
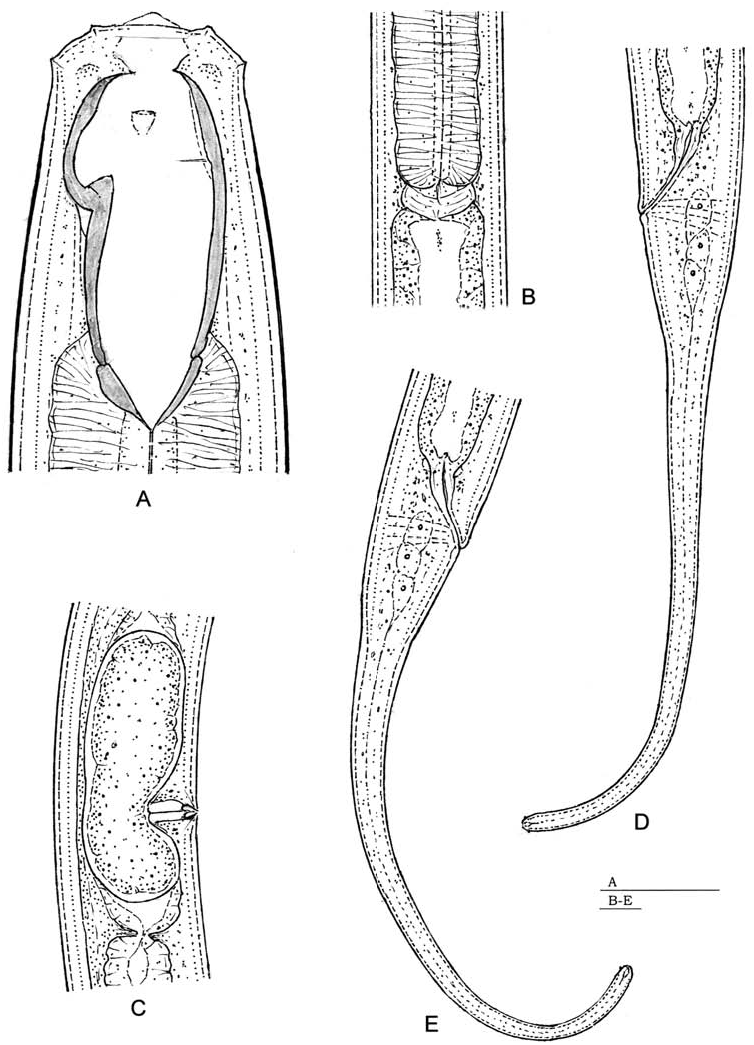
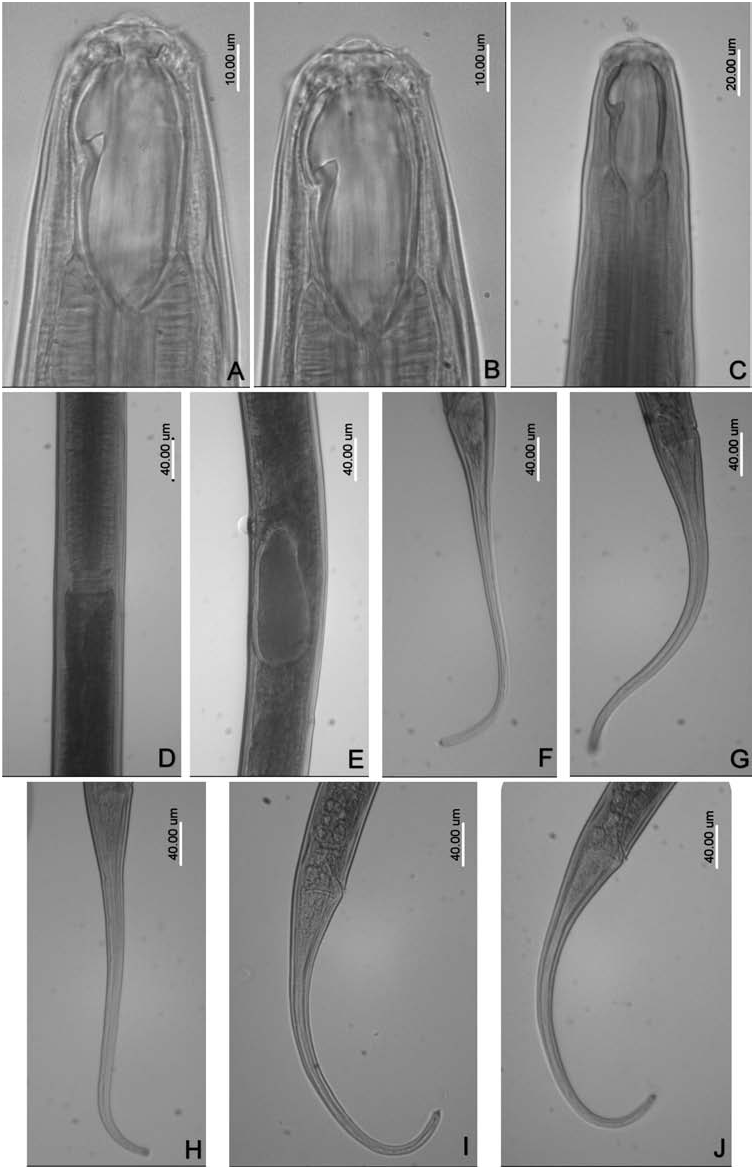
( Figures 2A–E View Figure 2 and 3A–J View Figure 3 )
Holotype female: L = 2.73 mm; a = 39; b = 3.7; c = 7.4; c’ = 8.3; V = 54 %. Paratype females (n = 8): L = 2.61–2.78 mm; a = 38–42; b = 3.7–3.8; c = 7.5–8.6; c’ = 7.7–8.7; V = 53–56%.
General characters
Body large and fairly slender, 2.6–2.8 mm long, 45–46 µm wide at posterior end of stoma, 62–65 µm wide at cardia, 62–70 µm wide at mid-region, and 44–46 µm wide at posterior anal lip; nearly straight or only slightly bent ventrally upon fixation. Cuticle practically smooth, thin, 2.0–2.5 µm thick all along the body, except for tail where it is 2.5–3.5 µm thick. Labial region almost continuous with neck contour, 31–33 µm wide, lips low, conical with small papillae. Oral field somewhat protruded, about 3 µm high. Body at proximal end of pharynx 1.9–2.1 times as wide as labial region. Amphids small, their opening located halfway between the beginning of buccal capsule and the dorsal tooth apex.
Distance between the oral field and beginning of buccal capsule 10–12 µm. Buccal capsule large, oval, 57–61 µm long, 24–27 µm wide at anterior third and 21–23 µm wide at posterior third, 2.1–2.3 / 2.5–2.6 times as long as wide, or 1.7–1.9 times as long as labial diameter, occupying 7.8–8.5% of entire length of pharynx (measured from oral field). Buccal wall 1.5–2.0 µm thick, just posterior to dorsal tooth 3 µm thick. Dorsal tooth strong, from base to apex 6–7 µm long, its apex located 16–18 µm from beginning of buccal capsule or at 28–30% of buccal length. Distance between tooth apex and opposite stomatal wall 14–16 µm. Subventral transversal ribs lying anterior to tooth apex. Pharynx 680–732 µm long, cylindrical, heavily muscular, surrounding the posterior 18–20% of buccal capsule. Nerve ring situated at anterior third of the total neck length. Cardia discoidal with acute posterior tip. Intestinal cells often with a large vacuola each. Rectum length about equal to anal body width.
Female
Genital apparatus amphidelphic. Genital branches relatively short, each as long as 3.7–5.3 body diameters or occupying 9.5–12.5% of body length. Reflexed ovaries reaching close to vulva. Distinct sphincter between uterus and oviduct present. Vulva a transverse slit, with sclerotized, drop-shaped inner lips, vagina 25–30 µm long, extending inwards for about 40% of body diameter. Gravid females with one uterine egg at a time, 124–134 by 52–55 µm, nearly twice the body width long. Distance between posterior end of pharynx and vulva as long as or slightly (1.1–1.2 times) longer than pharynx. Distance vulva–anus equal to 2.3–3.0 tail lengths. Tail 313–368 µm (on average 335 µm) long, occupying 11.6–13.4% of entire length of body, conical at first, then tapered to cylindrical shape; the cylindrical part (posterior third) 10–12 µm wide, rounded on tip, and generally ventrally curved. Caudal glands moderately developed, spinneret terminal, flanked by two small subterminal papillae.
Male
Not observed.
Diagnosis and relationships
This comparatively large Mononchus species is characterized by an average body length of 2.68 mm, thin cuticle, continuous labial region 31–33 µm wide, large buccal cavity of 57–61 by 24–27 µm, dorsal tooth apex at about 30% of buccal capsule, transversal ribs anterior to tooth apex, vulval lips sclerotized, tail on the average eight anal body widths long and cylindrical in its posterior section.
Mononchus altiplanicus sp. nov. belongs to the larger species (2.6–6.4 mm) of the genus, and among them to the species possessing a longer tail (four to eight anal body diameters). The latter are M. niddensis Skwarra, 1921 , M. superbus Mulvey, 1978 and M. agilis Gagarin and Mataphanov, 2004 . The new species simply differs from M. superbus by the much shorter body (2.6–2.8 vs 5.0– 6.4 mm). It is distinguished from the other two species as follows. From M. niddensis by the somewhat shorter body (2.6–2.8 vs 2.7–3.5 mm), the longer tail (313–368 vs 200–270 µm), and especially by the posterior position of the tooth apex (28–30 vs 12–16%). From M. agilis by the somewhat shorter and more slender body (2.6–2.8 vs 2.9–3.1; a = 38–42 vs 17–19), much shorter buccal cavity (57–61 vs 81–84 µm), posterior position of the tooth apex (28–30 vs 12–14%), and by the longer tail (8–9 vs 3.2–4 anal body diameters).
Type specimens
Holotype female on slide no. 15003. Paratypes: eight females and two juveniles; deposited with the nematode collection of the Department of Systematic Zoology and Ecology of the Eötvös Loránd University , Budapest .
Type habitat and locality
Fine mud and sediment around the roots of water plants from the Lago di Chungará, at the foot of the volcano Parinacota, Altiplano, 4500 m above sea level, northern Chile at the Chilean–Bolivian border. Collected in November 1965 by the present author.
Etymology
The species name refers to the Altiplano, the high plateau in western South America.
| V |
Royal British Columbia Museum - Herbarium |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Mononchus altiplanicus
| Andrássy, István 2011 |
Mononchus altiplanicus
| Andrássy 2011 |
M. agilis
| Gagarin and Mataphanov 2004 |
M. agilis
| Gagarin and Mataphanov 2004 |
M. superbus
| Mulvey 1978 |
M. superbus
| Mulvey 1978 |
M. niddensis
| Skwarra 1921 |
M. niddensis
| Skwarra 1921 |