Pseudexostoma yunnanensis ( Tchang, 1935 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.5331935 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039887C1-0174-FF9A-0007-C6ED636AFC5D |
|
treatment provided by |
Diego |
|
scientific name |
Pseudexostoma yunnanensis ( Tchang, 1935 ) |
| status |
|
Pseudexostoma yunnanensis ( Tchang, 1935) View in CoL
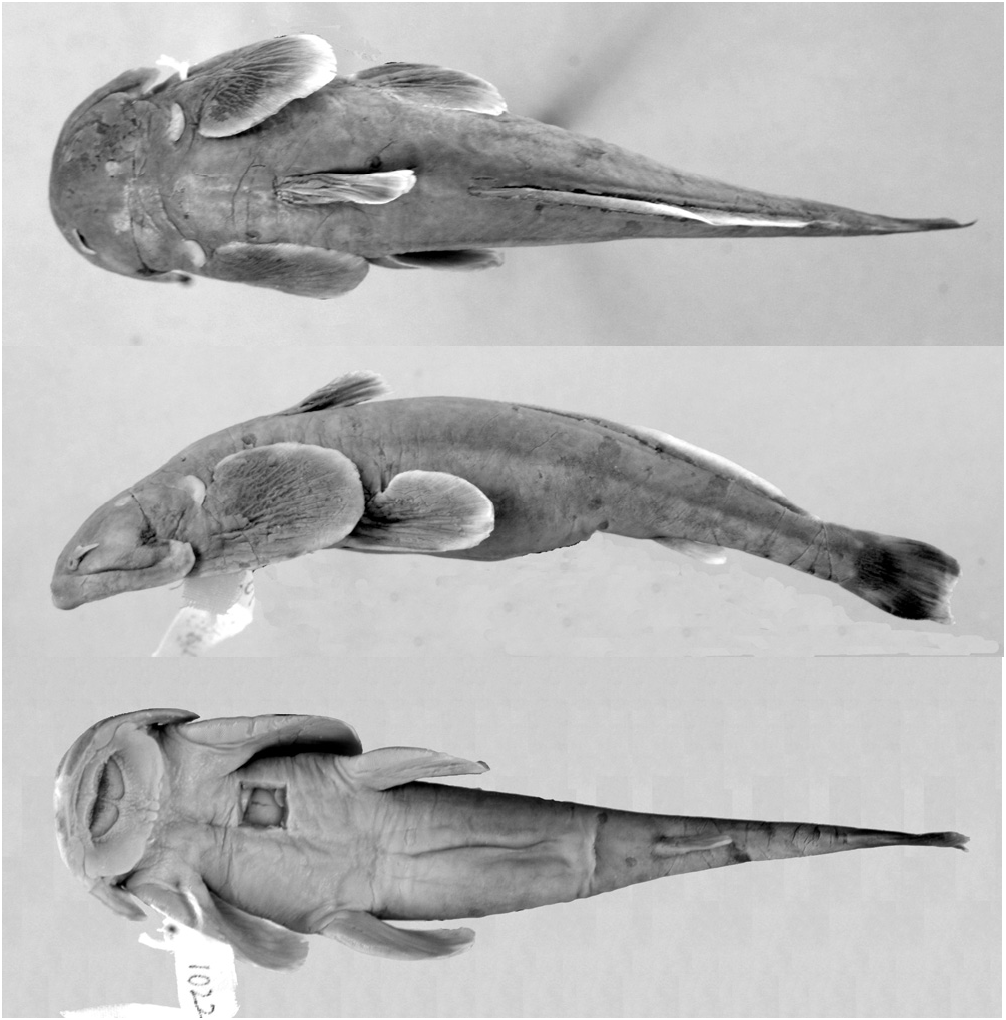
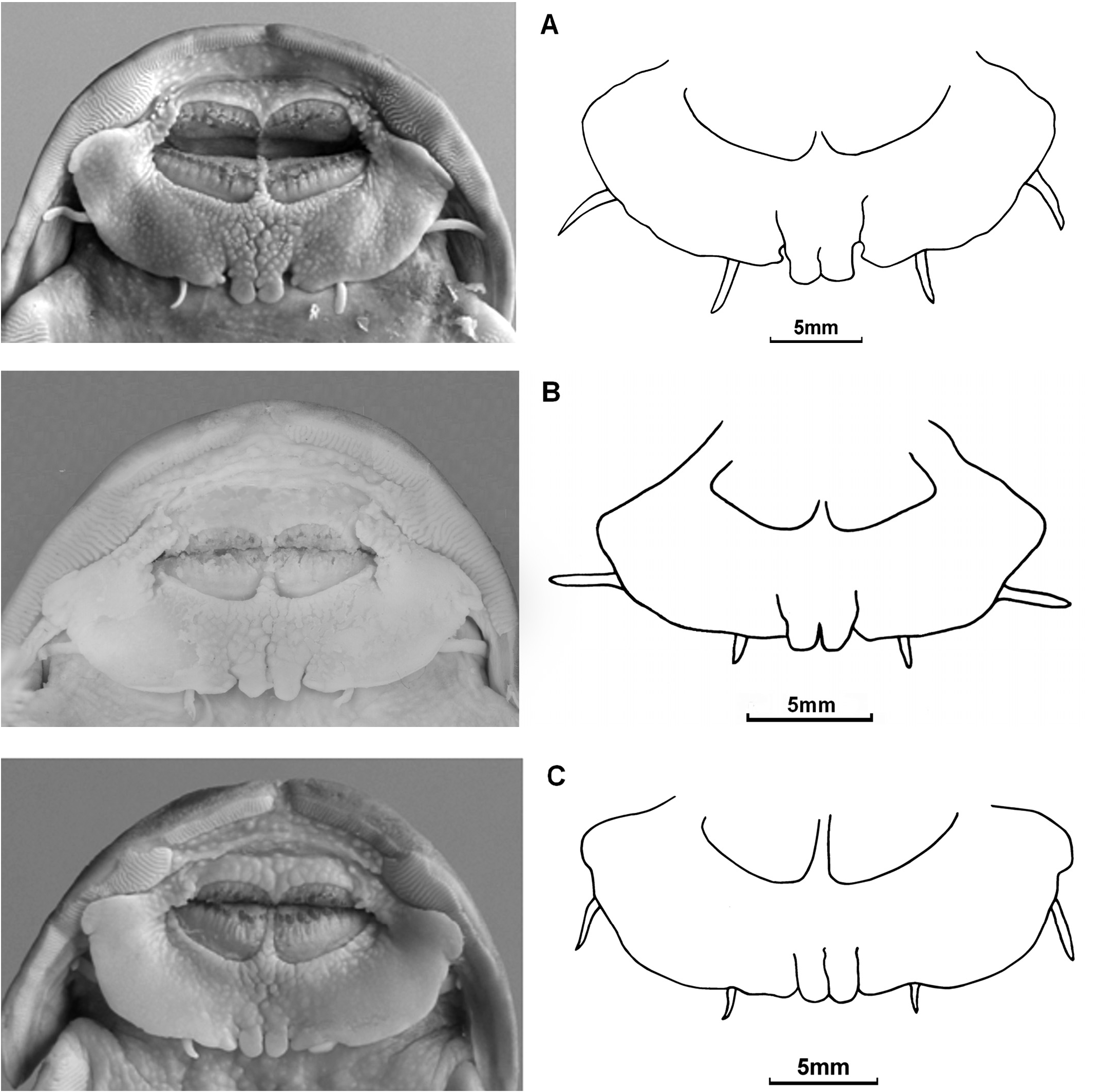
( Figs. 2C View Fig , 3C View Fig , 4, 6 View Fig )
Glyptosternum yunnanensis Tchang, 1935: 174-175 (Yunnan) View in CoL .
Pseudexostoma yunnanensis yunnanensis View in CoL - Chu, 1979: 78-79 (Guyong, Tengchong County); Chu, Mo & Kuang, 1990: 212- 214, Fig. 213 (Guyong, Tengchong County); Chu & Mo, 1999: 178-179, Fig. 117 (Guyong, Tengchong County).
Material examined. – SWFC 200102172–173, 200102175–186, 200102190, 200102197, 200102201–202, 18 ex., 81–125 mm TL, 72–111 mm SL, Guyong , Tengchong County, Yunnan Province .
Diagnosis. – Pseudexostoma yunnanensis is distinguished from P. brachysoma and P. longipterus by the following combination of characteristics: posterior margin of lower lip with three notches, depth of middle notch the same depth as lateral ones (vs. shallower), length of two smaller median lobes of lower lip the same length as lateral lobes ( Fig. 2C View Fig ) (vs. longer, Fig. 2A–B View Fig ); pelvic fin i, 5 (vs. i, 3–4); base of adipose fin shorter (28.8–39.8% SL vs. 36.1–46.0); caudal peduncle deeper (depth of caudal peduncle 6.4–8.3% SL and 32.6–42.7% in length of caudal peduncle vs. 4.2–6.9 and 20– 33.7); premaxillary tooth band with 18–22 teeth (vs. 16–18), premaxillary tooth band divided into two and connected partially ( Fig. 3C View Fig ) (vs. isolated, Fig. 3A–B View Fig ).
Description. – Morphometric data as in Table 1.
Body moderately compressed. Dorsal profile rising evenly and somewhat steeply from tip of snout to origin of dorsal fin, then sloping gently ventrally to end of caudal peduncle.
Head and abdominal region before origin of anal fin broad and flat. Body after adipose fin compressed gradually.
Head depressed and broad, triangular when viewed laterally and with rounded snout when viewed from above. Eye small and ovoid, subcutaneous and located at middle of dorsal surface of head. Mouth transverse and inferior, premaxillary and mandibular tooth bands exposed when mouth closed. Teeth embedded in skin, shovel-shaped, tips exposed and arranged in irregular rows. Premaxillary tooth band divided into two, with 18–22 teeth, and connected partially ( Fig. 3C View Fig ). Anterior nostril tubular, separated from posterior nostril by nasal barbel base. Gill opening narrow, extending from onethird of last ray of pectoral fin to the first ray. Dorsal surface smooth without tubercles. Barbels in four pairs. Maxillary barbel flattened, with surrounding flap of skin and rounded tip, extending beyond pectoral fin origin, but not reaching to gill opening and far from posttemporal. Nasal barbel with small flap of thin skin fringing posterior margin and not reaching anterior margin of orbital. Post labial groove connected. Lower lip broad with three notches along posterior margin, divided into two bigger lateral lobes and two smaller median lobes. Depth of middle notch as the same depth as lateral ones, length of two smaller median lobes of lower lip as the same length as lateral lobes. Inner mandibular-barbel close to midline, extending to pectoral fin origin. Outer mandibular-barbel precedes lateral inner mandibular barbel, extending to pectoral fin origin ( Fig. 2C View Fig ).
Unbranched dorsal fin ray not ossified. Post-dorsal margin of dorsal fin concave slightly. Origin of dorsal fin located at point through anterior third of body. Adipose fin base not connected with caudal fin. Caudal fin emarginate, upper lobe smaller than lower lobe. Anal fin post-ventral margin emarginate. Distance of anal fin origin to caudal fin base shorter than to end of pelvic fin base. Origin of pelvic fin precedes vertical end of dorsal fin base. Pelvic fin margin convex slightly, not extending to anus. Pectoral fin greatly enlarged and first unbranched ray not ossified. First unbranched ray of paired fins broadened with regular striae on ventral surface. Anus and urogenital openings located at end of pelvic fin and before origin of anal fin. Lateral line midlateral and complete.
Coloration. – Grey black on dorsal surface, no spots or patches. Grey yellow on ventral region. Caudal fin grey black with an irregularly, small, yellow patch in the middle. Fins with grey yellow around distal edge.
Distribution. – Only known from the upper Dayinjiang (an upper branch of the Irrawaddy River) ( Fig. 4).
Remarks. – The specimens of Pseudexostoma yunnanensis deposited in the museum of Kunming Institute of Zoology (KIZ), the Chinese Academy of Sciences were collected from Guyong of Tengchong County, Yunnan ( Chu, 1979; Chu et al., 1990; Chu & Mo, 1999). However, the specimens of Pseudexostoma yunnanensis were only collected from the same locality while Southwest Forestry College respectively investigated the Dayinjiang and collected fish specimens in 1999, 2001 and 2004.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Pseudexostoma yunnanensis ( Tchang, 1935 )
| Zhou, Wei, Yang, Ying, Li, Xu & Li, Ming-Hui 2007 |
Glyptosternum yunnanensis
| Tchang, C 1935: 175 |