Conostigmus rosemaryae Trietsch, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4792.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:326F6A15-216E-439A-AD59-3CDF7551D3F6 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5686606 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039687D1-FF0B-6583-9FA4-FD5944B9C4C3 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Conostigmus rosemaryae Trietsch |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Conostigmus rosemaryae Trietsch sp. nov.
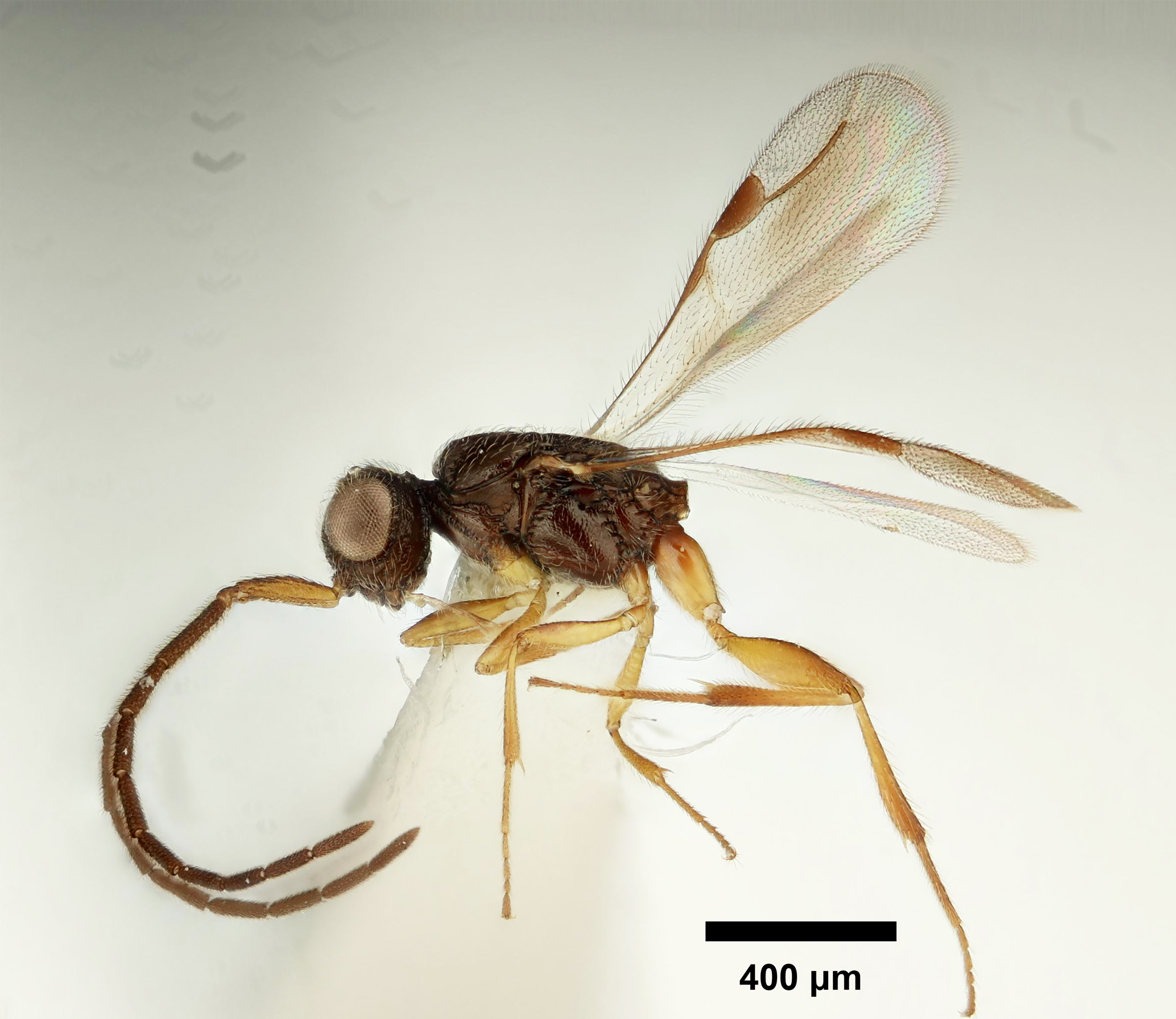
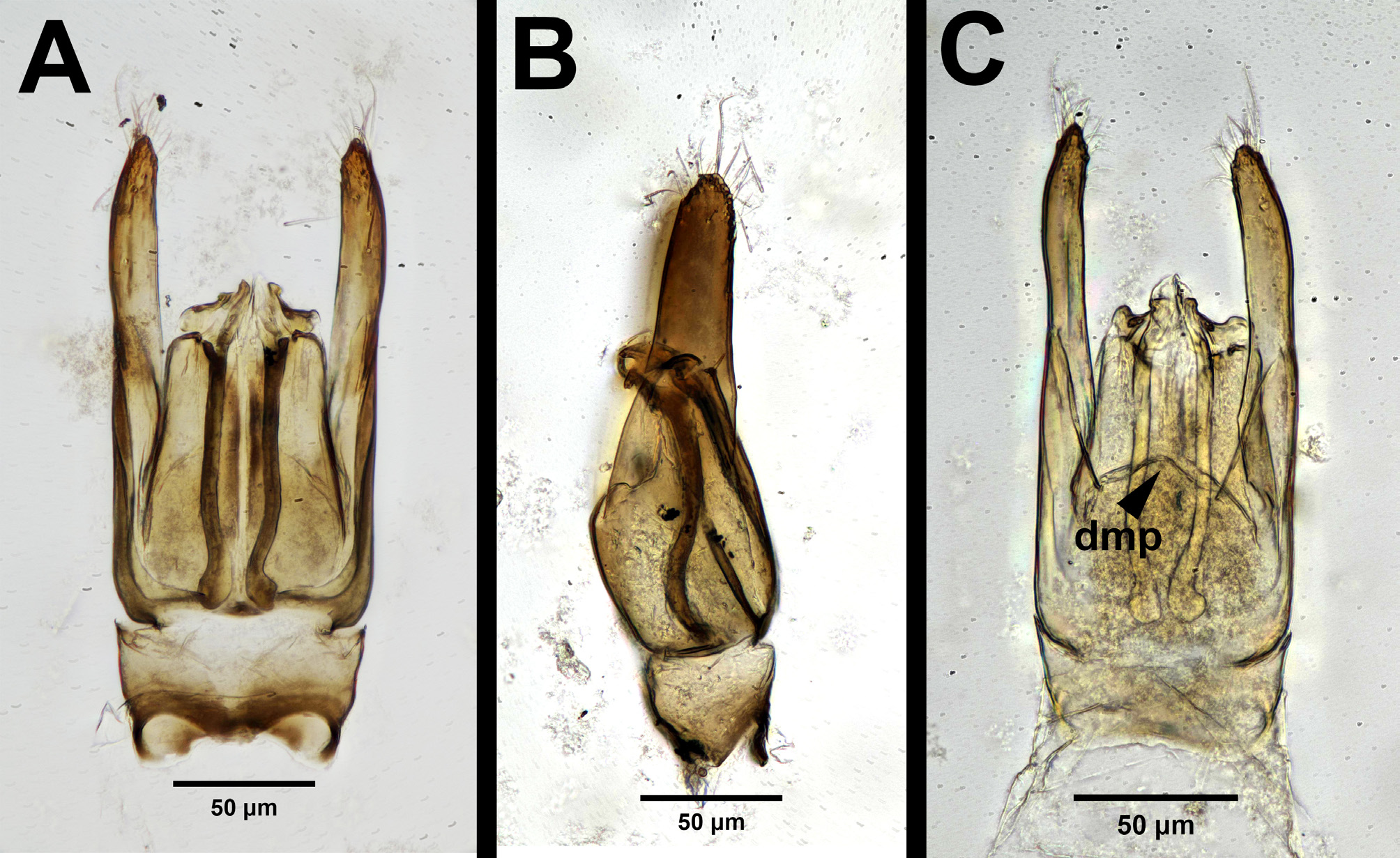
Figs. 78 View FIGURE 78 , 79 View FIGURE 79 , 80 View FIGURE 80
Diagnosis. This species can be distinguished from all other species of Conostigmus by the following combination of characters: facial sulcus present; sternaulus present and elongate, exceeding 1/2 of the mesopleuron length at the level of the sternaulus; dorsomedian projection of the gonostyle–volsella complex present; harpe not spatulate or spoon-shaped; and harpe shorter than the gonostipes in lateral view.
This species is most similar to C. pulchellus and C. abdominalis , but is distinguishable from both by the male genitalia. Conostigmus rosemaryae has the dorsomedian projection of the gonostyle–volsella complex present, harpe that are shorter than the gonostipes in lateral view and harpe that are not spoon-shaped or spatulate. Conostigmus rosemaryae also has 1 apical parossicular seta, whereas C. pulchellus has 4 or more ( C. abdominalis can have 1–3).
Variability. The sternaulus is elongate in all specimens, but in some it exceeds 3/4 of the mesopleuron length at the level of the sternaulus (CMNHENT0022801, CMNHENT0022798) whereas in others it reaches between 1/2 and 3/4 of the mesopleuron length at the level of the sternaulus (CMNHENT0022821, CMNHENT0022771). The median process on the intertorular carina is present and acute in all specimens, but extends towards the dorsal margin of the clypeus in some (CMNHENT0022821, CMNHENT0022801) and not in others (PSUC_FEM 9042). There is also variation in the POL to OOL ratio, with POL equal to or shorter than OOL (ocellar triangle with short base) in most specimens, but POL longer than OOL (ocellar triangle with a wide base) in one specimen (PSUC_ FEM 9042).
Description. Color hue pattern in male: cranium, mesosoma, metasoma brown to black except pronotum; pronotum light brown to black; F1–F9 brown to dark brown; scape, pedicel ochre to brown; legs ochre to brown. Color intensity pattern in male: metasoma and mandible lighter than mesosoma; flagellomeres and pedicel darker than scape; pronotum sometimes lighter than rest of mesosoma. Color intensity dorsal and ventral to the site of the sternaulus: concolorous. Color intensity pattern of syntergite: petiole neck and anterior region of syntergite concolorus with the posterior region of the syntergite. Foveolate sculpture on body count: absent. Rugose sculpturing count: present on head. Rugose region on upper face count: present.
Antennae: Male scape length vs. pedicel length: 3.6–6.4. Male scape length vs. F1 length: 0.8–1.2. Male F1 length vs. pedicel length: 3.6–6.5. Male F1 length vs. male F2 length: 1.3–1.5. Longest male flagellomere: F1. Length of setae on male flagellomere vs. male flagellomere width: setae shorter than width of flagellomeres. Sensillar patch of the male flagellomere pattern: F5–F9.
Head: Head width, dorsal view: equal to or only slightly wider than mesosoma (less than 1.3× wider than mesosoma). Head height (HH, lateral view) vs. eye height (EHf, anterior view): HH:EHf=1.4–1.8. Head height (HH) vs. head length (HL): HH:HL=1.1–1.3. Head width (HW) vs. interorbital space (IOS): HW:IOS=1.7–1.9. Head width (HW) vs. head height (HH): HW:HH=1.3–1.6. Cephalic size (csb): Mean: 450–650 μm. Maximum eye diameter vs. minimum eye diameter: 1.1–1.3. POL:OOL: POL equal to or shorter than OOL and ocellar triangle with short base OR POL longer than OOL and ocellar triangle with wide base. Male ocular ocellar line (OOL) vs. lateral ocellar line (LOL): OOL:LOL=1.6–2.5. Male ocular ocellar line (OOL) vs. posterior ocellar line (POL): OOL:POL=0.8– 1.2. Male ocular ocellar line (OOL): posterior ocellar line (POL): lateral ocellar line (LOL): 1.8–2.5:1.6–2.3:1.0. Head shape (anterior view): circular or triangular. Preoccipital lunula count: present. Preoccipital carina count: absent. Occipital carina structure: occipital carina complete. Occipital carina sculpture: crenulate. Preoccipital furrow count: present. Preoccipital furrow anterior end: preoccipital furrow ends inside ocellar triangle, but ends posterior to the anterior ocellus. Preoccipital furrow sculpture: crenulate. Postocellar carina count: present. Dorsal margin of occipital carina vs. dorsal margin of lateral ocellus in lateral view: occipital carina ventral to lateral ocellus in lateral view. Transverse scutes on upper face count: absent. Transverse frontal carina count: absent. Randomly sized areolae around setal pits on upper face count: absent. Setal pit on vertex size: smaller than diameter of scutes. Ventromedian setiferous patch and ventrolateral setiferous patch count: absent. White, thick setae on upper face count: absent. Antennal scrobe count: absent. Facial structure count: facial sulcus present. Facial sulcus count: present. Median facial keel count: absent. Supraclypeal depression count: present. Supraclypeal depression structure: present medially, inverted U-shaped. Intertorular area count: present. Intertorular carina count: present. Median process on intertorular carina count: present. Median process on intertorular carina shape: acute. Median process of intertorular carina structure: process extends across intertorular area towards dorsal margin of clypeus; process does not extend across intertorular area to dorsal margin of clypeus. Median region of intertorular area shape: convex. Ventral margin of antennal rim vs. dorsal margin of clypeus: not adjacent. Torulo–clypeal carina count: present. Subtorular carina count: absent. Mandibular tooth count: 2. Mandibular lancea count: absent.
Mesosoma: Weber length: WL=700–900 μm. Anterior mesoscutal width (AscW) vs. posterior mesoscutal width (PscW): AscW/PscW=0.5–0.9. Mesoscutal length (MscL) vs. anterior mesoscutal width (AscW): MscL/ AscW=1.2–2.1. Mesoscutal length (MscL) vs. mesoscutellar length (MscIL): MscL:MscIL= 0.9–1.0. Wing count: present. Fore wing size: wings present and macropterous with apex extending past petiole. Pronotum median length: less than longest median anatomical line of the mesoscutum. Notaulus count: present. Crenulae of notaulus width: width of the crenulae does not increase more than 2× anteriorly. Notaulus posterior end location: adjacent to transscutal articulation. Posterior region of notaulus orientation: posterior end of notaulus does not curve and is not adjacent to median mesoscutal sulcus. Median mesoscutal sulcus count: present. Median mesoscutal sulcus posterior end: adjacent to transscutal articulation. Scutoscutellar sulcus vs. transscutal articulation location: adjacent. Axillular carinae count: present. Axillular carinae shape: the left and right carinae are separated posteromedially. Speculum ventral limit: not extending ventrally of pleural pit line. Metapleural sulcus shape: straight. Mesometapleural sulcus count: present. Ventrolateral invagination of the pronotum count: present. Sternaulus count: present. Sternaulus length: elongate and exceeding 1/2 of mesopleuron length at level of sternaulus. Sternaulus sculpture: smooth. Epicnemial carina count: complete. Epicnemium posterior margin shape: anterior discrimenal pit present; epicnemial carina curved. Transverse striations on the ventral metapleural area count: absent. Scutes on posterior region of mesoscutum and dorsal region of mesoscutellum convexity: flat. Ventral projection of the metapleural carina count: absent. Lateral propodeal carina count: present. Lateral propodeal carina shape: inverted “Y” (left and right lateral propodeal are adjacent medially posterior to antecostal sulcus of the first abdominal tergum, and connected to the antecostal sulcus by a median carina representing the median branch of the inverted “Y”). Mesopostscutellum count: absent (scutellum flat).Anteromedian projection of the metanoto–propodeo–metapecto–mesopectal complex count: absent. Posterior margin of nucha in dorsal view shape: straight.
Metasoma: Transverse carina on petiole shape: concave. Paired blue iridescent ovoid patches on the syntergite count: absent. Shortest width of petiole neck vs. syntergal translucent patch maximum width: 1.8–2.8. Shortest width of petiole neck vs. synsternal translucent patch maximum width: 2.0–2.8. Syntergal translucent patch maximum width vs. minimum width: 1.7–2.5. Synsternal translucent patch maximum width vs. minimum width: 1.1–2.3. Syntergal translucent patch maximum width orientation: anterolaterally. Synsternal translucent patch maximum width orientation: anteromedially. Synsternal setiferous patch shape: linear, with a patch of setae lateral or posterior to the synsternal translucent patch. Synsternal setiferous patch structure: comprised of a single or double row of setae anterior to the synsternal translucent patch, with a patch of setae lateral or posterior to the synsternal translucent patch. Synsternal setiferous patch anterior end: synsternal setiferous patch begins anterior to the synsternal translucent patch anterior margin. Synsternal setiferous patch posterior end: synsternal setiferous patch ends lateral to the synsternal translucent patch posterior margin; synsternal setiferous patch ends posterior to the synsternal translucent patch posterior margin. Synsternal setiferous patch length vs. synsternal translucent patch maximum width: synsternal setiferous patch at least 2× as long as the maximum width of the synsternal translucent patch. S1 length vs. shortest width: S1 wider than long.
Male Genitalia: Distal margin of male S9 shape: convex. Proximolateral corner of male S9 shape: blunt. Male S9 distal setal line/setal patch count: distal setae composing transverse setiferous line or lines. Male S9 distal setal line / setal patch structure: single or double transverse row of distal setae. Distomedian hairless area interrupting transverse row of setae or patch on male S9 count: absent with distal setiferous patch/line continuous medially. Submedial projections on proximal margin of S9 count: absent. Cupula length vs. gonostyle–volsella complex length: cupula less than 1/2 the length of gonostyle–volsella complex in lateral view. Proximodorsal notch of cupula count: present. Proximodorsal notch of cupula shape: arched (inverted U-shape). Proximodorsal notch of cupula width vs length: wider than long. Proximolateral projection of the cupula shape: acute. Gonocondyle count: present. Gonocondyle shape: blunt. Distodorsal margin of cupula shape: straight. Distoventral submedian corner of the cupula count: absent. Dorsomedian projection of the gonostyle–volsella complex count: present. Dorsomedian projection of the gonostyle–volsella complex shape: simple (not bilobed). Dorsomedian conjunctiva of the gonostyle–volsella complex count: present. Dorsomedian conjunctiva of the gonostyle–volsella complex length relative to length of gonostyle–volsella complex: dorsomedian conjunctiva extending between 1/3 to 1/2 the length of gonostyle–vol-sella complex in dorsal view. Dorsomedial margin of gonostyle–volsella complex shape: straight with a median projection. Proximal end of dorsomedian conjunctiva of the gonostyle–volsella complex shape: blunt or straight. Parossiculus count or parossiculus and gonostipes fusion: present and parossiculi not fused with the gonostipes. Medioventral conjunctiva of the gonostyle–volsella complex count or fusion of parossiculi: medioventral conjunctiva present and parossiculi independent or fused proximally. Apical parossicular setae count: one. Distal projection of the parossiculus count: absent. Distal projection of the penisvalva count: absent. Gonossiculus spine count: 2. Gonossiculus spine length: one spine not more than 2× as long as the other(s) (spines of similar lengths). Harpe length: harpe shorter than gonostipes in lateral view. Harpe shape: simple and not bilobed. Harpe orientation: medial. Lateral margin of harpe shape: widest point of harpe is at its articulation site with gonostyle–volsella complex. Distal margin of harpe in lateral view: blunt. Lateral setae of harpe count: present. Lateral setae of harpe orientation: oriented distally. Lateral setae on harpe density: setae sparse. Dense patch of setae on the distoventral edge of the harpe count: absent. Distal setae on harpe length: setae of equal length across distal end of harpe. Distodorsal setae of sensillar ring of harpe length vs. harpe width in lateral view: setae as long as or shorter than harpe width. Distodorsal setae of sensillar ring of harpe orientation: distomedially. Sensillar ring area of harpe orientation: distomedially. Sensillar ring shape: circular. Distoventral margin of harpe in lateral view: convex.
Distribution. Nearctic.
Etymology. This species is named rosemaryae after the first author’s mother, Rosemary Trietsch, who underwent 2 surgeries, 4 chemotherapy sessions, a month of radiation, and triumphantly beat breast cancer during the course of this research.
Material Examined. Holotype male: USA: Ohio: CMNHENT0022770 ( CLEV) . Paratypes (7 males): USA: Ohio : 7 males. CMNHENT0022771, 0022798, 0022801, 0022821 ( CLEV); PSUC _ FEM 9042 View Materials , 27292 View Materials , 86284 View Materials ( OSUC) .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SubOrder |
Apocrita |
|
SuperFamily |
Ceraphronoidea |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |