Fagopyrum caudatum ( Samuelsson 1929: 185 ) Li (1998: 117) var. grandiflorum M.Zhou & Y.Tang
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/phytotaxa.587.2.9 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7734589 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039687BE-171F-9B00-FF06-FDB3DEDD822B |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Fagopyrum caudatum ( Samuelsson 1929: 185 ) Li (1998: 117) var. grandiflorum M.Zhou & Y.Tang |
| status |
|
Fagopyrum caudatum ( Samuelsson 1929: 185) Li (1998: 117) var. grandiflorum M.Zhou & Y.Tang View in CoL
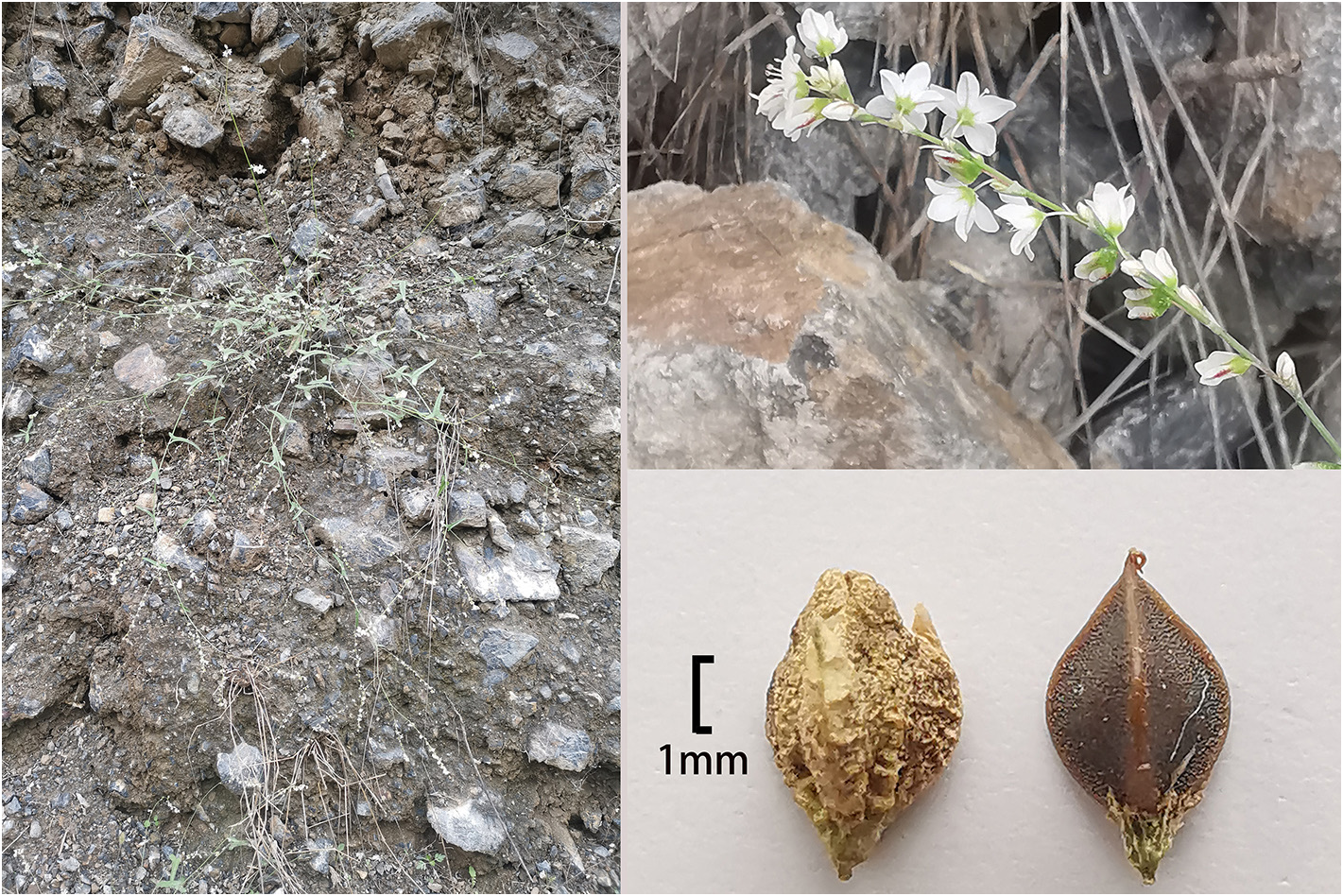
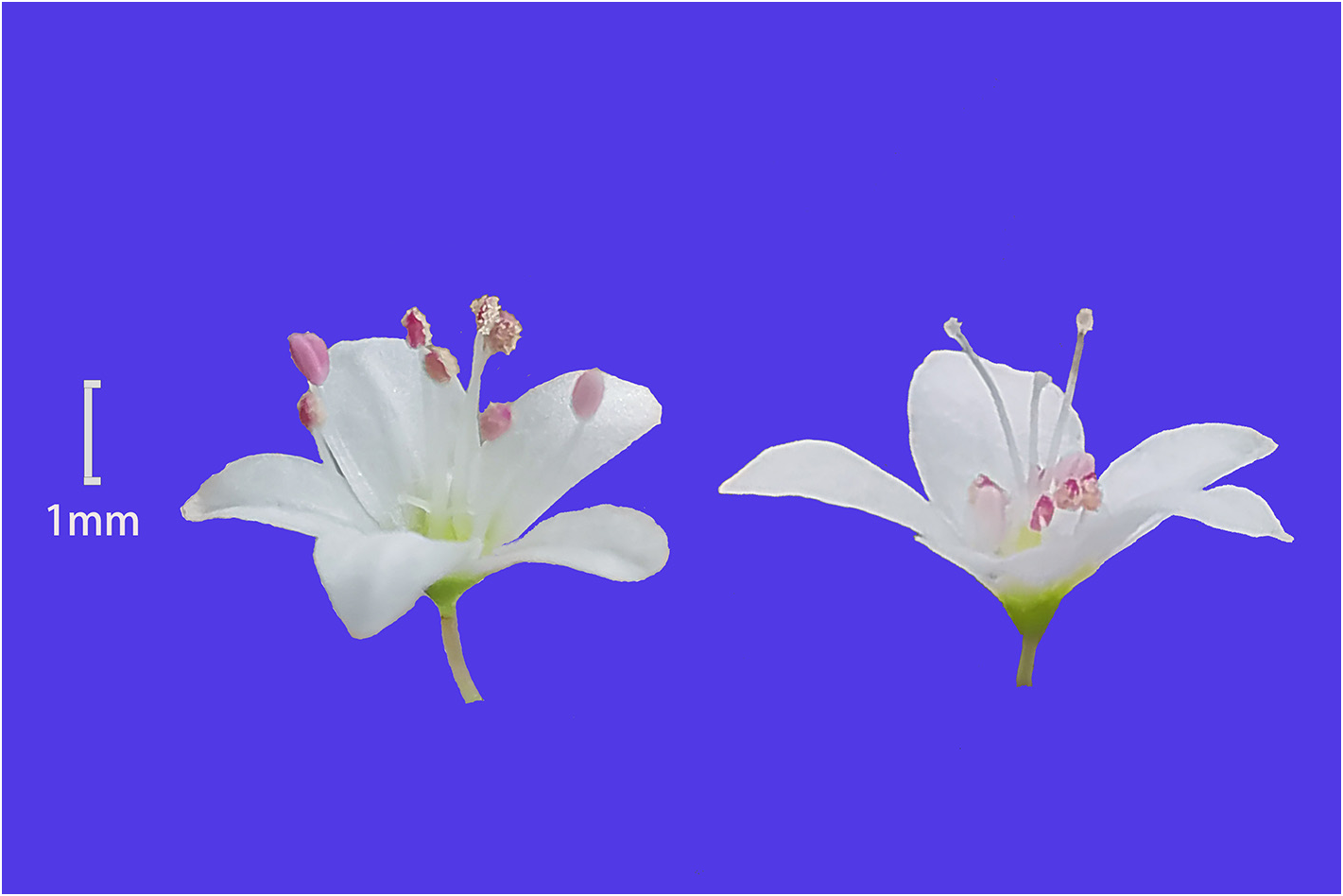
( Figs. 1–2 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 ), var. nov. .
Type : — CHINA. Gansu Province: Wen County, 1052–1220 m a.s.l., 18 October 2020, Zhou & Tang 202012 (holotype CAAS2205!)
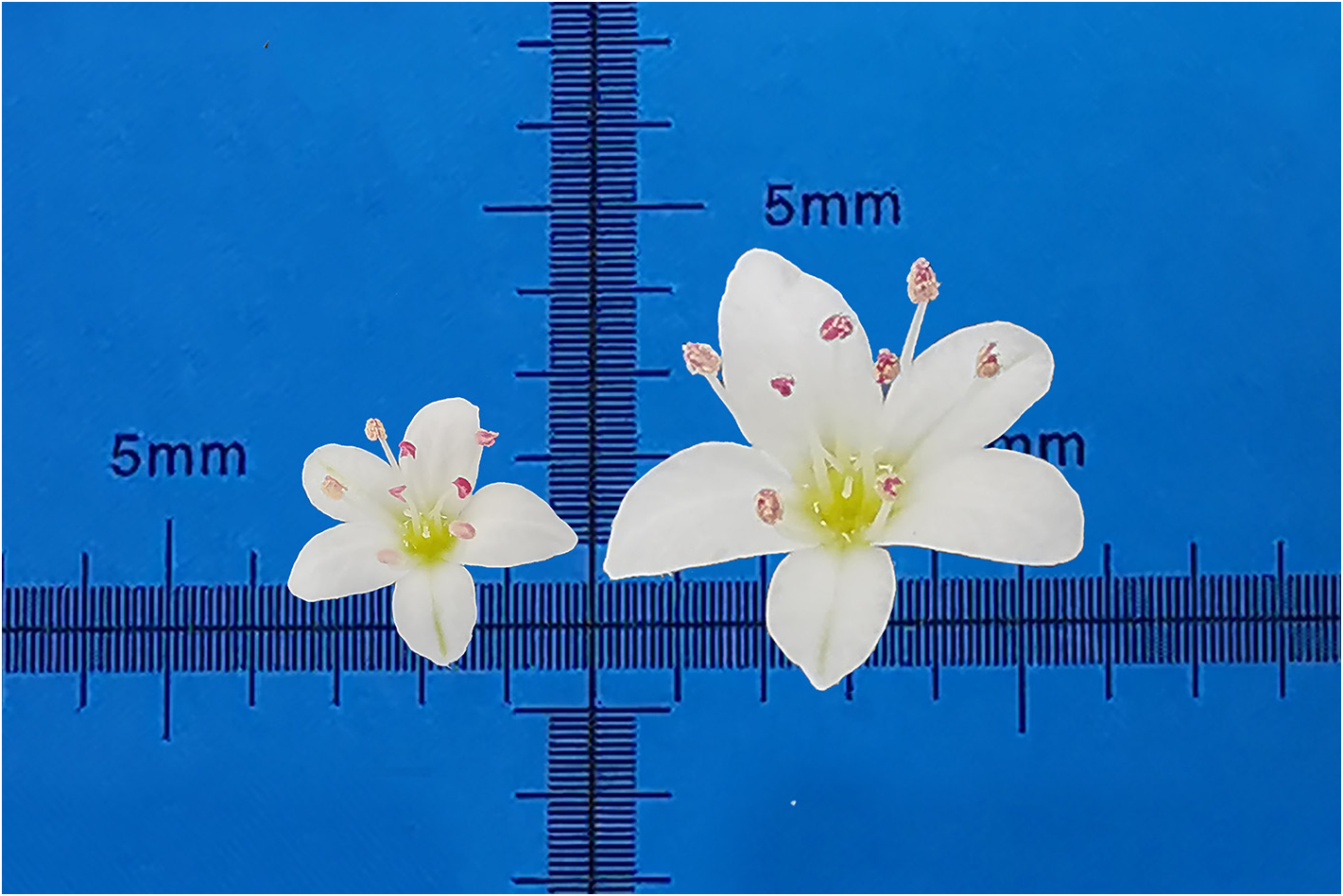
Diagnosis: — The new variety differs from the var. caudatum in flower diameter, lenght and width of the tepals, length of stamen, pistils, ovary, and style. Due to the increase in flower size, the inflorescence length was slightly longer than the original variety ( Table 1 View TABLE 1 , Fig.3 View FIGURE 3 ).
Description:— Annual herb, 59–87 cm high, with many branches at the base or middle and lower parts, and leaves from the base to the top. Stems creeping or oblique, cylindrical, with multiple longitudinal fine ribs, green; The nodes are sparse, and the internode length is 2.5–8.0 cm. Single leaves alternate, leaves papery, ear shaped arrow shaped, long arrow shaped or lanceolate heart–shaped, 1.3–6.4 cm long, 0.5–2.6 cm wide, the top is long acuminate or tail pointed, the base is wide arrow shaped, ear shaped lobes are on both sides, lanceolate, and the top is relatively sharp, green or dark green, sparsely short hairy above, glabrous or micro hairy below; Basal leaf veins 5–7, lateral veins 5–8 pairs, margin entire; Petiole 0.4–3.2 mm long, green, finely grooved above, sparsely pubescent, subglabrous below, glabrous; Ocrea membranous, obliquely tubular, 4–7 mm long, 5–7 green veins, lower end sparsely covered with white long hairs. Inflorescences racemose, axillary and terminal, 4.5–14.0 cm long, composed of several racemes and then forms panicle; Inflorescence axis terete, green, glabrous; Cymose clusters arranged more widely on the inflorescence axis. Bract oblique funnel–shaped, 2.0–3.0 mm long, tip acute, with 2–3 green veins, middle vein is thicker; 2–3 florets in each bract; Pedicel linear, 3.0– 3.5 mm long, white or light green, glabrous, with obvious joints at the top; Perianth segments 5, elliptic, ovoid, ovoid elliptic, outer 2 smaller, inner 3 larger; Length 2.8–3.4 mm, width 1.5–1.8 mm; The flower is dimorphic, one is long stamen short style flower, the other is short stamen long style flower; Stamens 8, arranged in 2 rounds, outer round 5, inner round 3, anthers reddish brown or brown, elliptic, filaments linear, white; Ovary ovoid triangular, style 3, white, glabrous. Achenes are wrapped in or slightly beyond the persistent perianth segments, dark brown or black, oval or wide oval triangular, 4.0– 4.9 mm long, 2.5–2.7 mm in diameter, slightly wrinkled on the surface, slightly shiny; Style bent downward close to fruit, persistent.
Etymology:— The epither “ grandiflora ” refers to the size of the flowers in comparison with the var. caudatum .
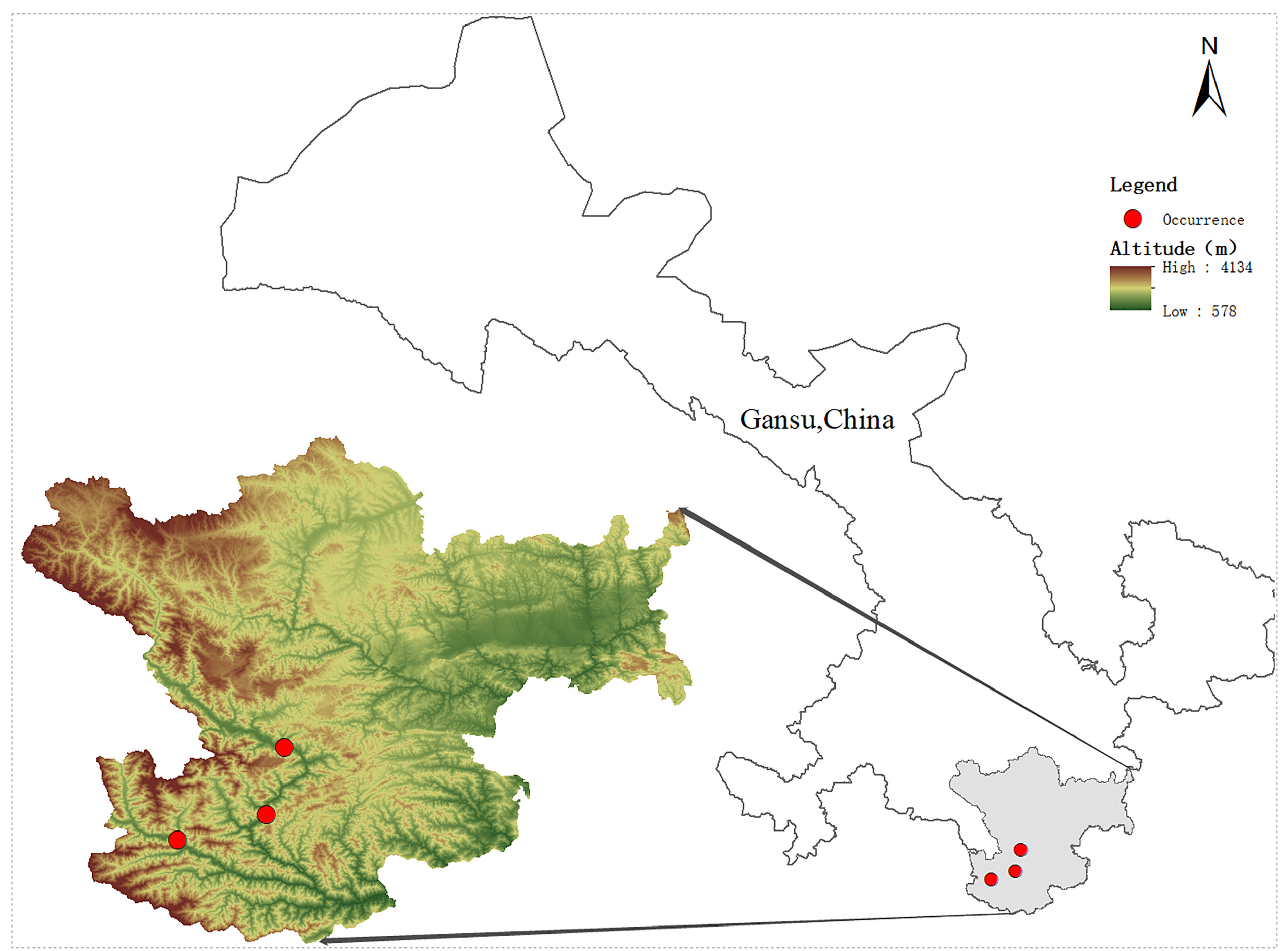
Habitat and distribution:— The plant grows in the hills and valleys of rocks and weeds at elevation 1000–1200 m ( Fig 1A View FIGURE 1 ) and occurs in Wudu Distract and Wenxian County in Longnan City GoogleMaps , Gansu Province (104° 36’ 55” E, 32° 59’ 44” N, 105 ° 1’ 25 “ E, 33° 20’ 45” N; 1000–1200 m a.s.l) ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ).
Phenology:— Flowering time June–October; fruiting time July–November.
Notes:— Though buckwheat usually has been considered a minor crop, the global market is continuously expanding due to its unique value as the healthy food sources ( Graziano et al. 2022). Thus, scientists are constantly seeking new materials for breeding improvement. The large-flower is important in agronomic terms, that needs to be improved in buckwheat breeding, because the too-small flower (~ 2mm) of Fagopyrum tataricum ( Linnaeus 1753: 364) Gaertner (1790: 182) seriously limits the attempt of crossbreeding ( Zhang et al. 2017), our new found variety with large flower trait may give a new insight into this issue.
The growth and morphology of plants are affected by various environmental factors ( Li et al. 2020). Wild buckwheat populations are mainly distributed in southwest China, especially Yunnan and Sichuan provinces ( Zhou et al. 2018). Gansu Province is located in the northwest of China, and the environment is generally different from the above two provinces. Our transplanting experiments processed in Sichuan (south of Gansu) and Beijing (north of Gansu) both confirmed the genetic stability of the large flower of the new variety, implying that the latitude may not the only factor affecting the flower size. Previous study revealed that the Ophrys fuciflora complex presented clinal variation of flower form (size and shape) under local climate and latitudinal factor (Pauši et al. 2019), the variation of flower size in Fagopyrum caudatum may be due to the comprehensive ecological environment factors of the Longnan region , but the background mechanism still needs further investigation.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |