Tridentata loculosa ( Busk, 1852 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5085.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:12FC3342-F2A0-4EE1-9853-9C5855076A10 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5802984 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039687B7-0D04-E041-7DA0-252E6609F8D7 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Tridentata loculosa ( Busk, 1852 ) |
| status |
|
Tridentata loculosa ( Busk, 1852) View in CoL
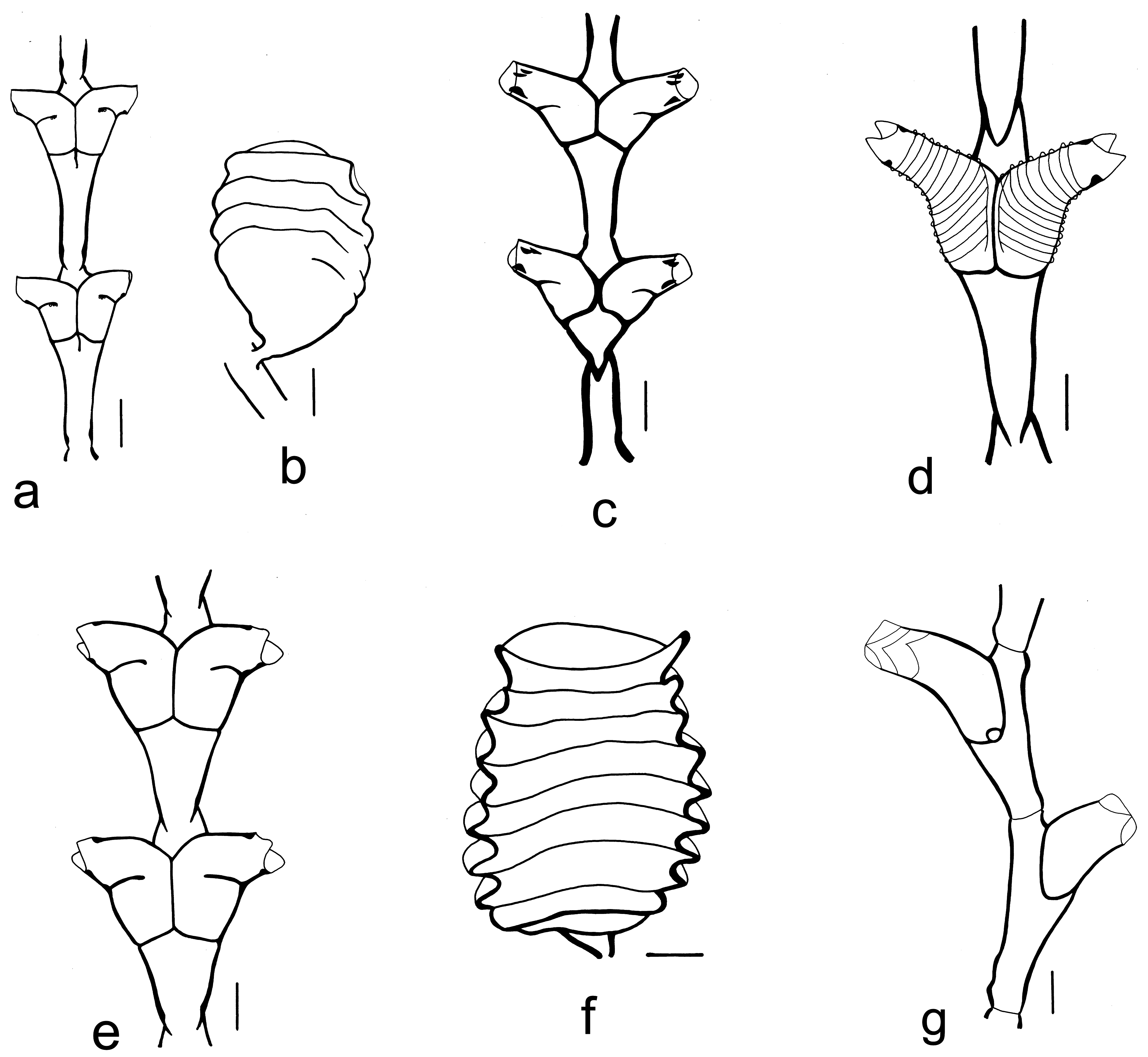
Fig. 10a, b View FIGURE 10
Sertularia loculosa Busk, 1852: 393 View in CoL .
Sertularia ligulata View in CoL .— Cooke, 1977: 97, fig. 24.— Coles et al., 2002a: 318.
Tridentata ligulata View in CoL .— Coles et al., 2002b: 177.
Tridentata loculosa View in CoL .— Carlton & Eldredge, 2009: 39.— Calder, 2020: 221, fig. 6f.
Type locality. Australia: Bass Strait , 45 fm ( 82 m) ( Busk 1852, as Sertularia loculosa ) .
Voucher material. Midway Atoll, 23.ix.2002, five colony fragments, to 1.3 cm high, with gonothecae, coll. A. Faucci, ROMIZ B5434 .—Gardner Pinnacles, on calcareous rubble, 14.ix.2002, one colony, 4 mm high, without gonothecae, coll. A. Faucci, ROMIZ B5435 .
Remarks. DNA sequences are as yet unavailable for Tridentata loculosa ( Busk, 1852) , and its genetic affinities remain uncertain. Following previous work ( Calder 2013, 2020), it has been assigned temporarily here to Tridentata Stechow, 1920 given the general resemblance of its trophosome and gonosome to species of that genus (including its type species, Sertularia perpusilla Stechow, 1919b ). Its indistinct marginal cusps, markedly dissimilar upper and lower opercular valves, and presence of a ligula (an intrathecal modification of the mantle, resembling a nematophore), set it apart from them. In particular, the taxonomic significance of the ligula is uncertain. Given its unusual characters, Hirohito (1974) suggested that a new genus might be warranted for the species, but later ( Hirohito 1995) retained it in Sertularia Linnaeus, 1758 following Vervoort & Vasseur (1977). With respect to its generic name, this species bears little morphological resemblance to Sertularia argentea Linnaeus, 1758 , type species of Sertularia . Thus, it can certainly be excluded from that genus ( Calder 2013, 2020), where it has usually been assigned.
Taxonomic reviews of T. loculosa were provided by Migotto (1996, as Sertularia loculosa ) and Calder (2013). Of note, Sertularia ligulata Thornely, 1904 was shown by Billard (1927) to be conspecific with S. loculosa . Although widely distributed and possibly circumglobal in tropical and subtropical waters, this species has not been recorded to date in the eastern Pacific Ocean. Colonies examined here from Midway Atoll (ROMIZ B5434), collected during September 2002, bore gonothecae.
Reported Distribution. Hawaiian archipelago. Oahu: Kaneohe Bay, 2 m, on Porites lobata ( Cooke 1977, as Sertularia ligulata ); Kaneohe Bay, Waiahole Reef ( Coles et al. 2002a, as S. ligulata ; Calder 2020); Waikiki, Aquarium Outside Reef, 3 m ( Coles et al. 2002b, as Tridentata ligulata ); Waikiki, Atlantis wreck, 20–30 m ( Coles et al. 2002b, as T. ligulata ).
Elsewhere. Warm waters of the Indian Ocean ( Millard 1975, as S. ligulata ), western and central Pacific ( Hirohito 1995, as S. ligulata ; Schuchert 2003, as S. ligulata ; Calder 2020), and western and eastern Atlantic ( Vervoort 1959, as S. ligulata ; Calder 2013).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
SubClass |
Hydroidolina |
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Tridentata loculosa ( Busk, 1852 )
| Calder, Dale R. & Faucci, Anuschka 2021 |
Tridentata loculosa
| Calder, D. R. 2020: 221 |
| Carlton, J. T. & Eldredge, L. G. 2009: 39 |
Tridentata ligulata
| Coles, S. L. & DeFelice, R. C. & Eldredge, L. G. 2002: 177 |
Sertularia ligulata
| Coles, S. L. & DeFelice, R. C. & Eldredge, L. G. 2002: 318 |
| Cooke, W. J. 1977: 97 |
Sertularia loculosa
| Busk, G. 1852: 393 |