Nisitrus crucius Robillard & Tan, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5852/ejt.2021.761.1449 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:519E2F56-40E1-4431-BC90-8484E308D16E |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5169999 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/3140F3A4-21FB-4BB4-ACC6-57BD749A6C3B |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:3140F3A4-21FB-4BB4-ACC6-57BD749A6C3B |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Nisitrus crucius Robillard & Tan |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Nisitrus crucius Robillard & Tan sp. nov.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:3140F3A4-21FB-4BB4-ACC6-57BD749A6C3B
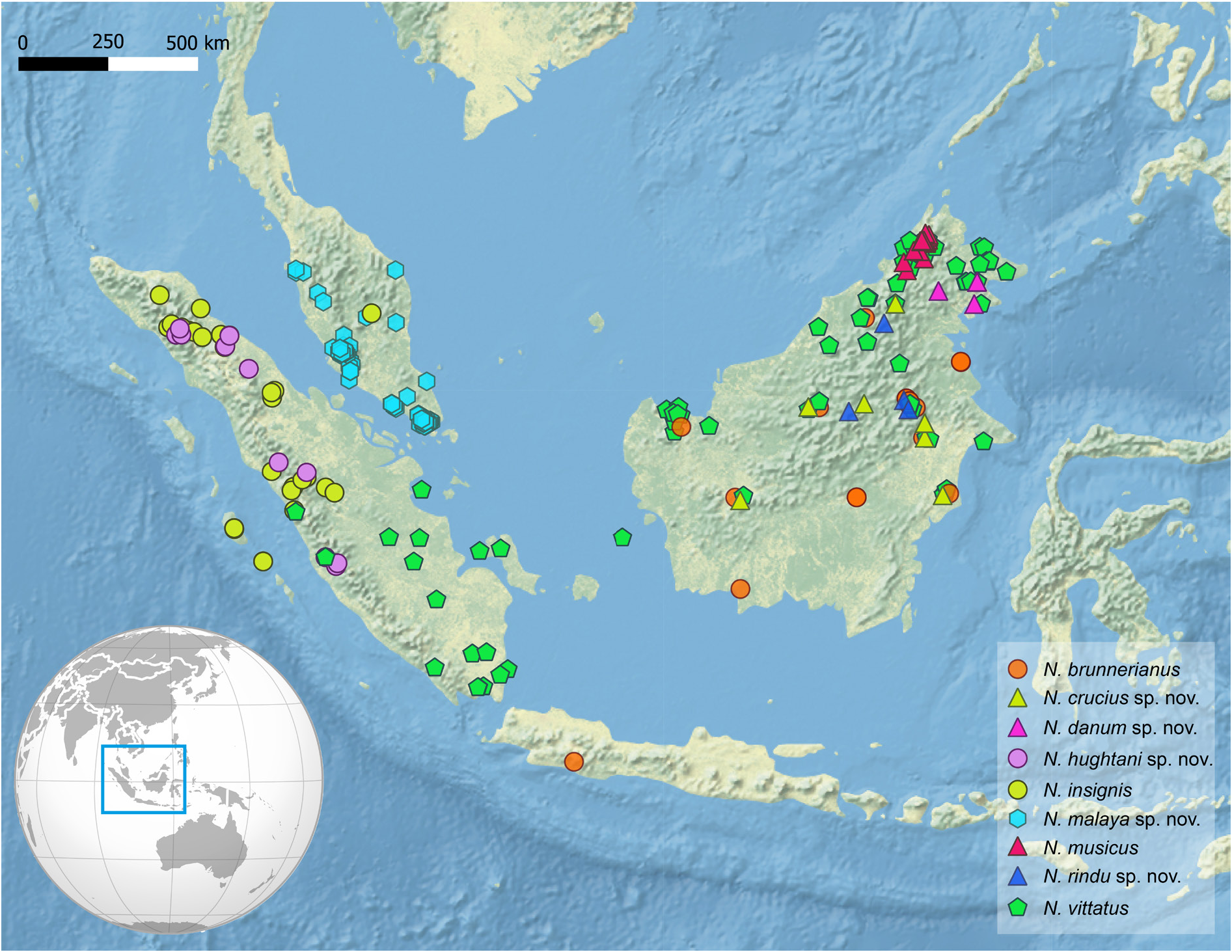
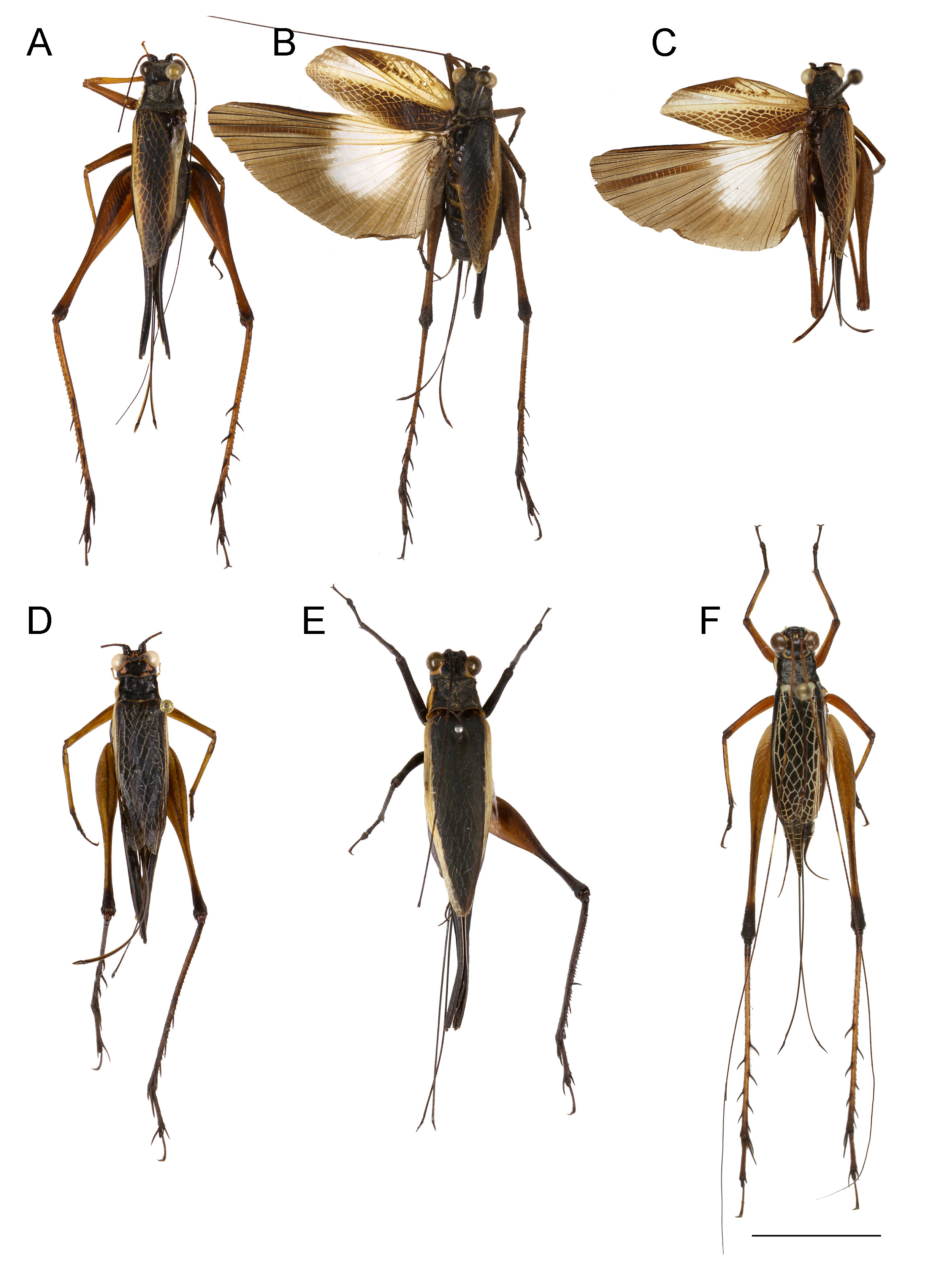
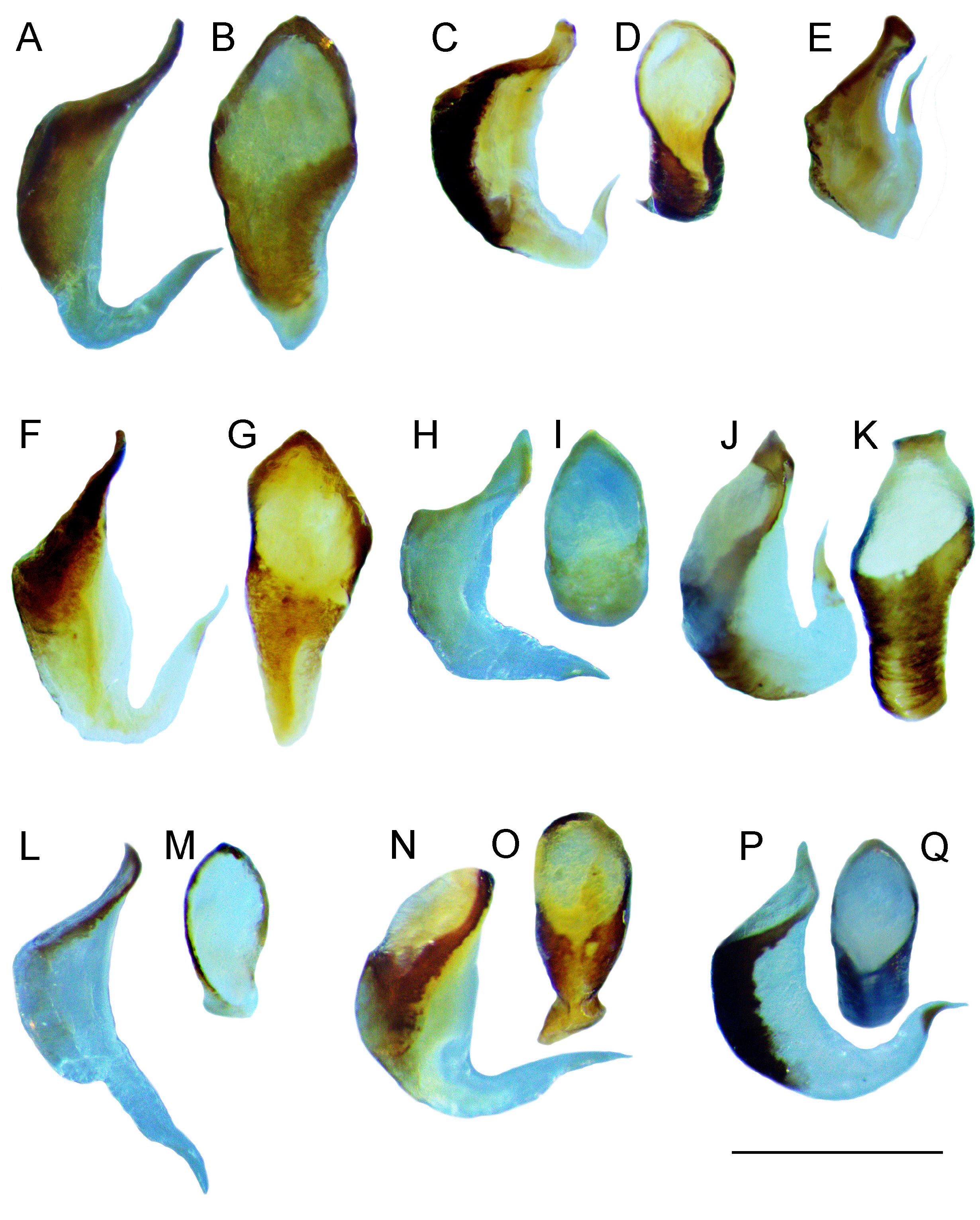
Figs 5 View Fig , 7B View Fig , 8C View Fig , 10B View Fig , 11B View Fig , 12B View Fig , 13B View Fig , 14B View Fig , 16B View Fig , 17C–D View Fig ; Tables 2, 4
Diagnosis
This species differs from all known congeners by the following combination of characters: frons yellow, with a cross-shaped black pattern above mouthparts; face part of fastigium between eyes black. Male FWs with a basal area generally paler; female ovipositor only about as long as FIII. Nisitrus crucius sp. nov. is similar to N. brunnerianus , from which it differs by smaller size and shorter ovipositor. It is also similar in size to N. vittatus and N. malaya sp. nov. but differs by female FW with cells on dorsal field mostly infumated black, gradually becoming yellow near CuA, M and R veins.
Etymology
The species name refers to the dark cross marking on the frons (ʻ crucis ʼ = ʻcrossʼ, in Latin).
Material examined
Holotype INDONESIA – Kalimantan • ♂; “ Biv. Long Hoet ”; 1°21′7.2″ N, 116°31′4.1″ E; 16–20 Aug. 1925; H.C. Siebers leg.; MNHN-EO-ENSIF11261 . GoogleMaps
Paratypes INDONESIA – Kalimantan • 1 ♀; “ Long Navang ” [Long Nawang]; Mjöberg leg.; MNHN-EO- ENSIF11262 • 1 ♀; “ Midden O. Borneo, Marah ”; 0°58′31″ N, 116°33′14.8″ E; 10–28 Nov. 1925; H.C. Siebers leg.; MNHN-EO-ENSIF11263 GoogleMaps • 1 ♀; “ Biv. Long Hoet ”; 1°21′7.2″ N, 116°31′4.1″ E; 16– 20 Aug. 1925; H.C. Siebers leg.; MNHN-EO-ENSIF11264 GoogleMaps • 1 ♀; “ Melawi W Borneo ”; 0°34′28″ S, 111°45′5″ E; Nov.–Dec. 1924; Blanchemanche leg.; MNHN-EO-ENSIF1732 GoogleMaps • 1 ♂; same collection data as for preceding; MNHN-EO-ENSIF11265 GoogleMaps • 1 ♀; “ Samarinda ”; 0°29′47″ S, 117°8′23″ E; M.-E. Walsh leg.; ZMLU GoogleMaps .
MALAYSIA – Sarawak • 1 ♂; “ Kapit ”; 1°46′0″ N, 113°32′12″ E; 9 Jul. 1970; Baebe leg.; Ind. Mus.; PII: N56; MNHN-EO-ENSIF1750 GoogleMaps . – Sabah • 1 ♂; “nr. Long Pa Sia ( West )”; 4°24′21″ N, 115°43′47″ E; “c. 1200m ”; 2–13 Apr. 1987; C. v. Achterberg leg.; RMNH GoogleMaps .
NO COUNTRY • 1 ♀; “ Borneo ”; 1891; Chaper leg.; MNHN-EO-ENSIF11266 .
Description
Average size ( Fig. 7B View Fig ). Colour pattern somewhat intermediate between N. brunnerianus and N. vittatus . Vertex black with cream-coloured margin around eyes ( Fig. 11B View Fig ). Fastigium velvety black with creamcoloured margins. Scapes black dorsally, sometimes reddish ventrally or along dorso-inner margins. Antennae black. Frons yellow, face part of fastigium black between eyes, with a cross-shaped black pattern above mouthparts; clypeus sometimes darkened, mouthparts dark red brown to black ( Fig. 10B View Fig ). Maxillary palpi cream-coloured. Head lateral side generally black. Pronotal disk black with white setae ( Fig. 11B View Fig ). Lateral lobes of pronotum with dorsal third black, cream-coloured ventrally ( Fig. 12B View Fig ). Legs red brown, sometimes internal-basal area black. FIIIs dark red brown, knees dark brown to black; TIIIs brown with black spines and spurs, dark brown to black near distal end; tarsomeres dark brown to black. Hindwings dark hyaline, with a rounded transparent window near internal-basal area; longer than FWs, the dark brown tail exceeding the FWs about twice as long as pronotum. Tergites black, with a pale band laterally of variable thickness; sternites pale, with a black median area.
Male
FOREWINGS. FW colouration ( Fig. 13B View Fig ): dorsal field cells mostly transparent; veins mostly creamcoloured, sometimes black. Basal area brown, basally cream-coloured, brown towards distal part. R and Sc projections cream-coloured. Lateral field hyaline, with dorsal parts infumated cream-coloured. FW venation ( Fig. 13B View Fig ): 1A somewhat straight. Harp slightly longer than wide, with 2 oblique veins, distal one bifurcate basally. Cell c1 long and wide, c2 diamond-shaped; mirror (d1) longer than wide, not rounded, generally separated into two parts by a distinct straight transverse vein, the posterior part somewhat rectangular, much shorter than anterior part. Cell d2 narrower than d1, usually subdivided by accessory veins. Apical field short and rounded, with 3 wide cell alignments posterior to mirror and a narrow apical alignment; veins cream-coloured. Lateral field with 5 projections of Sc. Epiproct black. Subgenital plate pale cream-coloured with median area and anterior and posterior margins black.
GENITALIA ( Fig. 16B View Fig ). Pseudepiphallus sclerotized, stout (small but broad) compared to congeners, anterior margin somewhat broad and straight, posterior margin also straight, lateral margins faintly converging posteriorly. Posterior apex with paired lophi slightly longer than wide (at base), obtuse at apex, sclerotized laterally only and covered with short strong setae; narrowly spaced apart from one another. Rami swollen preapically, anterior apex somewhat truncated. Pseudepiphallic parameres narrow, divergent posteriorly, their basis membranous, with a sclerotized lobe on anterior apex. Ectophallic arc transverse, complete, with anterior and posterior margins straight. Ectophallic fold strong rounded lateral sclerites appearing bean-shaped. Ectophallic apodemes long, straight and slightly divergent basally. Endophallic sclerite large and sclerotized, its posterior apex with divergent lateral arms and with a short median expansion curved dorsally. Endophallic apodeme with lateral lamellae stout.
Female
FOREWINGS. FW with cells on dorsal field mostly infumated black, gradually becoming yellow near CuA, M and R veins; veins generally yellow ( Fig. 14B View Fig ). Sc projections cream-coloured. Lateral field transparent, sometimes infumated black apically.
GENITALIA. Ovipositor: only slightly longer than FIII. Copulatory papilla conical, smaller and stout; apex folded ventrally, short, pointed; dorsal face with a sclerotized area; ventro-anterior end forming an oval to pyriform rim ( Fig. 17C–D View Fig ).
Juvenile
Unknown.
Measurements
See Table 4.
Ecology
Unknown.
Distribution
Borneo (Kalimantan, Sabah, Sarawak).
Type locality
Indonesia, Kalimantan.
Calling song
Unknown.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |