Polystichum jinpingense Z.L.Liang, Liang Zhang & Li Bing Zhang, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/phytotaxa.539.1.8 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6345974 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03943E02-FA72-FFA5-FF23-FF7FB376089D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Polystichum jinpingense Z.L.Liang, Liang Zhang & Li Bing Zhang |
| status |
sp. nov. |
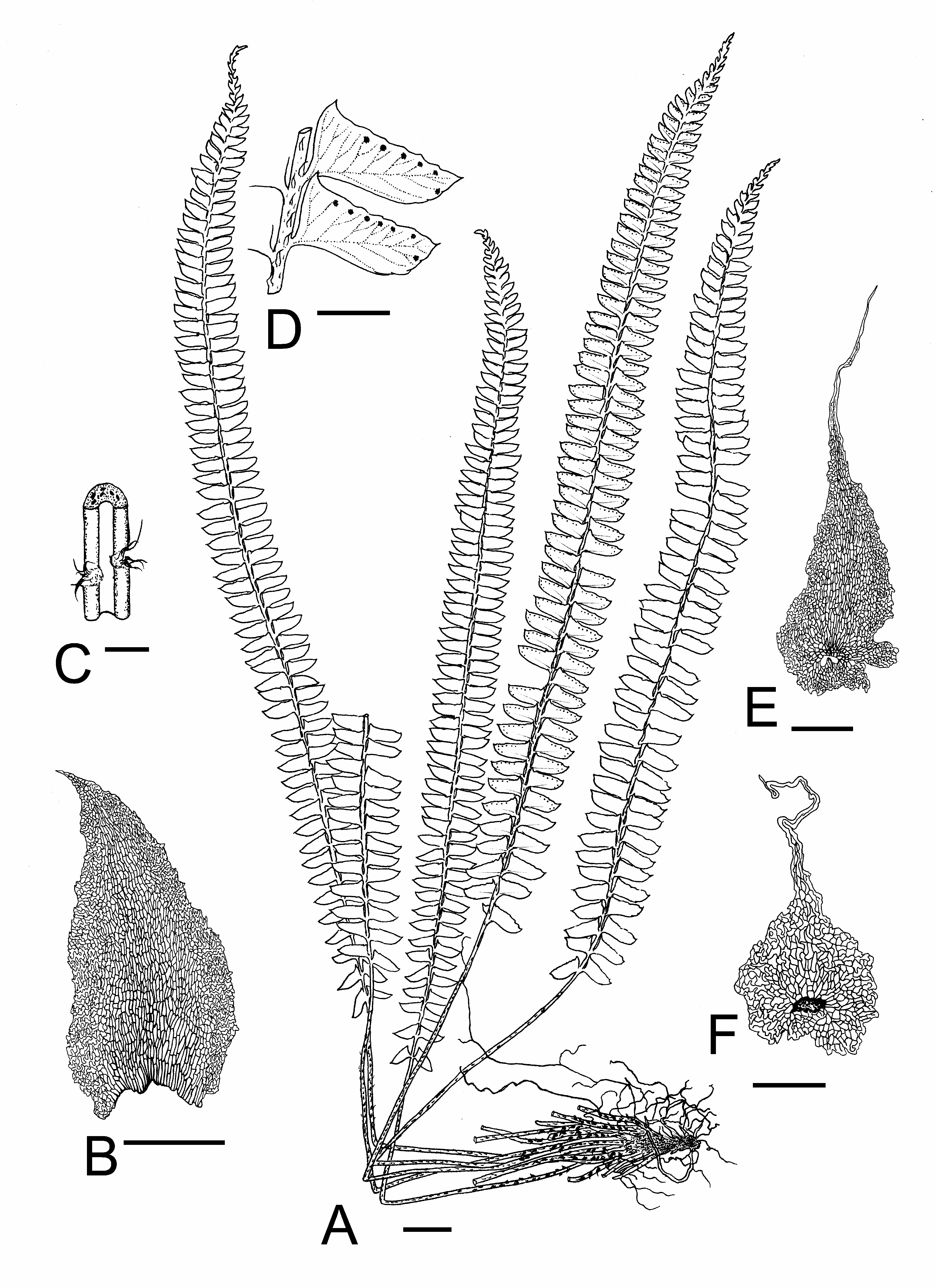
Polystichum jinpingense Z.L.Liang, Liang Zhang & Li Bing Zhang View in CoL , sp. nov. ( Figures 1 View FIGURE 1 , 2 View FIGURE 2 ).
Type:— CHINA. Yunnan Province: Jinping County, Tongchangxiang Town , Maobeiwan Village , elev. 1800–2000 m, 22°45’53.45”N, 103°01’22.20”E, on limestone rocks in disturbed secondary forest, 9 September 2019, Z.- L. Liang , Y.- M. Shui , W.- H. Chen & Z.- Y. Yu LZL605 (holotype KUN1497023 About KUN !, isotype CDBI!) GoogleMaps .
Diagnosis:— Polystichum jinpingense is most similar to P. subacutidens Ching ex L.L. Xiang (1994: 261) by having similar plant size and numerous pairs of pinnae, but the former has more or less straight pinnae forming a right angle with rachis (vs. mostly reflexed in the latter), pinna margins undulate (vs. serrate in the latter), pinna apex round (vs. acute in the latter), and sori that are closer to pinna margins (vs. sori that are in the middle between pinna margins and midribs in the latter).
Plants perennial, evergreen, (38–) 45–48.5 cm tall. Rhizomes erect, ca. 2 cm long, ca. 1.5 cm in diam., with remnant bases of old petioles; roots dull brown when dried, up to 10 cm long, ca. 0.5 mm in diam. Leaves in tufts; petioles 9.5– 16.5 cm long, ca. 1.5 mm in diam., stramineous basal portions covered with scales; proximal petiole scales ovate to ovate-lanceolate, 1–2 × 0.5–1 mm, papery, dull brown or brown, margins subentire, apex acuminate, cells rectangular in the middle, twisted in the margins; distal petiole scales ovate-lanceolate, 0.8–1.2 × 0.4–0.8 mm, membranous, margins subentire, apex long-acuminate or caudate. Laminae lanceolate, 1-pinnate, (25.5–) 28–32 cm long, 1.8–2.8 cm wide, apex acuminate; rachises ca. 0.9 mm in diam., stramineous, adaxially sulcate; rachis scales ovate or ovatelanceolate, light brown, up to 1 mm long including tip, 0.5 mm wide at base, margins fimbriate, apex long-caudate; or scales bristle-like, ca 1 mm long, margins entire and fimbriate at base. Pinnae in 58–62 pairs, alternate, separate from each other, 2–3 mm distance, oblong, base cuneiform, apex cuspidate, papery, maximal pinnae 0.9–1.3 × 0.35–0.5 cm, basal pinnae narrowing down and basal 1 pair reflexed, largest pinnae located above middle part of lamina, proximal margins not overlapping rachis, acroscopic and basiscopic margins cartilaginous, undulate or with irregular teeth, forming a (80–)90–100° angle with rachis, apex acuminate; basal pinnae margins undulate or entire, apex obtuse; pinna petioles 0.5–1 mm long; adaxially glabrous; abaxially with microscales; microscales broad, ovate or ovatelanceolate, or lanceolate, whitish brown, 0.5–1(–1.5) mm long, 0.15–0.45 mm wide at base, margins fimbriate; costa sunken abaxially and protruding adaxially, veins obscure and invisible on adaxial side, bulging and thickened on abaxial side, lateral veins free, forked. All pinnae bear sori on fertile fronds excluding 5–8 pairs at base; sori terminal on lateral veins of fertile pinnae, 0.8–1.2 mm in diam., closer to pinna margins than to midrib (centers of sori 0.5–1 mm from pinna margins, 1.5–2 mm from midrib), 1–3 on acroscopic side and 6–8 on distal basiscopic side, centers 1–1.5 mm apart from one another. Indusia not seen.
Geographical distribution:— Polystichum jinpingense is only found in Jinping County, Yunnan Province, and may represent an endemic species to southern Yunnan.
Ecology:— Polystichum jinpingense was observed to grow on limestone rocks in the planted forest at elevations between 1800 and 2000 m.
IUCN Red List category:—Only one population of Polystichum jinpingense was found in Jinping. Based on current information and following the IUCN (The International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) guidelines ( IUCN, 2017), this new species should be classified as Critically Endangered (CR).
Etymology:—The species epithet jinpingense is based on the Chinese pinyin, jinping, the county name in southeastern Yunnan, and the Latin suffix -ense, of origin, referring to the type locality and the current known distribution of the species in Jinping County, Yunnan.
Vernacular name:— İ平Ąĸ (jin ping er jue).
Taxonomic notes:— Polystichum jinpingense was initially identified as P. subacutidens for its striking similarity of numerous pairs of pinnae to those of the latter. Polystichum subacutidens was the only species known in the genus with so many pairs of pinnae ( Xiang 1994, Zhang & Barrington 2013). Careful comparison showed that they two are quite different morphologically. In addition, P. jinpingense grows at higher elevations (1800–2000 m), whereas P. subacutidens occurs between 700–1500 m. Interestingly, both P. jinpingense and P. subacutidens were first discovered and have types collected from the same county. Now the known distribution of P. subacutidens has been expanded to southern Guizhou (Changshun, Ziyun), northwestern Guangxi (Leye, Nandan), in addition to southeastern Yunnan ( Zhang & Barrington 2013). It is even found in northern Vietnam ( Lu et al. 2014). It remains to discover where else P. jinpingense occurs.
| Z |
Universität Zürich |
| L |
Nationaal Herbarium Nederland, Leiden University branch |
| Y |
Yale University |
| M |
Botanische Staatssammlung München |
| W |
Naturhistorisches Museum Wien |
| H |
University of Helsinki |
| CDBI |
Chengdu Institute of Biology |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |