Dolichothrips Karny, 1912
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1080/00222933.2015.1113316 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:10E53C17-530E-4737-A7B9-D111956C7C22 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5206217 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039287CE-FFC8-2A37-FDC7-FA83FD45F908 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Dolichothrips Karny |
| status |
|
Dolichothrips Karny View in CoL
Type species: Dolichothrips longicollis Karny.
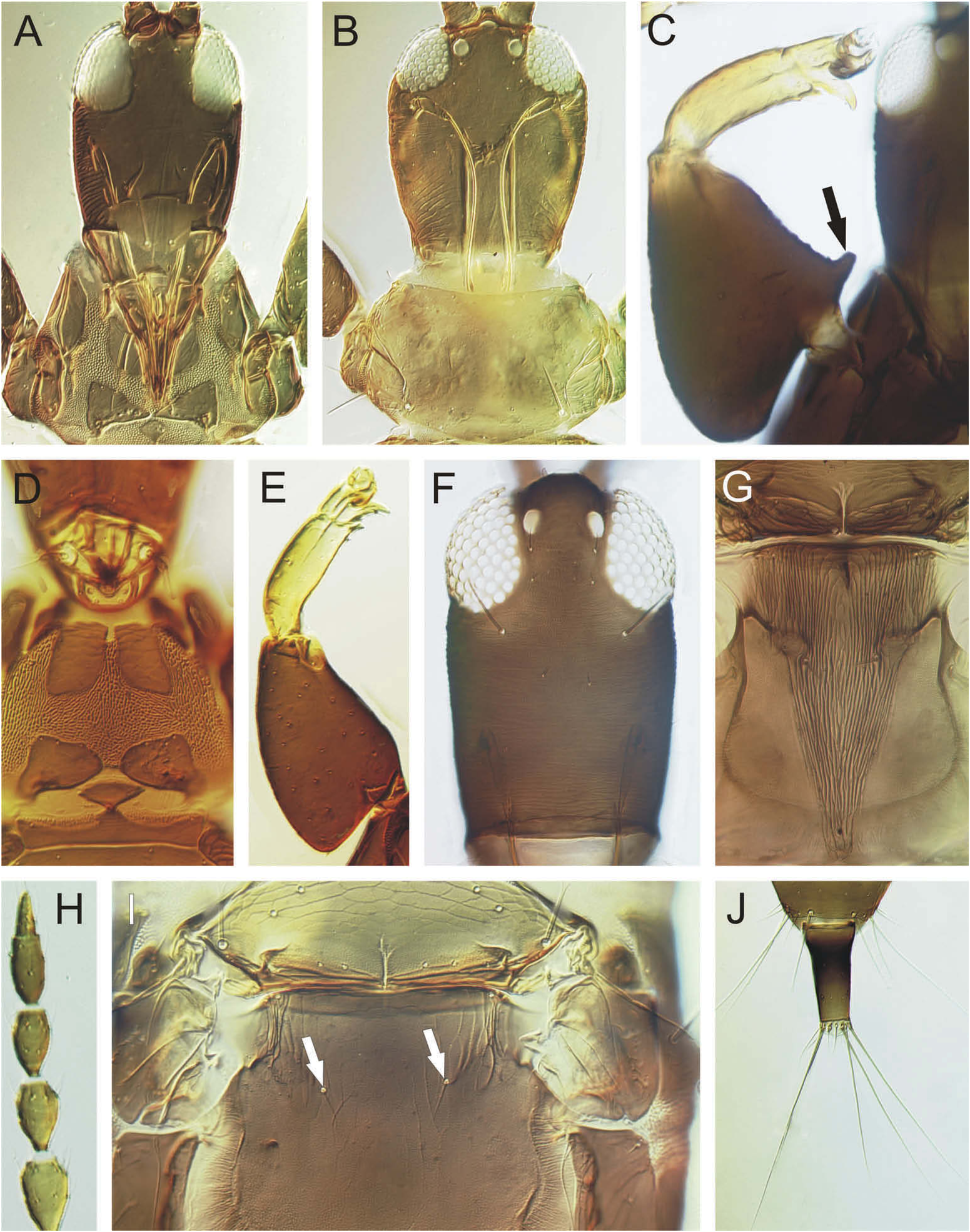
This genus comprises about 20 species, mostly from south Asia (ThripsWiki 2015) . They are all presumably phytophagous, feeding in flowers and buds ( Mound and Minaei 2007). Almost all of the species bear three sense cones on antennal segment III and four on IV, and the mouth cone is unusually long and pointed, extending between the fore coxae ( Figure 1A View Figure 1 ). The only species recorded from the Americas is the Asian D . indicus, which was collected in pepper and eggplants in Puerto Rico ( Cabrera-Asencio 1998). Lima (2011) referred this species living in Acacia flowers in north-eastern Brazil. This species has been shown to have spread to the New World tropics, including Barbados, Trinidad and Florida ( Susan Broda and Laurence Mound, unpublished records), and is often associated with plants of the family Malvaceae . Apart from the long mouth cone, D. indicus is characteristic in exhibiting basantra longer than wide, and mesopresternum forming two lateral triangles.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.