Aglaophenia cupressina Lamouroux, 1816
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4790.2.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:CDBDED59-95EE-4666-A4B6-F33AD6AA31E5 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039187E0-FF8D-FFBA-FF13-9B84FAA7FEDA |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Aglaophenia cupressina Lamouroux, 1816 |
| status |
|
Aglaophenia cupressina Lamouroux, 1816 View in CoL
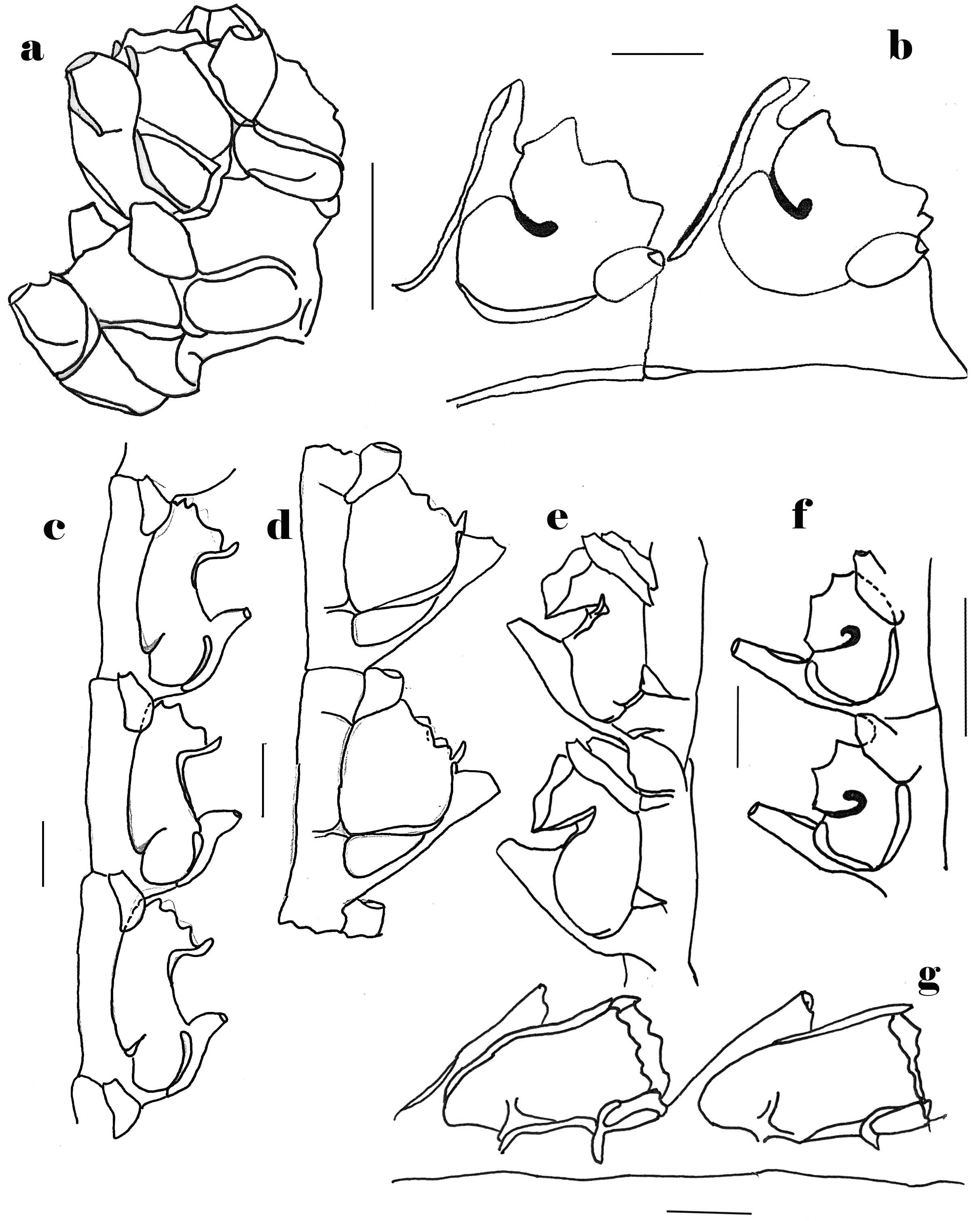
( Fig. 2a View FIGURE 2 )
Aglaophenia cupressina Lamouroux, 1816: 169 View in CoL ; Kirchenpauer 1872: 27, pl. 1: fig. 11; Billard 1913: 107, fig. 96; pl. 6; Bale
1915: 319, pl. 47: figs 6–8; Leloup 1932b: 1–3. Vervoort 1941: 233, fig. 11; Millard 1975: 408, fig. 128A–C; Schuchert
2003: 242-245, fig. 81; 2015: 351, fig. 24. Plumularia bipinnata Lamarck, 1816: 126 ; Billard 1907: 331. Aglaophenia macgillivrayi Busk, 1852: 400 ; Allman 1883: 34, pl. 10, pl. 20: figs. 4–6; Billard 1909: 331. Corbulifera macgillivrayi .— Naumov 1969: 530, figs 380– 381.
Material examined. Stn. 43: ZSI/ANRC- 21539, 6 m.
Description. Colony large, up to 11.6 cm in height, branched up to second order. Primary hydrocaulus thick, bearing equally thick secondary hydrocauli at regular intervals. Branching nearly opposite and all branches thickly polysiphonic. Hydrocladia thick, alternately arranged resembling a fir twig. Hydrocladia segmented by transverse nodes. Each node bears one hydrotheca and two internal ridges at the level of hydrotheca extending to the rear. Hydrothecae campanulate, completely adnate and very narrow ( Fig. 2a View FIGURE 2 ). Opening of hydrothecal mouth at an angle of 30.4° to the adnate hydrothecal wall. Lateral margin undulating with a prominent antero-lateral cusp. Adcauline shelf present, extending from the adcauline to the abcauline side of the hydrotheca at the lower level. Median inferior nematotheca very stout and completely adnate to the hydrotheca. Hydrothecal breadth about 2/3 rd the hydrothecal width. Median inferior nematotheca reaches the level of the hydrothecal mouth and bears an internal septum in the upper part. No gonothecae were observed.
Remarks. This species is recorded for the first time from Indian waters.Although only one specimen of the species was encountered during the study period, it was easily identified due to its characteristic hydrothecal structure ( Fig. 2a View FIGURE 2 ). Also, zooxanthellae were observed to be associated with the species. A. cupressina is known to occur in very shallow waters, 1–2 m and 10m ( Schuchert, 2003), however, it has been reported up to depths of 564 m ( Billard, 1913).
Distribution. Type locality; East Indies ( Lamouroux, 1816)
India; Andaman and Nicobar Islands (Present study).
Elsewhere; Taiwan (Tseng et al., 2014), Bunaken, Indonesia (Ricciardi, 2007) and from Zanzibar and Mozambique to Great Barrier Reef, Indonesia, New Guinea, Philippines, Japan.?Sea of Okhotsk. ( Schuchert, 2003).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Aglaophenia cupressina Lamouroux, 1816
| Chakraborty, Oishinee & Raghunathan, C. 2020 |
Aglaophenia cupressina
| Billard, A. 1913: 107 |
| Kirchenpauer, G. H. 1872: 27 |
| Lamouroux, J. V. F. 1816: 169 |