Nops
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4427.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:A13A4AB4-0E53-463B-A835-72C193728BB5 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5996374 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03901723-FFBA-FFFD-FF04-FEDCFD5D4409 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Nops |
| status |
|
Distribution of Nops View in CoL View at ENA
Nops is Neotropical, ranging from the Caribbean islands to northern Argentina . After this work, the genus comprises 34 species, of which 15 (44%) occur in the Caribbean Islands , four (12%) in Central America and 15 (44%) in South America. We greatly increased the richness of species from South America , whence have been described most of the new species found during this study. However, the highest species richness still remains concentrated in the Wider Caribbean Region , including Central America and the north of Colombia and Venezuela where 64.7% of the species occur.
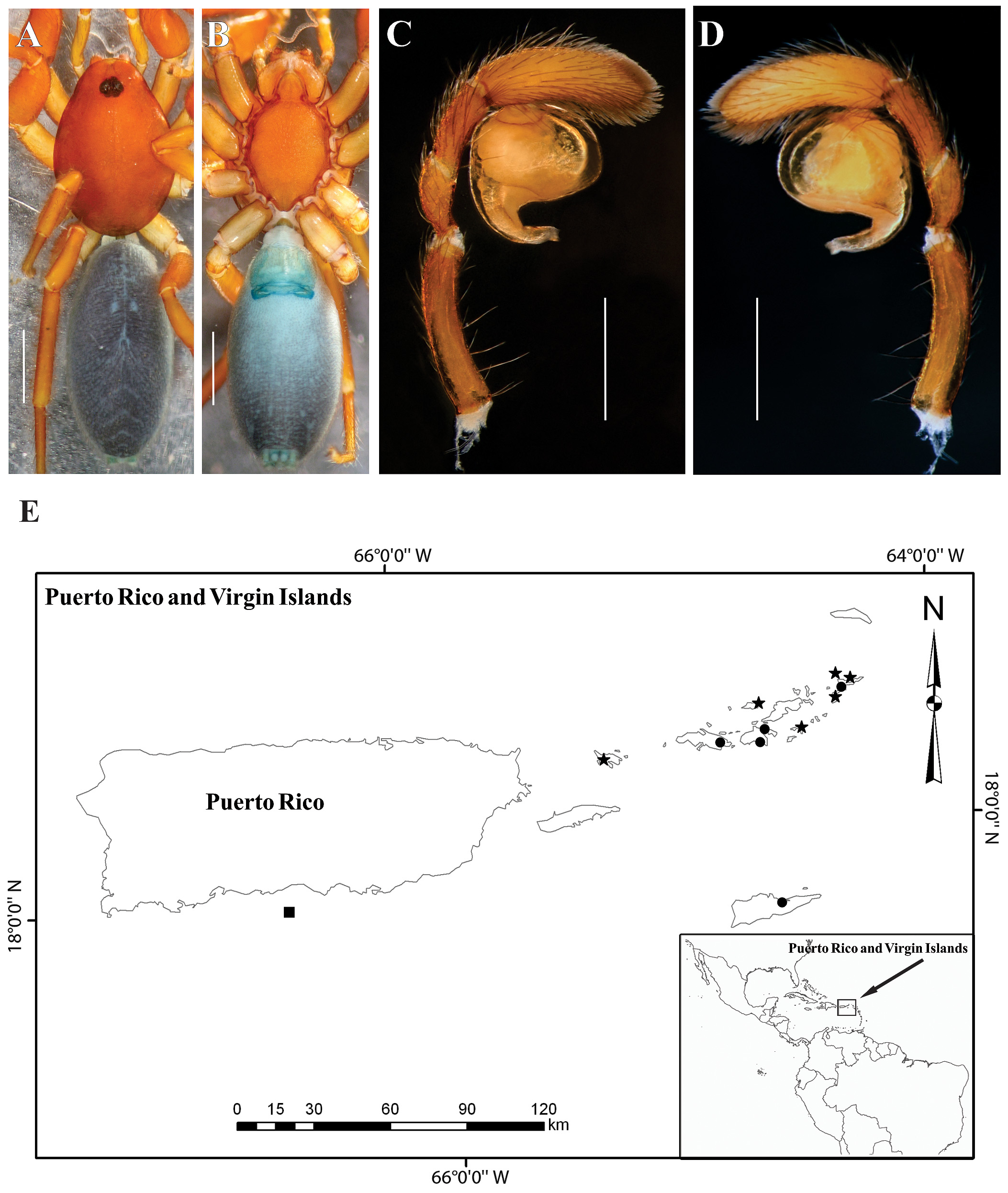
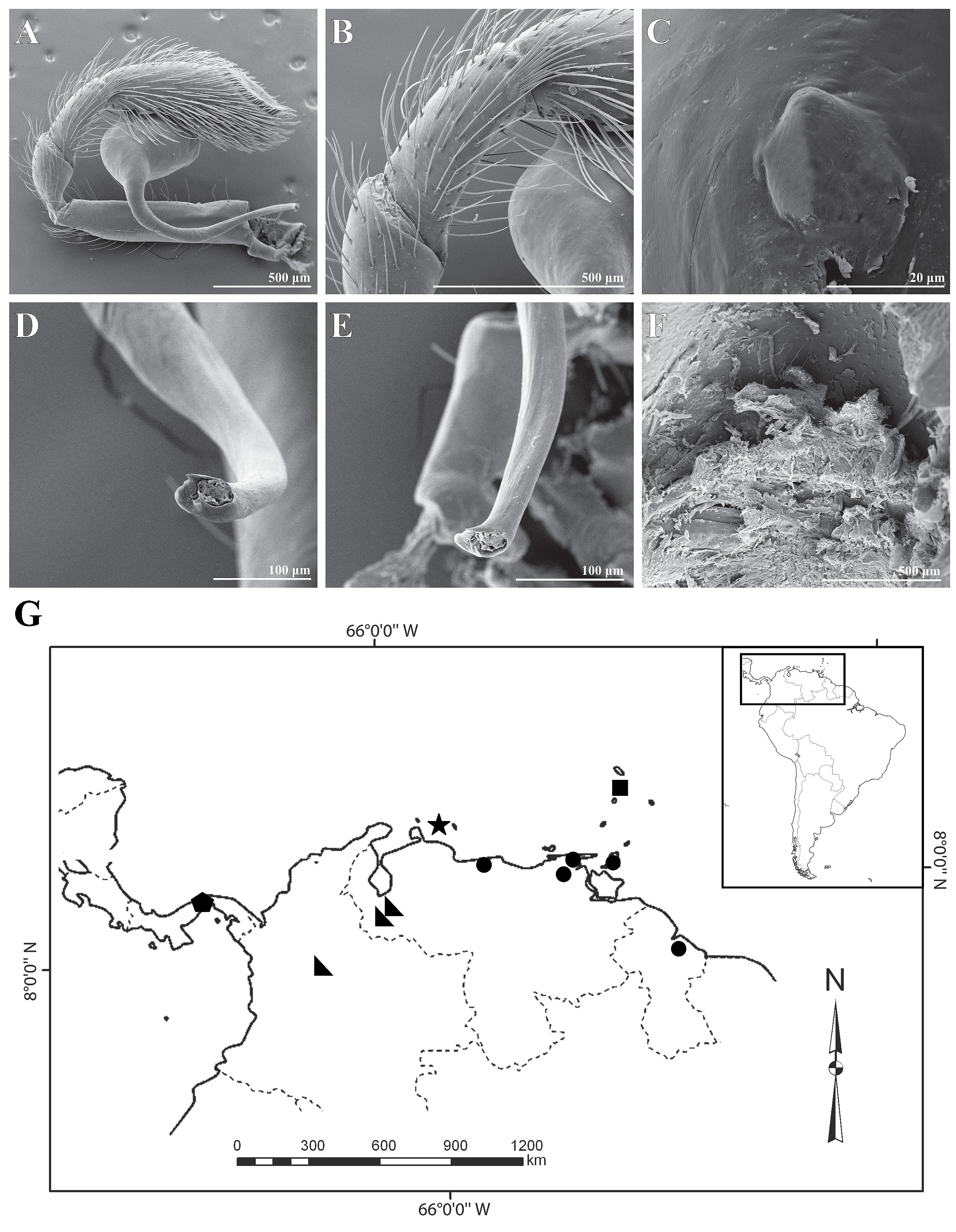
Endemism in the Caribbean islands is very high, after this study, most of the species continue being single island endemics, except N. blandus and N. finisfurvus , which occur in several small islands from the US and British Virgin Islands ( Fig. 8E View FIGURE 8 ). Cuba and Hispaniola, with four species each, are the most diverse islands, since they have the largest expanse of territory and the greater complexity of habitats throughout the insular Caribbean ( Dengo & Case, 1991). The other islands where Nops species have been recorded are only represented by a single species. To date, there are no records of Nops from the main island of Puerto Rico, nor from the Leeward Islands of the Lesser Antilles. However, heeding the known distribution of Nops in the Caribbean region, it is expected that these islands are represented each by at least one endemic species. N. maculatus from Trinidad Island is the only species with representatives also on the continent; including part of Venezuela and Guyana ( Fig. 57G View FIGURE 57 ).
Aside from Cuba and Hispaniola, Nops species are concentrated in three other areas ( Fig. 75 View FIGURE 75 ). 1) The area occupied by Panama, the north coastal regions of Colombia and Venezuela, and their adjacent islands, where seven endemic species were recorded; 2) the region of the Amazon River with three species, and 3) the Brazilian state of Bahia with 4 sympatric species. However, these apparent patterns may result from non‒homogeneous sampling. South America caponiid diversity is likely to be significantly underestimated given that there are still many unexplored and poorly sampled areas in the continent.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |