Walshina, López-Torres & Silcox & Holroyd, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.26879/756 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:5EE56527-5F98-4724-8120-18F7471BB497 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.11187391 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038D8789-9230-4866-21E0-FC5CFC94B1A2 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Walshina |
| status |
gen. nov. |
Genus WALSHINA gen. nov.
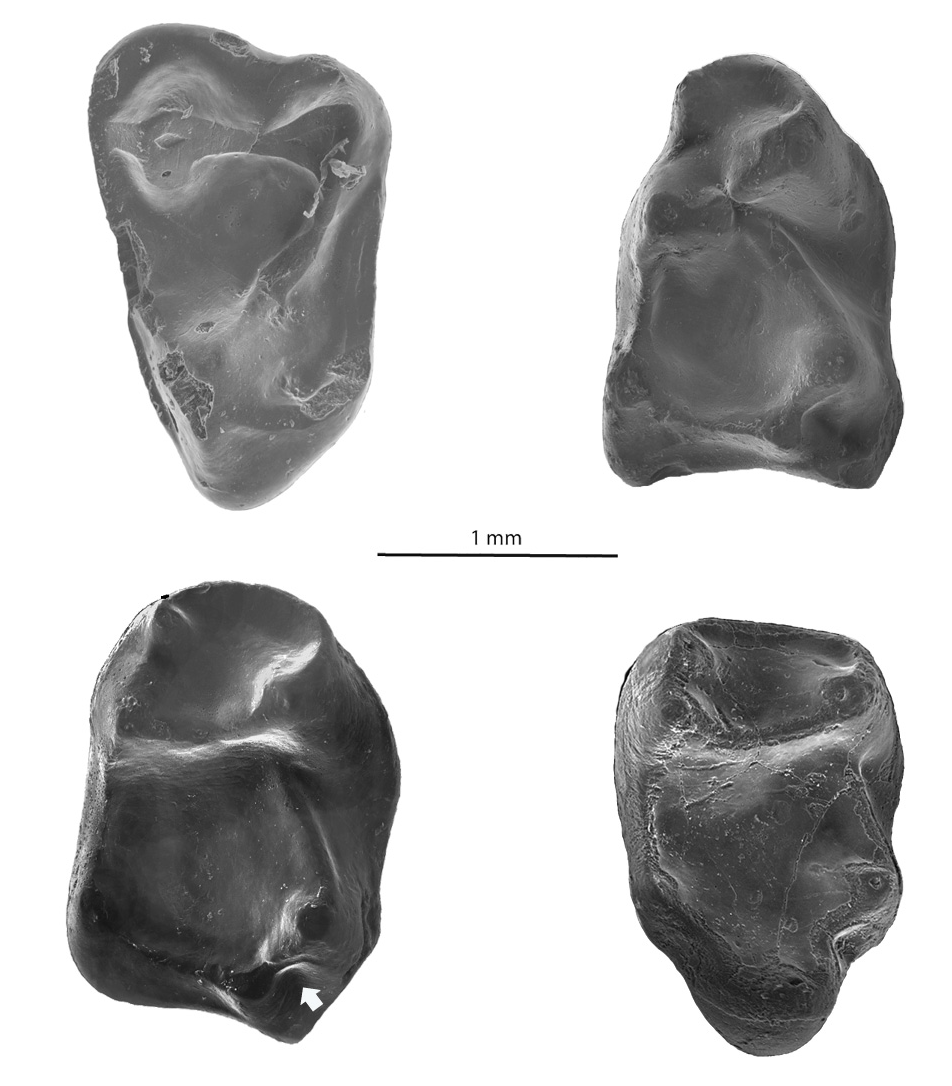
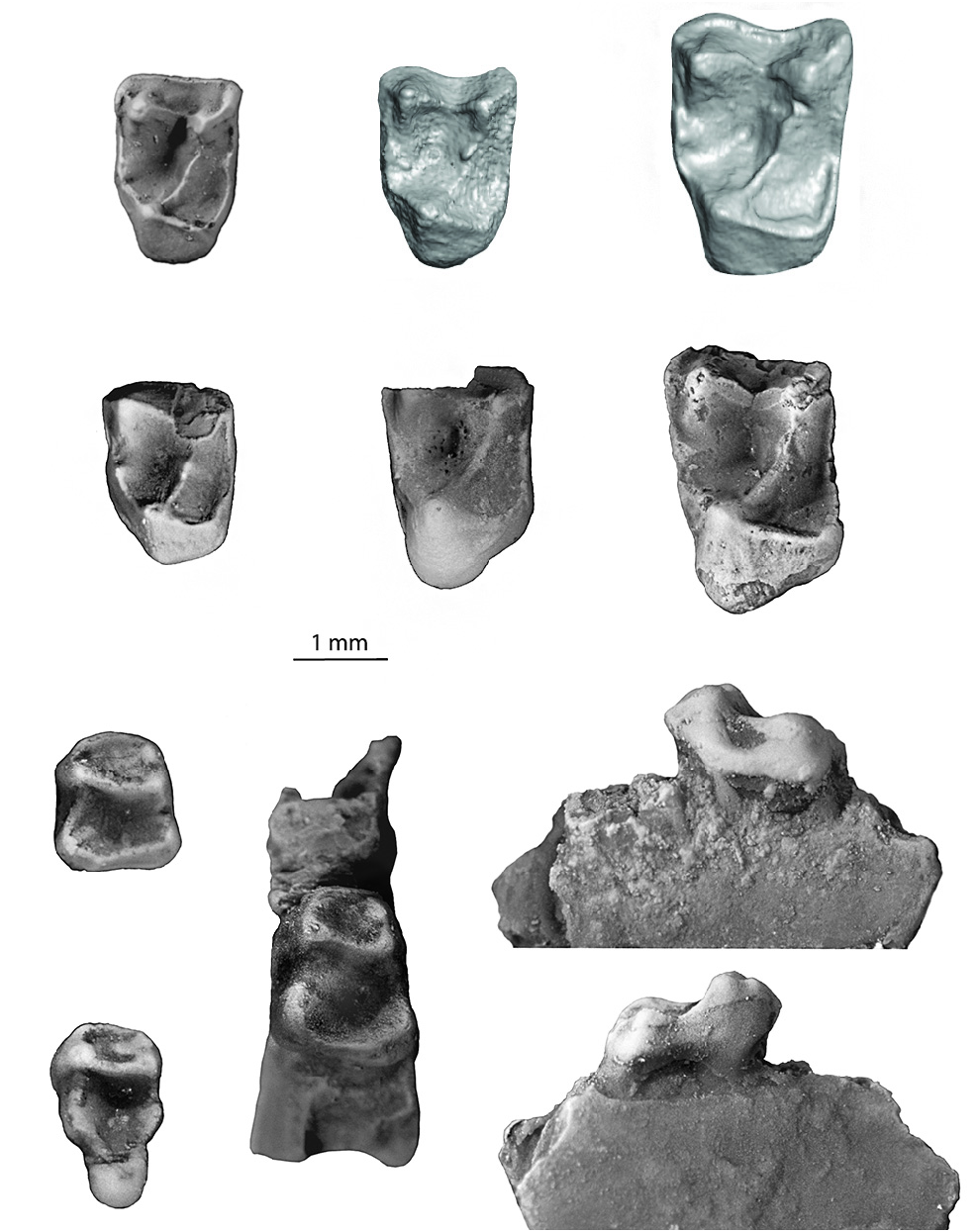
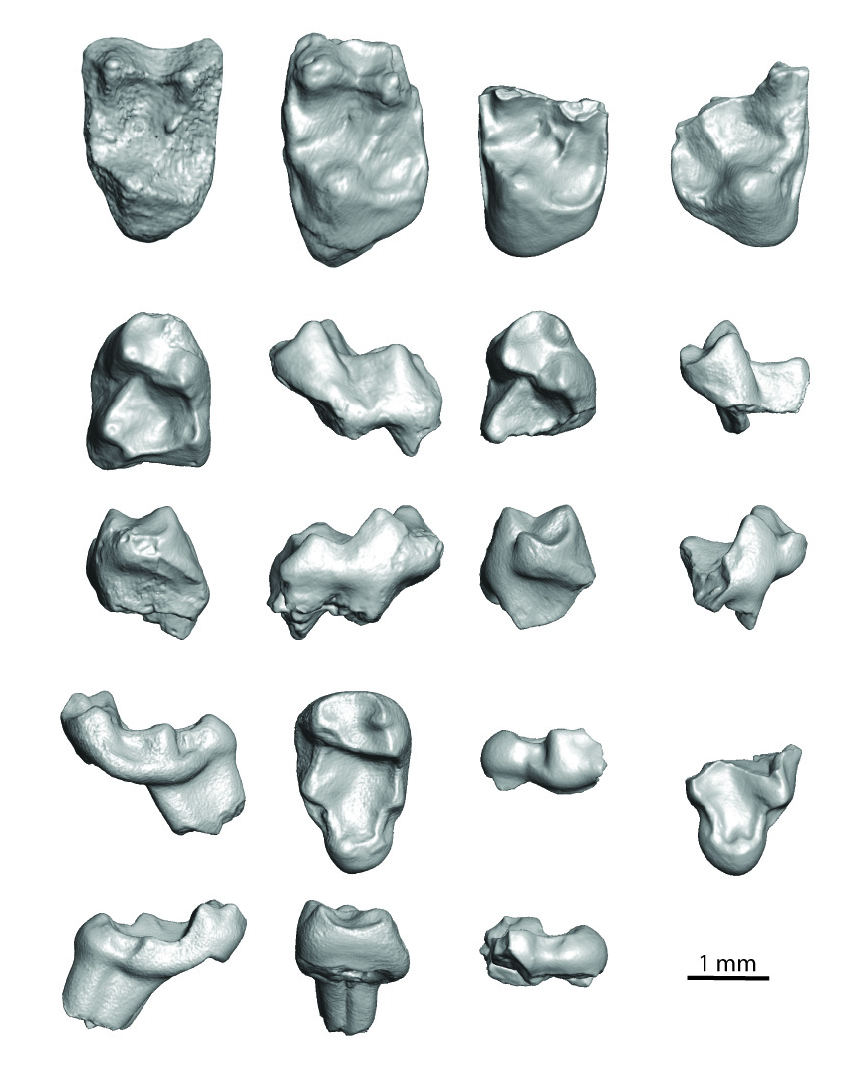
Figures 4.1-4.4 View FIGURE 4 , 5.1-5.11 View FIGURE 5 , 6.1-6.19 View FIGURE 6
zoobank.org/ 5F051939-CD72-4EBC-8BBC-3E6B637DC806
1968 Phenacolemur (Matthew, 1915) ; Robinson, p. 324
1976 Ignacius (Matthew and Granger, 1921) ; Bown and Rose, p. 112 (in part)
1978 Phenacolemur (Matthew, 1915) ; Krishtalka, p. 338, fig. 2-4
1990 Phenacolemur (Matthew, 1915) ; Mason, p. 2, fig. 2
1991a cf. Phenacolemur (Matthew, 1915) ; Walsh, p. 166, table 1
1996 Phenacolemur (Matthew, 1915) ; Walsh, p. 85, table 2
Type species. Walshina esmaraldensis gen. et sp. nov.
Included species. Type species, Walshina mcgrewi comb. nov. (= I. mcgrewi Robinson , 1968), and Walshina shifrae comb. nov. (= Ph. shifrae Krishtalka, 1978 ).
Distribution. Uintan and Duchesnean of Wyoming, and Uintan of California.
Etymology. In memory of Stephen L. Walsh of the San Diego Museum of Natural History, in recognition of his work on the San Diego County faunas.
Diagnosis. Paracristid of M 1 relatively long as in Trogolemur and Sphacorhysis , but paraconid less clearly distinct from the paracristid. Differs from Sphacorhysis (but not Trogolemur ) in having lower molar talonid basins that are relatively deep with smooth enamel. Differs from Trogolemur (but not Sphacorhysis ) in that the cristid obliqua of M 1 contacts the postvallid distal to the protoconid rather than between the protoconid and metaconid. Unlike the other trogolemurins, M 1 and M 2 of Walshina gen. nov. have strong hypoconulids with distinct foveae located below and buccal to the hypoconulid. As in Sphacorhysis , the distal aspect of M 1 and M 2 is convex, whereas in Trogolemur it is concave. M 3 hypoconulid narrower than in other trogolemurins. M 3 trigonid significantly taller than in Sphacorhysis (but not Trogolemur ). Like Sphacorhysis , lower molar entocristids form a rounded contour (i.e., forming a U-shaped entocristid) in lingual view, in contrast to the V-shaped entocristid in Trogolemur . Further differs from Trogolemur and Sphacorhysis in having much weaker buccal cingulids. Notably stronger precingulum on M 2 than in Trogolemur . Protocone lingual expansion on the upper molars not as pronounced as in Trogolemur . Compared to Trogolemur , mesial aspect of M 3 straighter, and the lingual border of that tooth much shorter mesiodistally relative to its buccal border.
Discussion. All trogolemurins share a distally expanded distolingual basin of the upper molars (particularly marked in W. mcgrewi comb. nov.), which is quite similar to that observed in paromomyid plesiadapiforms. This similarity is likely one reason why some members of Walshina gen. nov. have previously been considered paromomyids. However, in other ways the morphology of trogolemurins is inconsistent with that of paromomyids, including the presence of paraconids on M 3. Walshina gen. nov. remains quite poorly known, with the only record being isolated upper and lower molars. One likely reason for this limited record is that the genus includes the smallest North American omomyoids (see below).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.