Chrysogorgia ramificans Xu, Li, Zhan & Xu, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5321.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:A1F2E418-67A3-4D1F-ABC9-6C2BA0F5190E |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8203450 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0388878C-FFBD-9C55-099C-EF0A7663F9CC |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Chrysogorgia ramificans Xu, Li, Zhan & Xu, 2019 |
| status |
|
Chrysogorgia ramificans Xu, Li, Zhan & Xu, 2019 View in CoL View at ENA
Figs. 46 View FIGURE 46 , 47 View FIGURE 47
Chrysogorgia ramificans Xu, Li, Zhan & Xu, 2019: 94–97 View in CoL View Cited Treatment , figs. 2–3.
Material examined. MBM286861 View Materials , station FX-Dive 223 (10°4′42″N, 140°15′12″E), a seamount (tentatively named as M7) on the Caroline Ridge, 1047m, 11 June 2019 GoogleMaps .
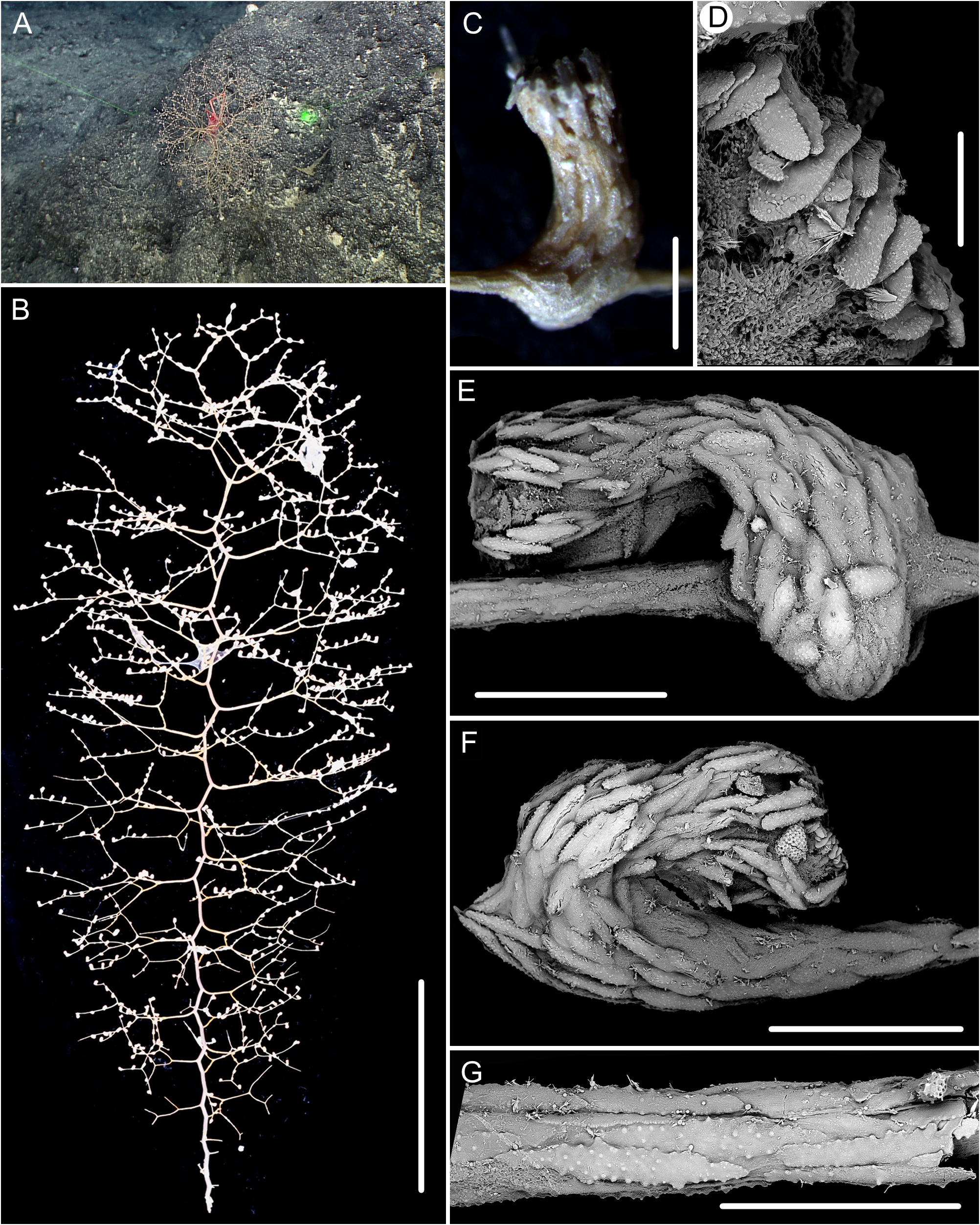
Description. Colony typical bottlebrush-shaped and attached to a rocky substrate ( Fig. 46 A View FIGURE 46 ). Specimen about 36 cm long and 15 cm wide in maximum with the holdfast not recovered ( Fig. 46 B View FIGURE 46 ). Main stem about 1.5 mm in diameter at base and brown to yellow with metallic luster. Branching sequence 1/ 3L. Branches subdivided dichotomously, up to five orders with branching angle 80°–100°. Distance between adjacent branch 6–12 mm, orthostiche intervals 17–34 mm, the first internode of branch 8–27 mm and the terminal branchlets up to 31 mm. Polyps cylindrical, some of them curved, usually perpendicular to the branches, 1.0– 2.5 mm tall average 2 mm, and 0.5–1.0 mm wide ( Fig. 46C, E, F View FIGURE 46 ). Polyps up to three and became very small on the first internode, up to four in medial internodes and up to five in terminal branchlets. Polyps absent in stem internodes and verruae absent. Tentacular part 0.5–1.0 mm long with tentacle rachis forming eight obvious columns ( Fig. 46E View FIGURE 46 ).
Rods and spindles in polyp body wall longitudinally or obliquely arranged, large and thick, rarely branched with many large and coarse warts, occasionally with irregular edges and shape, measuring 115–529 × 49–141 μm ( Fig. 47D View FIGURE 47 ). Rods and spindles in tentacle rachis longitudinally arranged extending to the polyp neck, all covered with many large and coarse warts, some of them branched with irregular shape, measuring 135–459 × 23–106 μm ( Fig. 47A View FIGURE 47 ). Scales in pinnules transversely arranged, small with finely toothed ends and sparse warts on surface, some of them curved or twisted with a medial contraction, occasionally nearly smooth, measuring 114–148 × 21–60 μm ( Figs. 46D View FIGURE 46 , 47B View FIGURE 47 ). Scales in coenenchyme arranged along to the branch, elongated and flat with dentate edges and a few large warts, some of them smooth and thick, measuring 223–671 × 35–118 μm ( Figs. 46G View FIGURE 46 , 47C View FIGURE 47 ).
Distribution and habitat. The Kocebu Guyot in Magellan Seamounts, 1831 m ( Xu et al. 2019); a seamount on the Caroline Ridge in the Western Pacific, 1047 m.
Remarks. The colony of the Caroline specimen has a single bottlebrush-shaped branching part and smaller polyps compared with the holotype, and these differences may be caused by different growth stage or environment, and we treat as the intraspecific variation.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Chrysogorgia ramificans Xu, Li, Zhan & Xu, 2019
| Xu, Yu, Zhan, Zifeng & Xu, Kuidong 2023 |