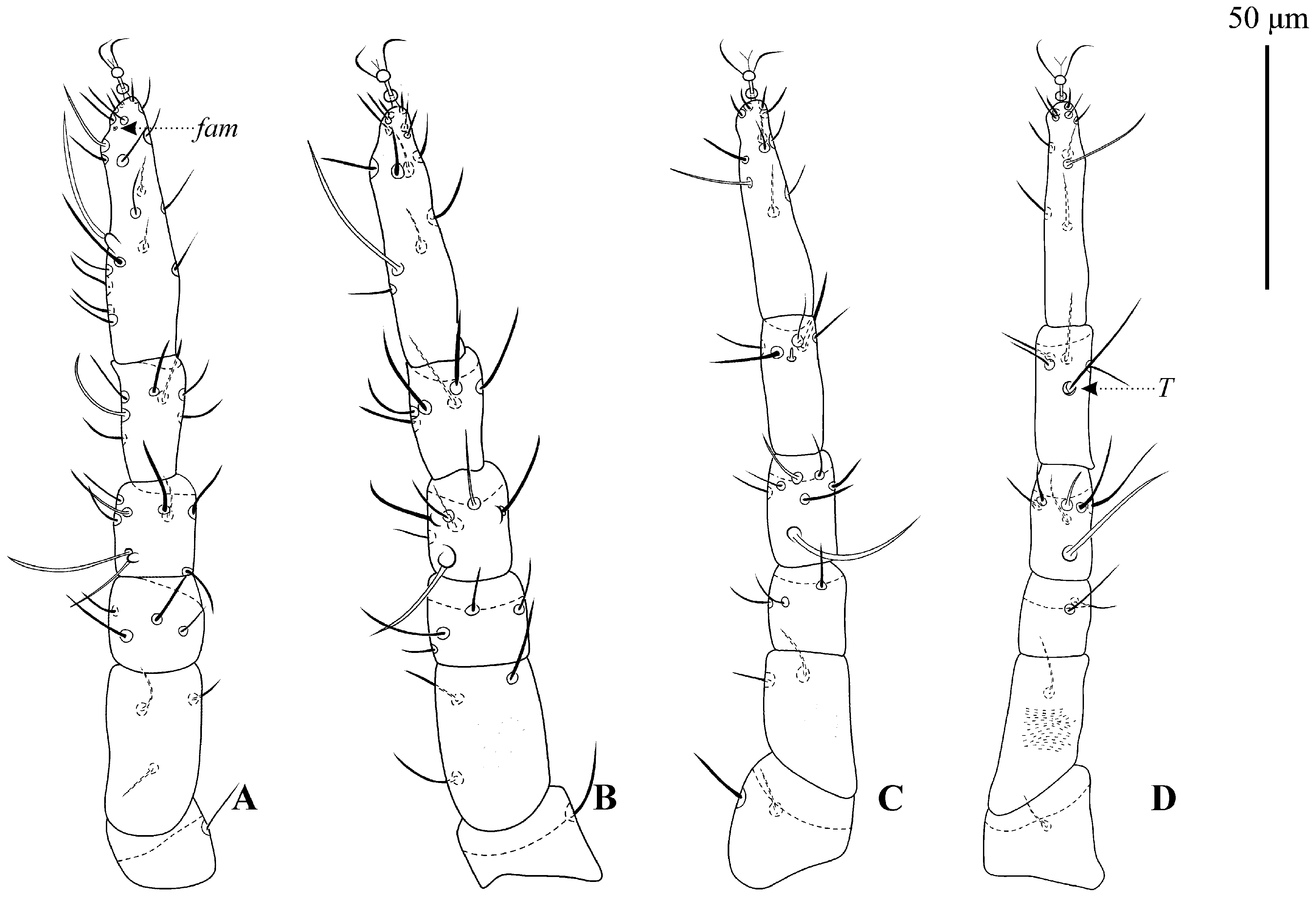Cunaxoides lajeadensis Wurlitzer & Monjarás-Barrera, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4718.3.8 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:0C6919E0-E3D7-4715-8BB4-E77BD292EBD8 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6BDE6C59-1648-439B-987F-66D5AABCE305 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:6BDE6C59-1648-439B-987F-66D5AABCE305 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Cunaxoides lajeadensis Wurlitzer & Monjarás-Barrera |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Cunaxoides lajeadensis Wurlitzer & Monjarás-Barrera sp. nov.
( Figures 1–8A View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 View FIGURE 7 View FIGURE 8 )
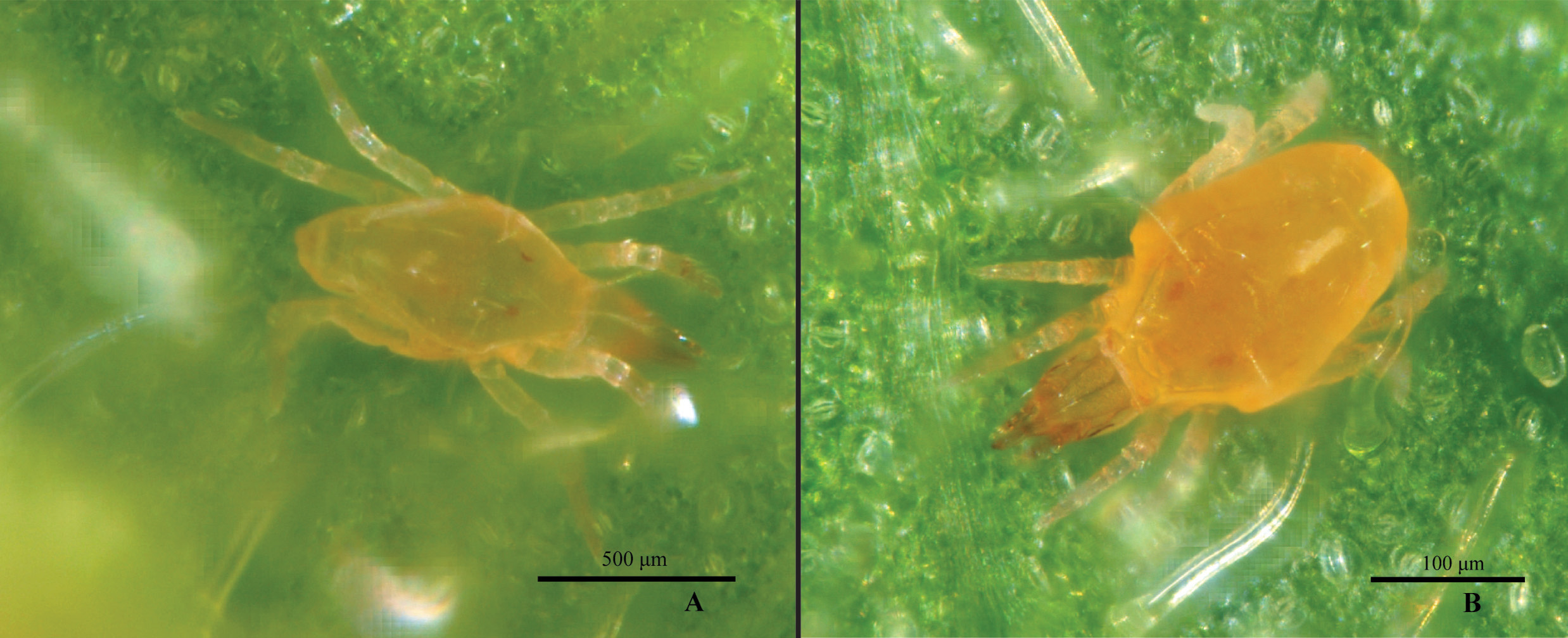
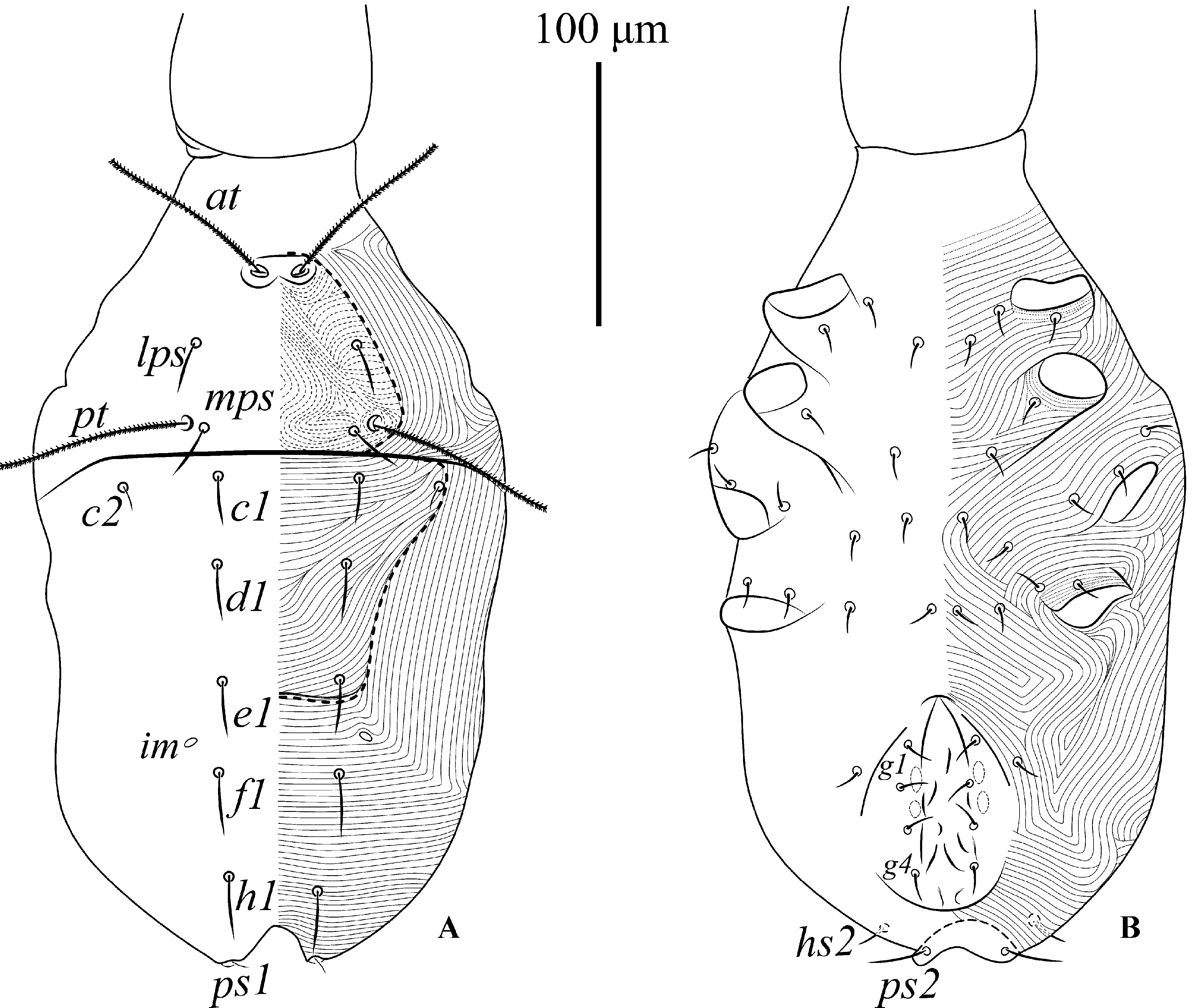
Description. Female (n = 6). Idiosoma length 299 (250–355); idiosoma width 182 (163–210)
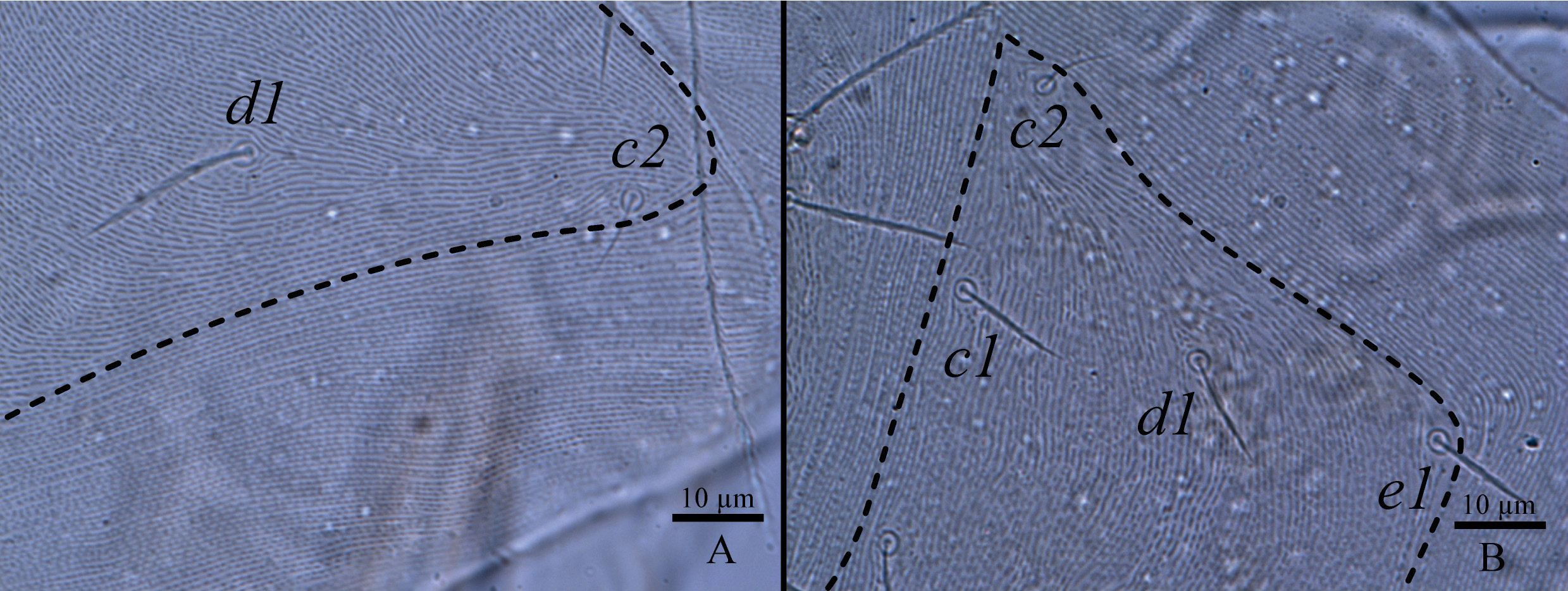
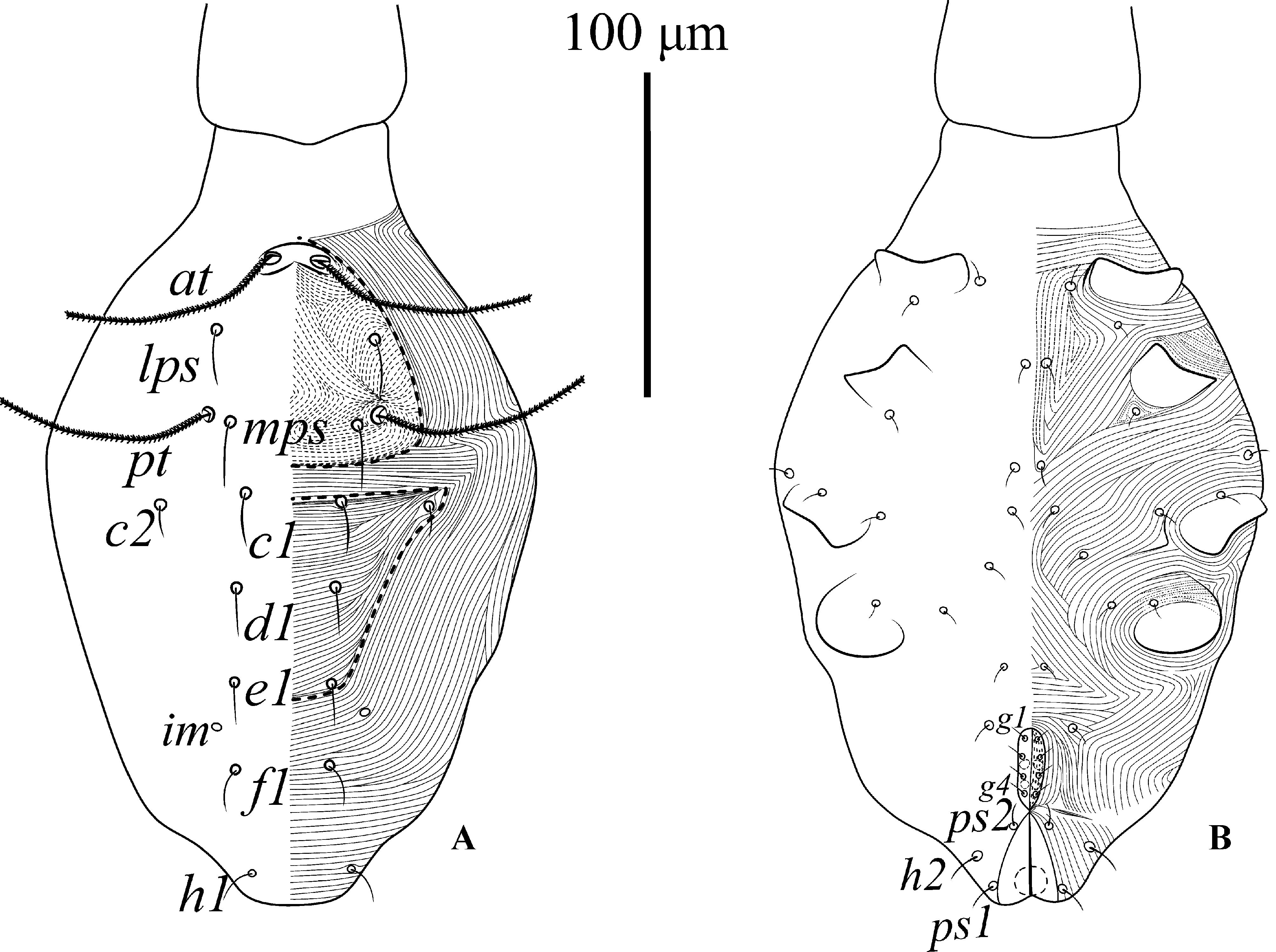
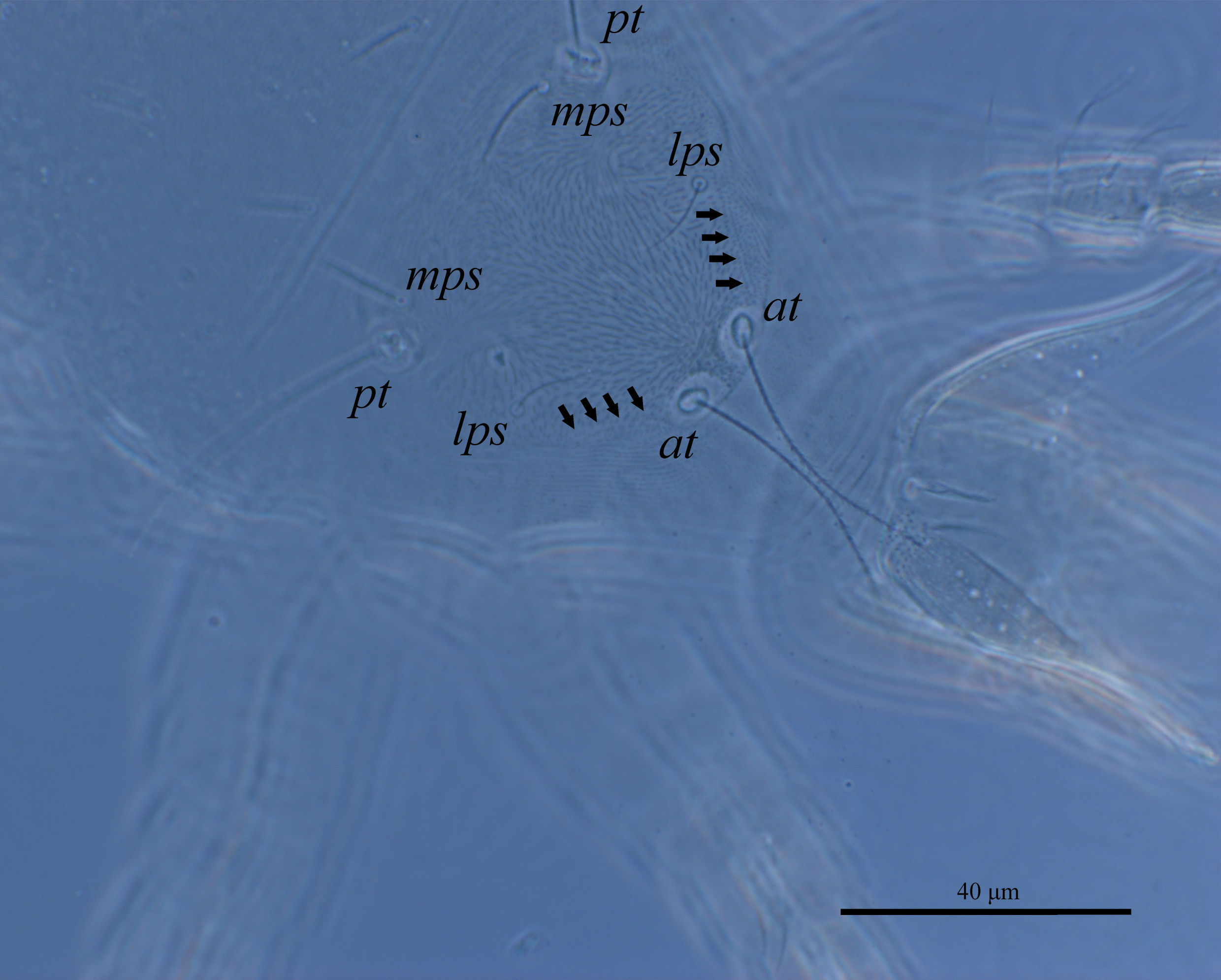
Dorsum ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 A–2A). Length and width of dorsal proterosomal shield: 71 (66–75); 73 (67–80), propodosomal region with dotted striations forming a subrectangular “shield” bearing setae lps, mps and sensilla (pt and at). Hysterosomal region with a “shield-like” area defined by surrounding striations, showing setae c 1, c 2, d 1 and e 1. Holotype with proterosomal and hysterosomal regions forming a “fosse” between setae (pt -mps) and (c 1 -c 2). Lyrifissures im located between setae e 1 and f 1. Setal lengths as follows: at 64 (57–70), pt 69 (65–75), lps 17 (10–22), mps 22 (20–24), c 1 18 (15–25), c 2 11 (10–13), d 1 19 (17–23), e 1 21 (18–25), f 1 23 (20–25), h 1 22 (18–25). Distance between setae: at -at 17 (15–20), at -lps 33 (29–35), lps -lps 57 (53–63), pt -pt 66 (62–72), pt -mps 10 (8–10), mps -mps 48 (45– 55), mps -c 1 28 (17–35), c 1 -c 1 44 (39–50), d 1 -d 1 43 (39–46), e 1 - e 1 43 (42–45), f 1 -f 1 48 (40–60), h 1 -h 1 33 (31–35).
Venter ( Fig. 1B View FIGURE 1 ). Ventral shield absent and genital shield recognizable. Integument with a pair of propodogastral setae, three pairs of hysterogastral setae and one pair of paragenital setae, near hysterogastral setae. Genital papillae and setae (g 1 -g 4) arranged longitudinally. Length of genital setae: g 1 10 (9–13), g 2 9 (8–10), g 3 13 (10–16), g 4 19 (15–25).
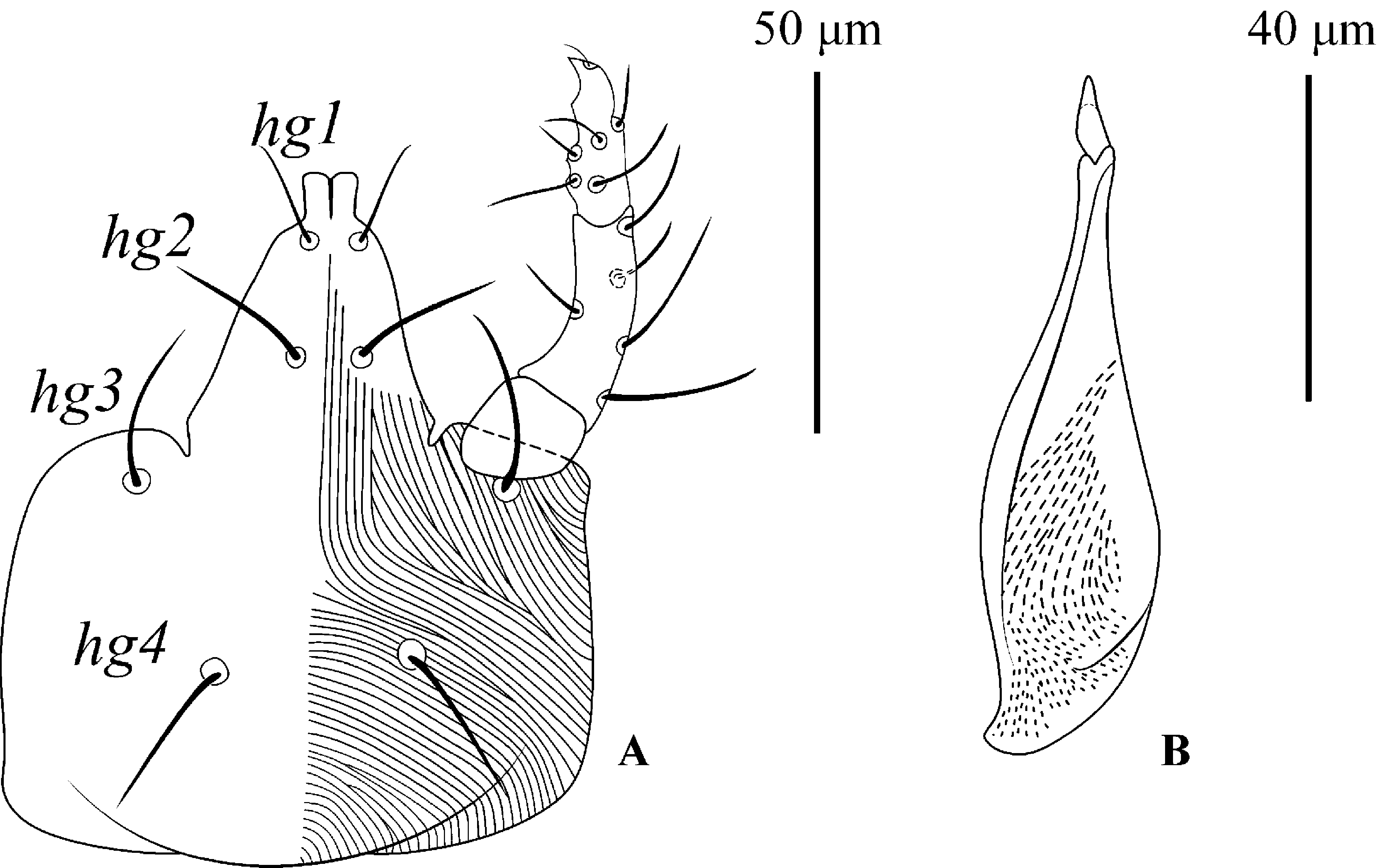
Gnathosoma ( Figs. 3 View FIGURE 3 A–B). Subcapitulum: Length 88 (85–90), width 65 (60–72), with the presence of four pairs of setae, hg 1 11 (10–12), hg 2 17 (15–20), hg 3 21 (20–25), hg 4 13 (10–15). Distance between setae: hg 1 -hg 1 6 (5–7), hg 2 -hg 2 8 (6–10), hg 3 -hg 3 36 (37–47), hg 4 -hg 4 23 (20–25), hg 4 -hg 3 24 (22–25), hg 2 -hg 4 37 (34–42), hg 1 -hg 2 18 (16– 22). Posterior ventral region of subcapitulum with longitudinal striation ( Fig. 2A View FIGURE 2 ). Palp 54 (48–59), divided into three segments; trochanter without setae; femorogenu with five sts; tibiotarsus with five sts, a terminal solenidion and a terminal claw. Length of chelicerae 82 (73–82) ( Fig. 3B View FIGURE 3 ).
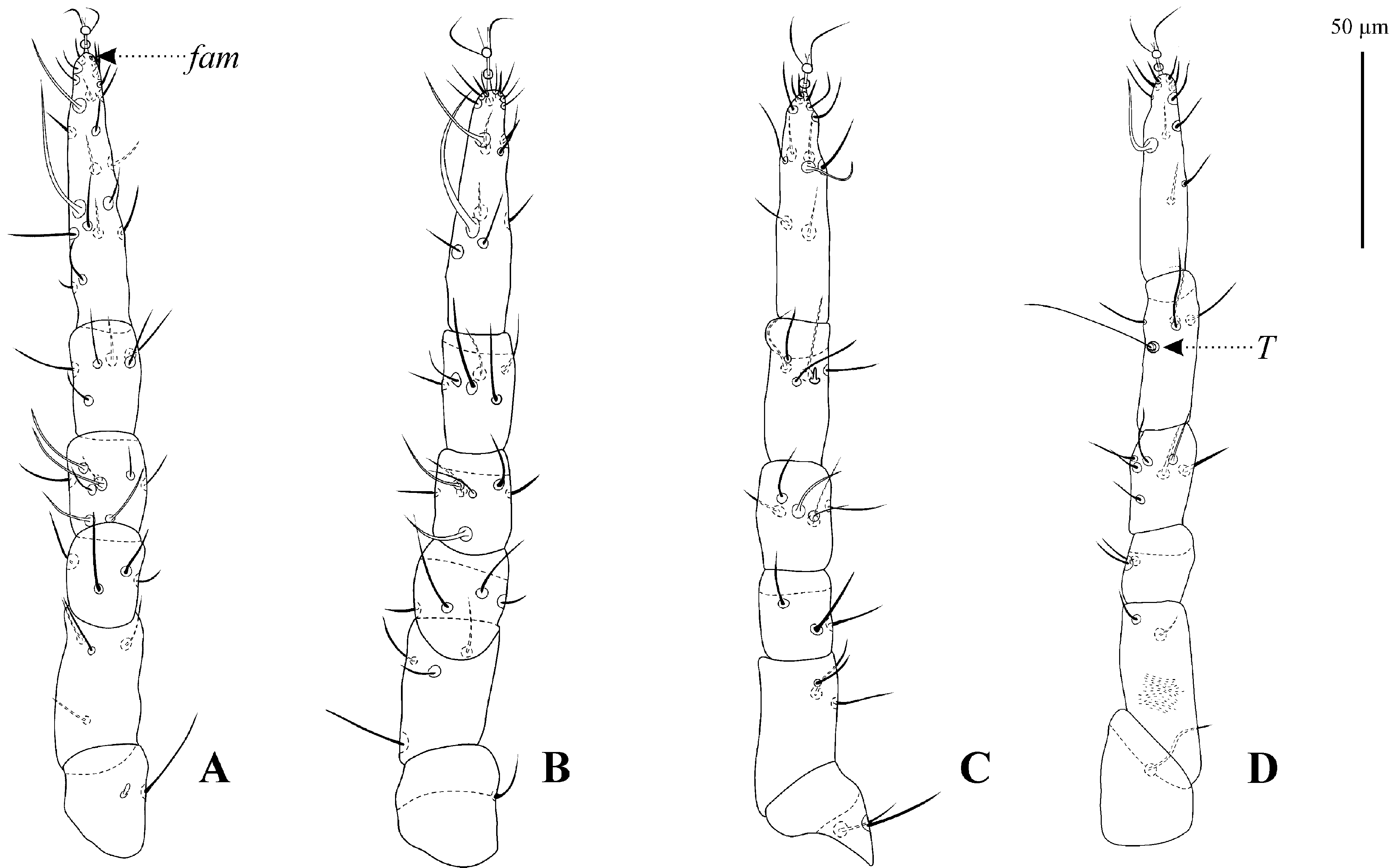
Legs ( Figs. 4 View FIGURE 4 A–D). Length of legs I–IV: 182 (175–193); 165 (150–182); 174 (165–188); 199 (188–213). Length of tarsi I–IV: 58 (55–68); 51 (45–57); 51 (48–55); 53 (49–58). Chaetotaxy: coxae ( Fig. 1B View FIGURE 1 ) I–IV, 3-1-3-3 sts; trochanters I–IV, 1 sts, 1 sbsl -1-2-1 sts; basifemora I–IV, 4-4-3-2 sts; telofemora I–IV, 4-4-3-2 sts; genua I–IV, 4 asl, 5 sts -2 asl, 5 sts,-1 asl, 5 sts -1 asl, 6 sts; tibiae I–IV, 6-6-5 sts, 1 bsl -4 sts, 1 T; tarsi I–IV: 2 asl, 1 fam, 16 sts, 2 tsl, 1 dtsl -2 asl, 1 tsl, 1 dtsl 14 sts -1 asl, 1 tsl, 1 dtsl, 10 sts -1 asl, 2 tsl, 8 sts.
Male (n = 3). Idiosoma length 222 (215–230); idiosoma width 136 (130–140). Dorsum ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 A-2B) Length and width of dorsal proterosomal shield: 64 (60–67); 62 (60–65), length and width of hysterosomal shield. 60 (58–65); 68 (65–70). Length of legs I–IV: 156 (150–163); 139 (135–140); 155 (150–163); 174 (168–180). Propodosomal region with dotted striations forming a subrectangular “shield” showing setae lps, mps and sensilla (pt and at). Hysterosomal region with a “shield-like” area defined by surrounding striation, shield bearing setae c 1, c 2, d 1 and e 1. Lyrifissures im located between e1 and f1 setae. Length of dorsal setae: at 56 (55–58), pt 58 (55–65), lps 17 (15–19) mps 20 (17–23), c 1 15 (14–15), c 2 9 (8–10), d 1 13 (12–13), e 1 13 (12–14), f 1 15 (10–17), h 1 11 (10–13). Distance between setae at -at 15 (15–16), at -lps 30 (29–32), lps -lps 49 (48–52), pt -pt 57 (55–60), pt -mps 8 (8–9), mps -mps 39 (39–40), mps -c 1 22 (20–25), c 1 -c 1 32 (30–35), d 1 -d 1 33 (31–35), e 1 - e 1 30 (28–31), f 1 -f 1 27 (26–28), h 1 - h 1 34 (32–35).
Venter ( Fig. 4B View FIGURE 4 ). Ventral shield absent and genital shield recognizable. Integument with a pair of propodogastral setae, three pairs of hysterogastral setae and one pair of paragenital setae, near hysterogastral setae. Genital papillae and setae (g1-g4) with longitudinal directions. Length of genital setae: g 1 5 (5-5), g 2 5 (5-5), g 3 4 (5-5), g 4 5 (5-5).
Gnathosoma . Subcapitulum: Length 71 (70–74), width 44 (40–48), with four pairs of setae, hg 1 9 (8–10), hg 2 13 (10–15), hg 3 18 (16–20), hg 4 13 (11–15). Distance between setae: hg 1 -hg 1 5 (4–5), hg 2 -hg 2 6 (5–7), hg 3 -hg 3 26 (38–39), hg 4 -hg 4 20 (19–21), hg 4 -hg 3 20 (19–20), hg 2 -hg 4 30 (28–32), hg 1 -hg 2 12 (9–15). Posterior ventral region of subcapitulum with longitudinal striation. Palp 43 (42–45), divided into three segments; trochanter without setae; femorogenu with five sts; and tibiotarsus with five sts, a terminal solenidion and a terminal claw. Length of chelicerae 68 (65–72).
Legs ( Figs. 6 View FIGURE 6 A–D). Chaetotaxy: coxae ( Fig 2 View FIGURE 2 ) I–IV, 3-1-3-2 sts; trochanter I–IV, 1-1-2-1 sts; basifemora I–IV, 3-3-2-1 sts; telofemora I–IV, 4-4-3-2 sts; genua I–IV, 3 asl, 5 sts -2 asl, 5 sts -2 asl, 5 sts -2 asl, 5 sts; tibiae I–IV, 6 sts, 1 asl -6 sts -5 sts, 1 bsl -1 T, 4 sts; tarsi I–IV: 2 asl, 1 fam, 16 sts, 2 tsl, 1 dtsl -1 asl, 11 sts,2 tsl -1 asl, 8 sts, 2 tsl -1 asl, 7 sts, 1 tsl, 1 dtsl.
Tritonymph (male) (n = 1). Idiosoma length 200; idiosoma width 125.
Dorsum ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 ) Length and width of dorsal proterosomal shield: 55; 55, length and width of hysterosomal shield. 65; 45. Length of legs I–IV: 130; 112; 137; 142. Propodosomal region with dotted striations forming a subrectangular “shield” showing setae lps, mps and sensilla (pt and at). Hysterosomal region with a “shield-like” area defined by surrounding striation, shield bearing setae c 1, c 2, d 1 and e 1. Lyrifissures im located between e 1 and f 1 setae. Length of dorsal setae: at 54, pt 55, lps 13, mps 15, c 1 13, c 2 9, d 1 13, e 1 11, f 1 14, h 1 10. Distance between setae at -at 15, at -lps 27, lps -lps 46, pt -pt 55, pt -mps 7, mps -mps 42, mps -c1 20, c1-c1 33, d 1 -d 1 33, e1- e1 31, f 1 -f 1 30, h 1 - h 1 21.
Venter. Ventral shield absent and genital shield recognizable. Integument with a pair of propodogastral setae, three pairs of hysterogastral setae and one pair of paragenital setae, near hysterogastral setae. Genital papillae and setae (g1-g4) with longitudinal directions. Length of genital setae: g 1 5, g 2 5, g 3 5, g 4 5.
Gnathosoma . Subcapitulum: Length 65, width 48, with four pairs of setae, hg 1 5, hg 2 8, hg 3 15, hg 4 10. Distance between setae: hg 1 -hg 1 5, hg 2 -hg 2 7, hg 3 -hg 3 34, hg 4 -hg 4 18, hg 4 -hg 3 25, hg 2 -hg 4 30, hg 1 -hg 2 12. Posterior ventral region of subcapitulum with longitudinal striation. Palp 32 (42-45), divided into three segments; trochanter without setae; femorogenu with five sts; and tibiotarsus with five sts, a terminal solenidion and a terminal claw. Length of chelicerae 63.
Remarks. The female and male were distinguished by the morphometry of the idiosoma and by the chaetotaxy the legs, which have fewer setae on coxae IV, trochanter I, basifemora I–IV; genua I, III and IV; tibiae I; and tarsi II–IV. The tritonymph resembles the adult male by the chaetotaxy of the legs and the size of some structures. However, it differs by presenting a clear ecdysial line dorsally on the propodosoma ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 ) ( Den Heyer 2006; Castro & Den Heyer 2008 b; Den Heyer & Castro 2009 and Paktinat-Saeij et al. 2016 b). Cunaxoides lajeadensis Wurlitzer & Monjarás-Barrera sp. nov. has a faint orange color ( Fig. 8A View FIGURE 8 ).
Diagnosis. Cunaxoides lajeadensis Wurlitzer and Monjarás-Barrera sp. nov (female) resembles Cunaxoides lootsi Den Heyer, 2013 , by presenting “shields” (propodosomal and hysterosomal) formed by striations of the idiosoma and the same chaetotaxy of coxae II, III and IV, trochanters II, III and IV, basifemora I–IV, telofemora I–IV, genua I–III, tibiae III and IV. Differences are presented in Table 1 View TABLE 1 .
Etymology. The epithet is in homage to the city of Lajeado, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, where the species was found.
Type material. Holotype: Female collected from tropical white morning-glory, Ipomoea alba L. ( Convolvulaceae ) in Lajeado, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, 29º26’13 ‘’S, 51º57’43’’W, 34 m above sea level, collector: Wesley Borges Wurlitzer and date: 14/I/2019 . The seven paratypes (five females, two males and one tritonymph) will be deposited at the Museu de Ciências Naturais ( MCN) of the Universidade do Vale do Taquari-Univates, Lajeado, Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil . The holotypes (one female one male) will be deposited at Acarology and Entomology Department, Escola Superior de Agricultura “Luiz de Queiroz”, Universidade de São Paulo ( ESALQ / USP), Piracicaba ( SP), Brazil
.
| MCN |
McNeese State University |
| USP |
University of the South Pacific |
| SP |
Instituto de Botânica |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |