Diaphorocleidus affinis ( Mizelle, Kritsky & Crane, 1968 ) Jogunoori, Kritsky & Venkatanarasaiah, 2004
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5403.1.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:0C3D7428-8B33-46F5-AC53-2C4D96E0E4F5 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10572768 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0384F651-FF99-877F-FF2F-0F75FA811869 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Diaphorocleidus affinis ( Mizelle, Kritsky & Crane, 1968 ) Jogunoori, Kritsky & Venkatanarasaiah, 2004 |
| status |
|
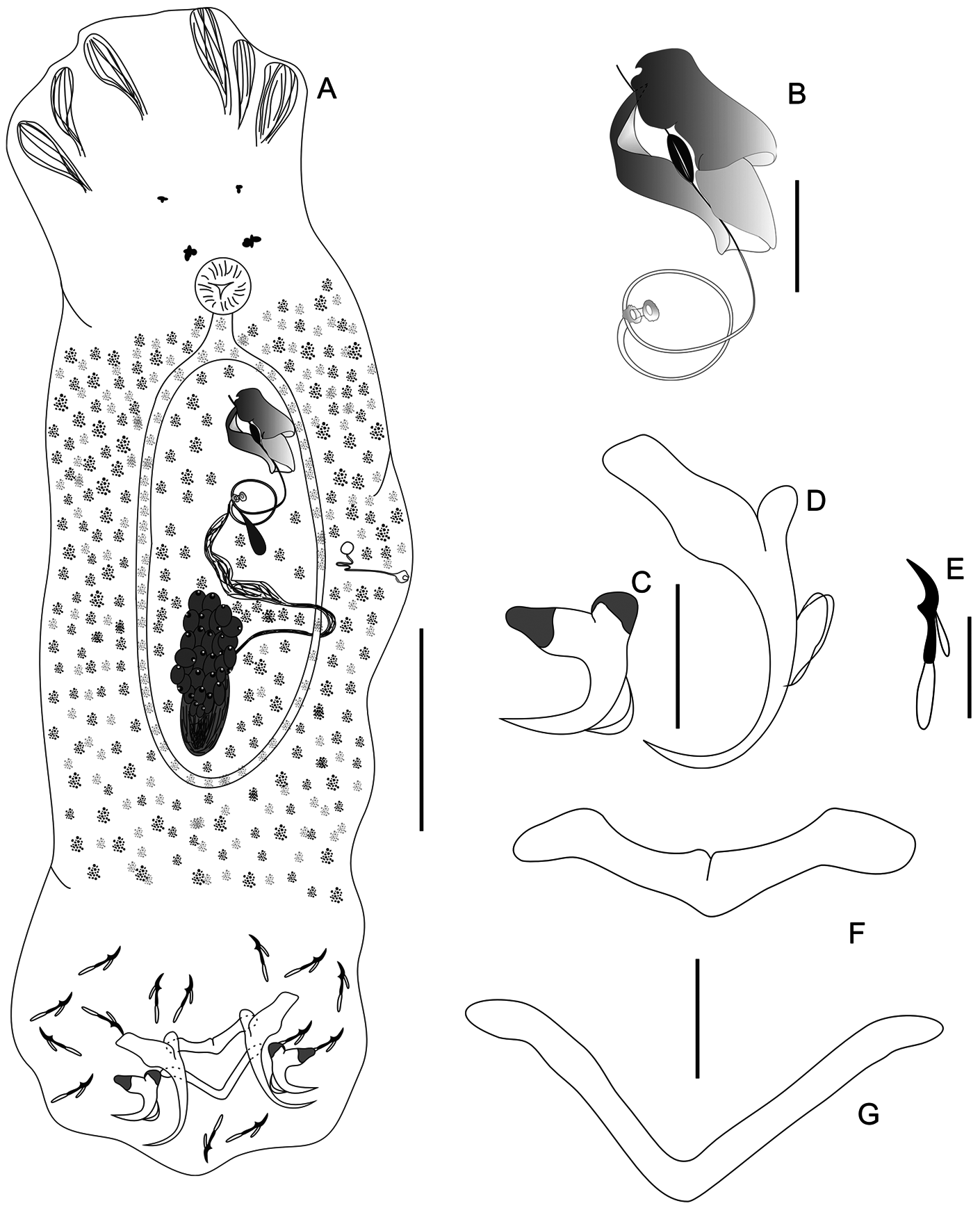
Diaphorocleidus affinis ( Mizelle, Kritsky & Crane, 1968) Jogunoori, Kritsky & Venkatanarasaiah, 2004 View in CoL ( Figure 5 View FIGURE 5 )
Type-host: Bryconops affinis [referred to as Creatochanes affinis (Günther) ]
Type-locality: Peixe Boi River, near Peixe Boi, State of Pará, Brazil
Site of infestation: Gills
Other host: Bryconops cf. affinis (present study)
Locality: Rural area of Chapadinha in the “Riacho Feio” (03º51’18.1’’S 043º17’14.0’’W) GoogleMaps and the urban area of Anapurus in the “Riacho Estrela” (03°40’15.6”S 043°7’9.7”W), tributaries of the Munim River, Munim basin, Maranhão, Brazil GoogleMaps .
Parasitological indexes: Total number of hosts: 64; number of infected hosts: 33; total number of parasites: 179; Range of intensity: 1–19
Specimens deposited: Voucher CHIOC 40271, 40272, 40273, 40274, 40275
New data from 34 specimens newly collected and mounted in Hoyer’s medium: Body fusiform, comprising cephalic region, trunk and haptor, 503 (272–665, n = 34) long by 172 (85–305, n = 34) wide at level of vagina. Tegument smooth. Anterior region with cephalic lobes moderately developed; three bilateral pairs of head organs; cephalic glands indistinct. Two pairs of eyes subequal, the anterior is smaller than the posterior pair; rare accessory granules in the cephalic region. Pharynx 37 (30–42, n = 3) in diameter. Oesophagus short, bifurcating into two intestinal caeca, confluent posteriorly to gonads, lacking diverticula. Gonads overlapping; testis elongate dorsoposterior to germarium; seminal vesicle a distal expansion of vas deferens. Vaginal aperture sinistral, sacshaped, opening ventrally near body mid-length, vaginal canal elongated, sclerotized. Oviduct, ooptype, and uterus not visualized. Vitelline follicles scattered throughout trunk but absent around the reproductive organs ( Fig. 5A View FIGURE 5 ). Copulatory complex comprising unarticulated male copulatory organ ( MCO) and accessory piece. MCO sclerotized, tubular, coiled with 1 ½–2 counterclockwise rings, 120 (92–131, n = 25) of total length and 22 (18–26, n = 15) diameter of the first ring; base forming a small tube with two circular flanges at each end. Accessory piece robust, formed by two wide plates, with the basal portion in a single unit that extends to the middle portion of the piece, where they separate and form a pincer, which serves as a guide for the MCO, 36 (30–43, n = 15) long and 17 (12–21, n = 30) wide ( Fig. 5B View FIGURE 5 ). Peduncle inconspicuous. Haptor subhexagonal, armed with 7 pairs of hooks, 71 (65–78, n = 12) long and 108 (71–141, n = 31) wide ( Fig. 5A View FIGURE 5 ). Anchors dissimilar in shape and size; ventral anchor superficial root well-developed, elongate, straight edges; deep root well-developed, rounded distally; slightly curved shaft and short tip; anchor filament present, 33 (29–37, n = 16) long, base 22 (20–24, n = 16) wide ( Fig. 5D View FIGURE 5 ); dorsal anchor wide, with superficial and deep roots exhibiting a sheath; slightly straight shaft stem and short, thick tip; anchor filament present, 12 (10–14, n = 16) long, base 14 (11–15, n = 16) wide ( Fig. 5C View FIGURE 5 ). Ventral bar slightly open V-shaped with depression in the anteromedial region and small medial fracture with expanded ends 36 (30–41, n = 15) long ( Fig. 5F View FIGURE 5 ). Dorsal bar V-shaped, 46 (37–65, n = 15) long ( Fig. 5G View FIGURE 5 ). Hook pairs similar in size and shape, hooks with inconspicuous pointed thumb; and slightly curved point tip, shank composed of two subunits, distal subunit slightly expanded; pair 1, 16 (12–20, n = 24), pair 2, 17 (15–20, n = 22), pair 3, 18 (12–21, n = 26), pair 4, 17 (11–21, n = 24), pair 5, 16 (12–19, n = 26), pair 6, 17 (11–19, n = 23), pair 7, 16 (12–19, n = 21) long. FH loop 0.3 shank length ( Fig. 5E View FIGURE 5 ). Egg 85 by 62.
Remarks: The morphology of the specimens studied herein is similar to the original description, differing only in the body size (specimens of the present study being much larger than the original description), with comparisons presented in Table 2 View TABLE 2 . Considering that Mizelle et al. (1968) examined only four specimens, the drawings shown are not clearly detailed, and Jogunoori et al. (2004) did not present morphological data, it is opportune to present new morphological data and new drawings for specimens of D. affinis found parasitizing the gills of Bryconops cf. affinis from the Rio Munim basin, which is now reported as a new geographical distribution for this species.
| FH |
Fort Hays |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |