Loxosoma (Loxosomina) aripes ( Nielsen, 1964b ), 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5325.3.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:089EB305-F420-4D84-8758-BF6DA5320545 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8243369 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03808797-6F5F-FF89-FF6D-0AFAFCD2FE95 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Loxosoma (Loxosomina) aripes ( Nielsen, 1964b ) |
| status |
comb. nov. |
Loxosoma (Loxosomina) aripes ( Nielsen, 1964b) n. comb.
( Figs 1–8 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 View FIGURE 7 View FIGURE 8 , Table 3 View TABLE 3 )
Loxosomella aripes Nielsen, 1964b: 4 View in CoL , fig. 2.
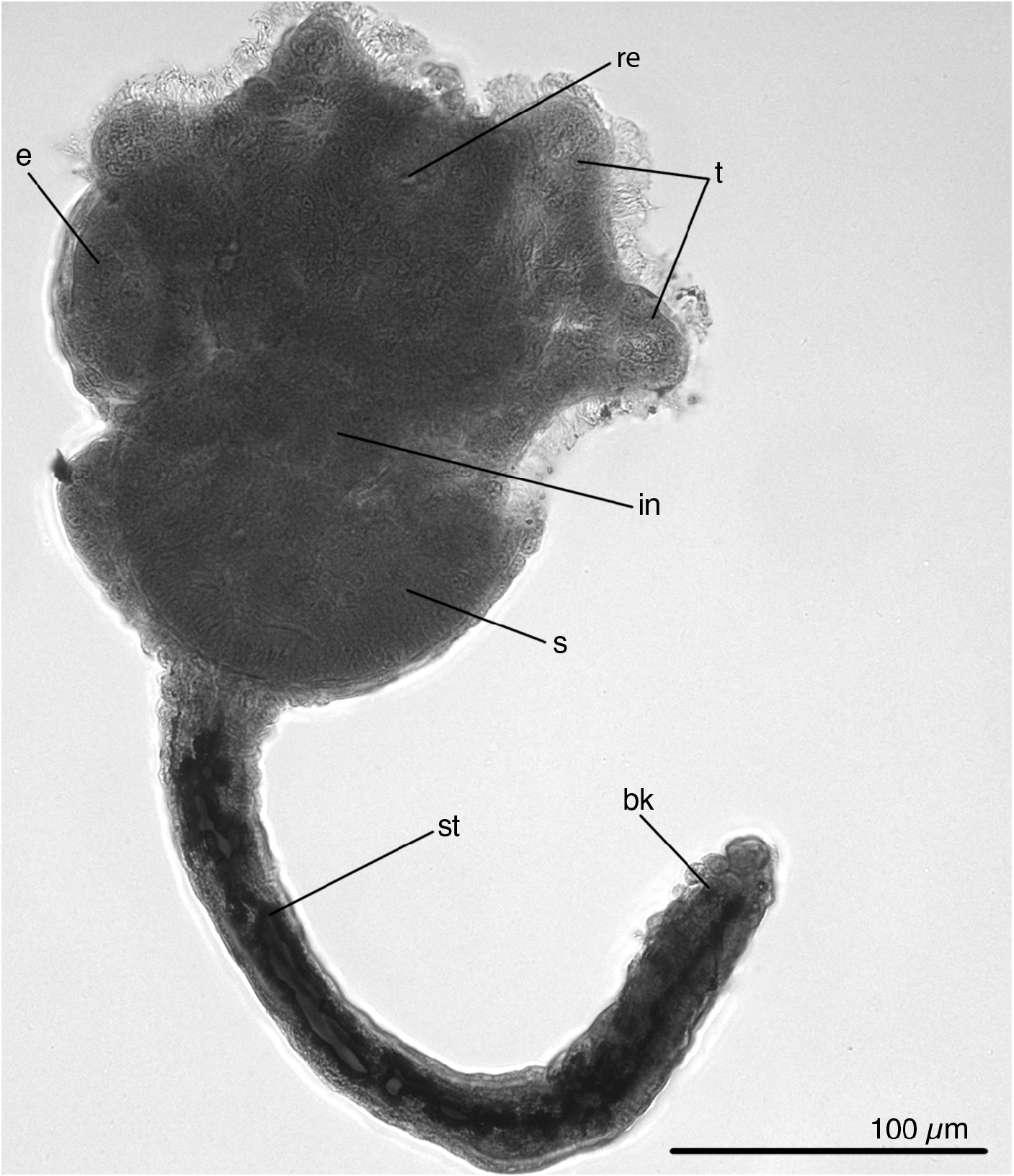
Original description. Small species, up to 470 µm. Lophophore has six very short, stout tentacles ( one specimen with 4 tentacles). Atrium narrow. Stomach big and rounded. Peduncle longer than calyx. Peduncle slender, terminating in laterally compressed expansion, which on each side bears 3–4 transverse furrows. Youngest buds formed laterally at lower level of stomach, and older buds found above this reaching upper level of stomach; up to three buds at time. Embryos very big and quite deform the calyx; 1–3 embryos at time. Usually buds and embryos found only in one side of animal. Host: Laonice cirrata View in CoL . Type locality: Raunefjorden, off Sletten ( 60°16.5′N, 5°12′E), depth 100– 120 m. The holotype is illustrated in Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 .
Material examined. Holotype (number 46395) ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ); No Uk-31 ( ZMMU)— six specimens from the Kandalaksha Bay, White Sea ( 66°34′N, 33°08′E), 30–70 m; six specimens from the White Sea from a personal collection. GoogleMaps
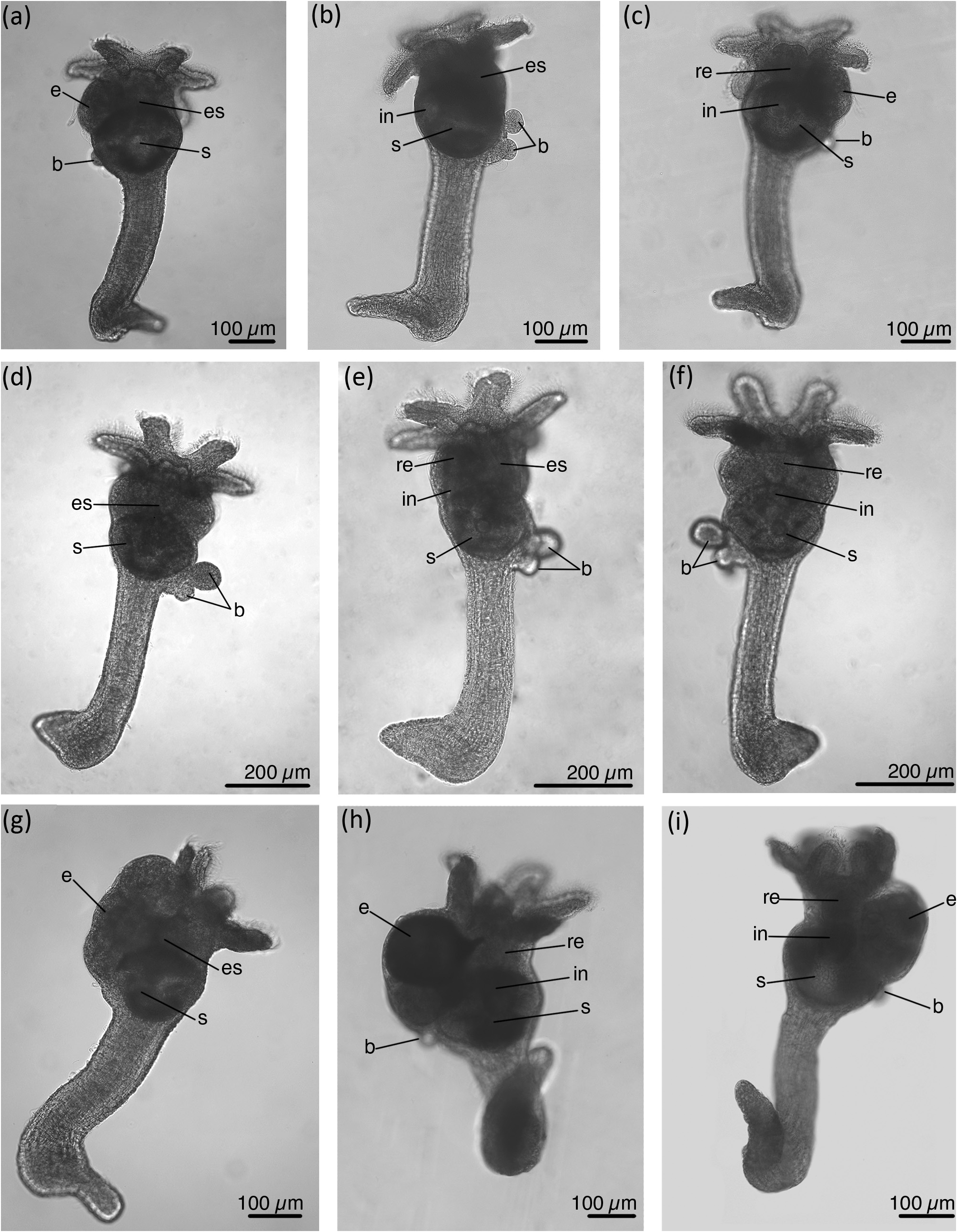
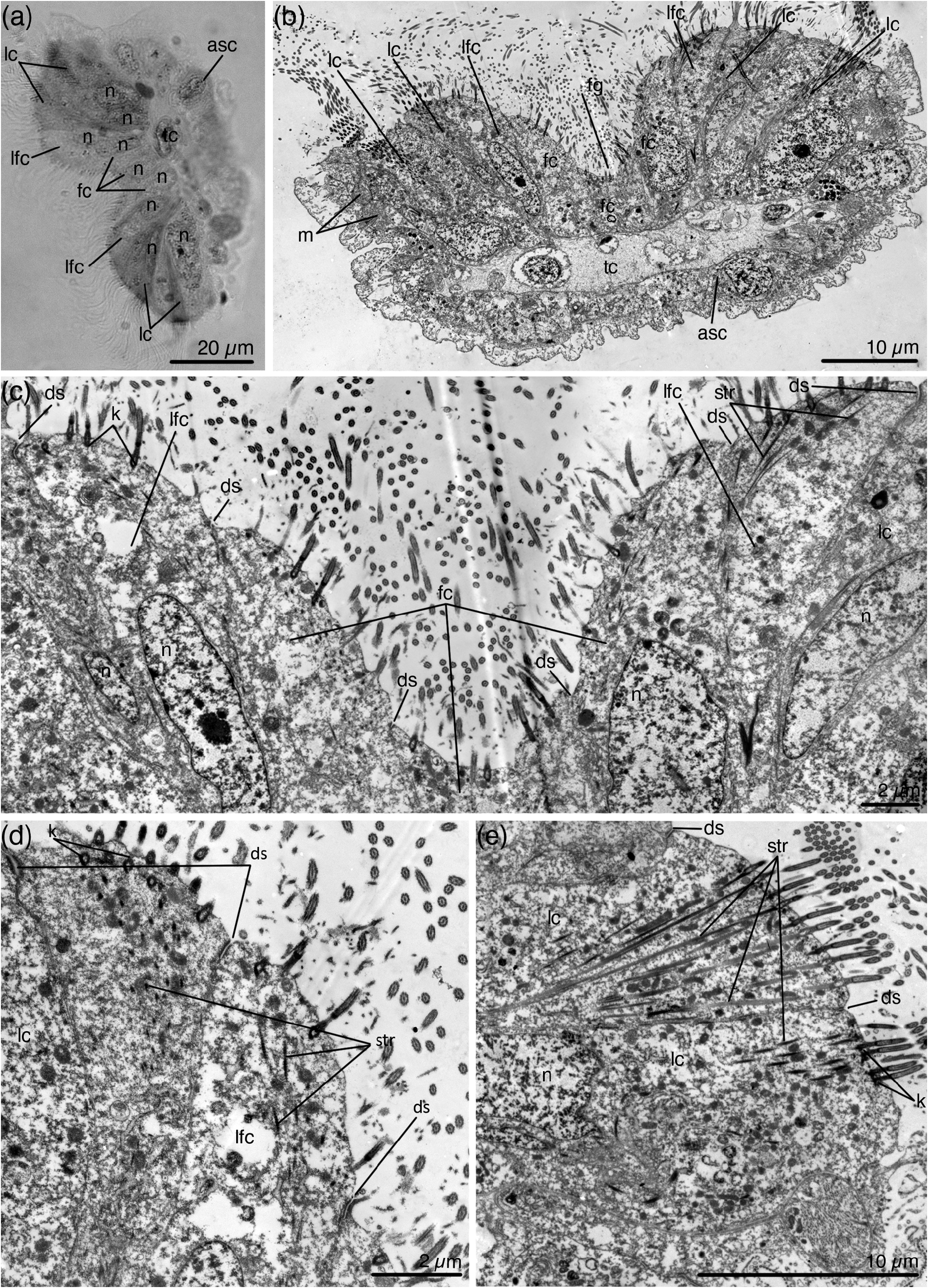
Description of the material from the White Sea. Medium-sized species with average body length of 596 µm ( Figs 2 View FIGURE 2 , 3 View FIGURE 3 ) (measurements for 11 specimens are provided in Table 3 View TABLE 3 on page 11). Calyx is up to one and a half times shorter than stalk (average calyx length 228 µm). Calyx bears six short tentacles directed distally when embryos are not developed. When embryos are developing the calyx strongly swells on one side and the tentacles are shifted to the side and directed disto-laterally. The tentacles are unusually wide and the frontal surface is formed by nine rows of ciliated cells ( Fig. 4a, b View FIGURE 4 ). The frontal groove is formed by three rows of frontal cells ( Fig. 4a–c View FIGURE 4 ). The latero-frontal cells border the frontal groove ( Fig. 4b–d View FIGURE 4 ), and the lateral cells form two rows on each side of the frontal surface of the tentacle ( Fig. 4a, b, e View FIGURE 4 ).
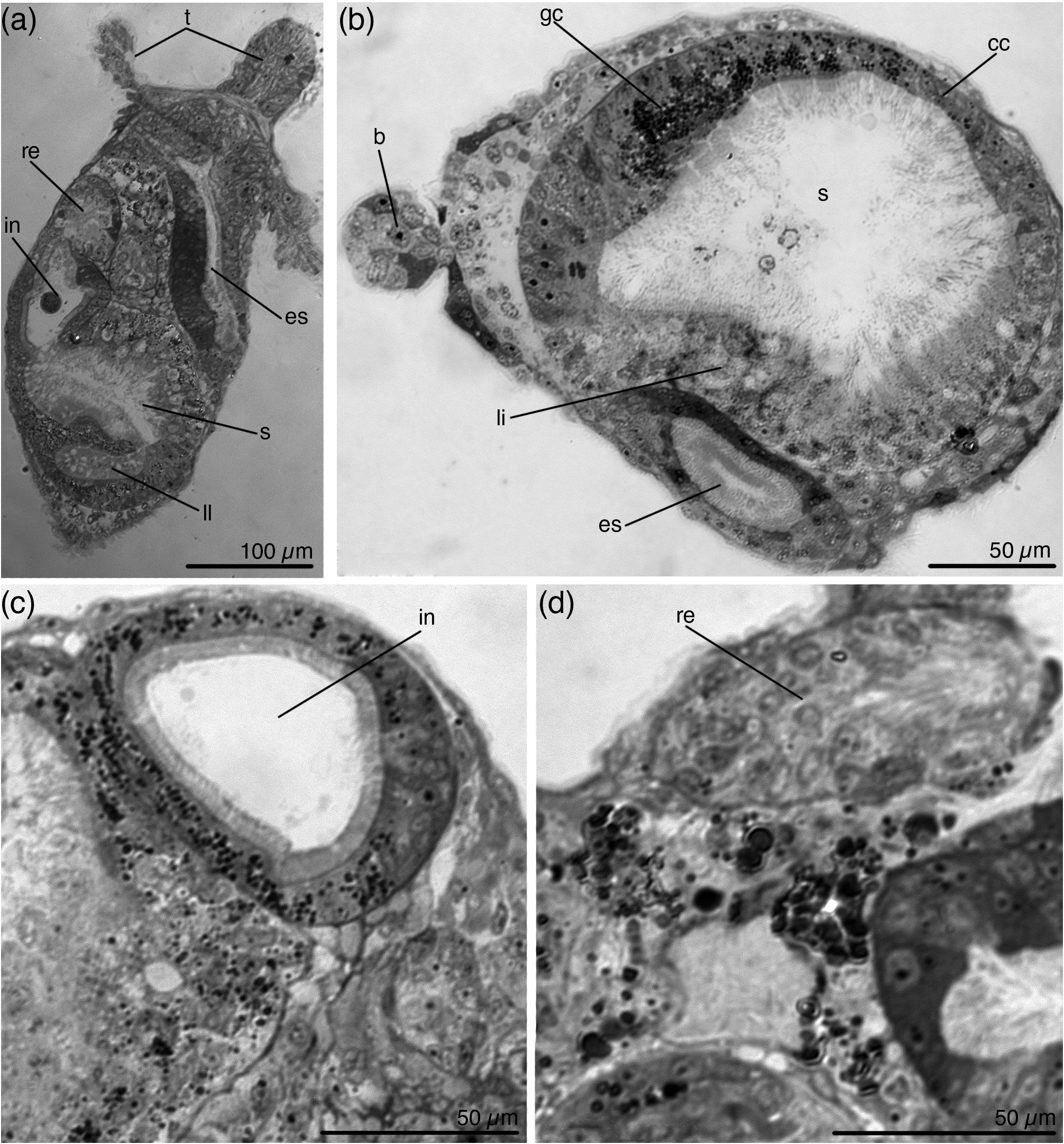
Digestive system includes esophagus, stomach, intestine and rectum ( Fig. 5a View FIGURE 5 ). The esophagus is lined with cuboidal epithelium ( Fig. 5b View FIGURE 5 ). The stomach is large, looks roundish ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ), but histological sections show that the stomach is three-lobed. In the lower part of the stomach lateral lobes are separated from the central zone by epithelial invaginations deeply protruding into the stomach cavity ( Fig. 5a View FIGURE 5 ). A roof of the stomach is lined with 'liver' cells; lateral sides and lateral lobes of the stomach are glandular; epithelium from the beneath intestine and esophagus to the bottom of the stomach is cuboidal ( Fig. 5b View FIGURE 5 ). The intestine is bulbous ( Fig. 5a View FIGURE 5 ), lined with prismatic epithelium, the cells with granular cytoplasm and numerous cilia on the apical surface ( Fig. 5c View FIGURE 5 ). Rectum oval, cells with long cilia ( Fig. 5d View FIGURE 5 ). Anal cone directed upward ( Fig. 2c, f, h, i View FIGURE 2 ).
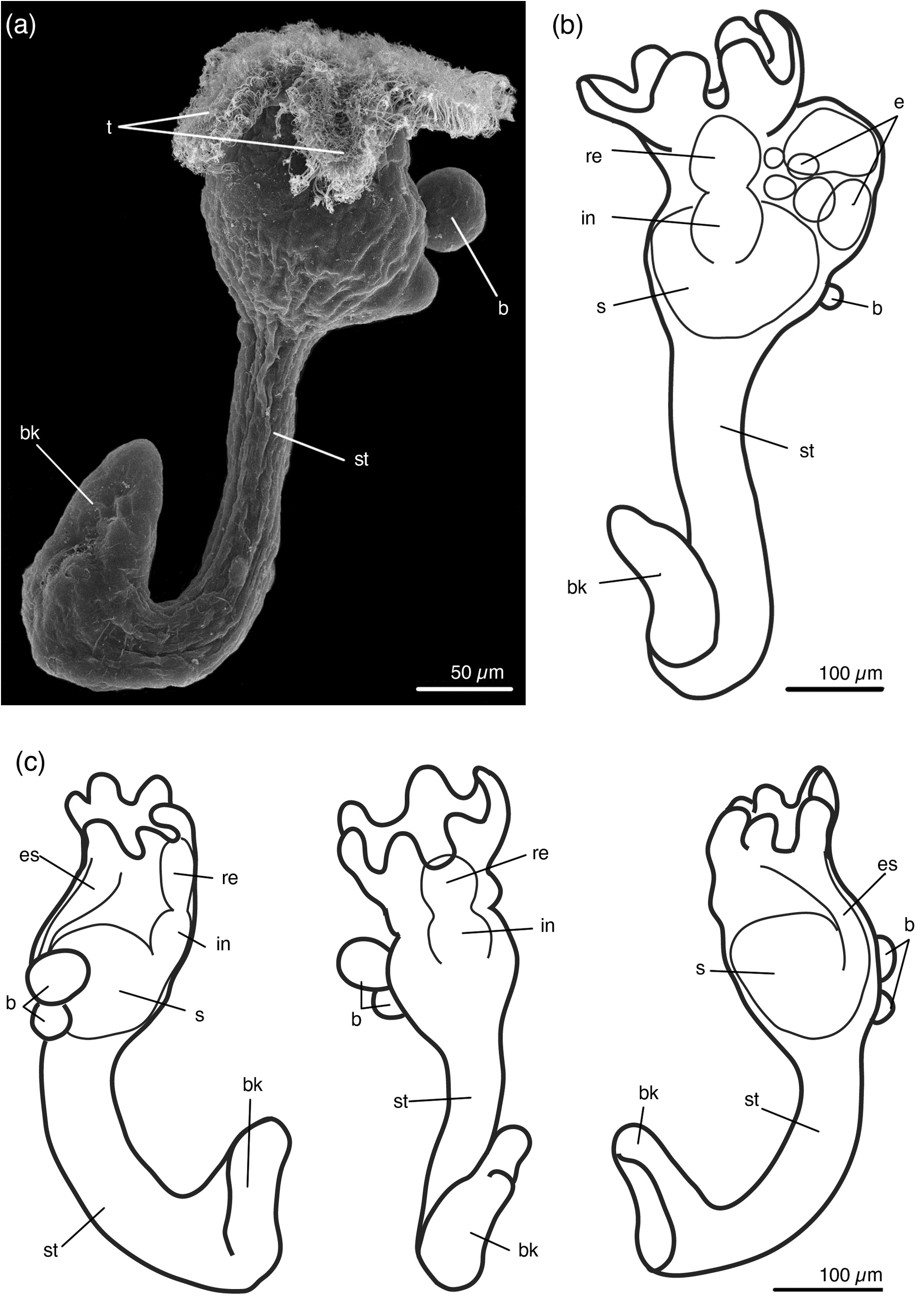
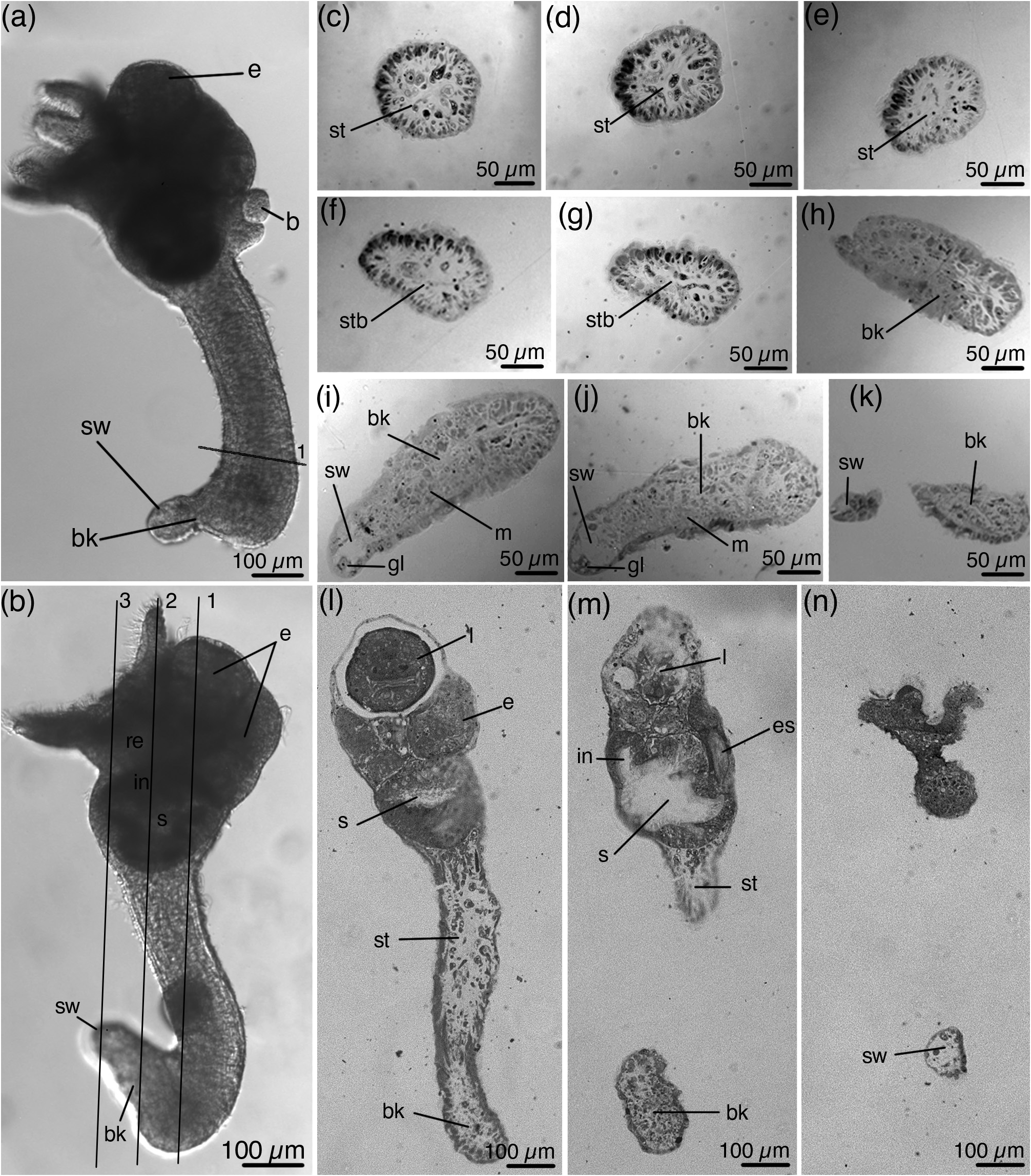
The cylindrical stalk has average length of 377 µm. Its width is almost uniform throughout its length (average width 83 µm). The attachment organ looks like a 'beak' extended backwards, often bent to the abfrontal side ( Figs 2 View FIGURE 2 , 3 View FIGURE 3 , 6a, b View FIGURE 6 ). Beak gradually narrows towards the apical part. At the tip of the beak there is usually a small swelling ( Fig. 6a, b View FIGURE 6 ). The stalk gradually passes into the beak, there is no pedal gland at the base of the stalk ( Fig. 6c–g, l–n View FIGURE 6 ). The cavity of the beak contains many muscular cells and several glandular cells, the pedal groove and accessory cells are absent ( Fig. 6h–k View FIGURE 6 ). The cavity of the swelling is empty; several large glandular cells lie in epithelium ( Fig. 6i, g View FIGURE 6 ).
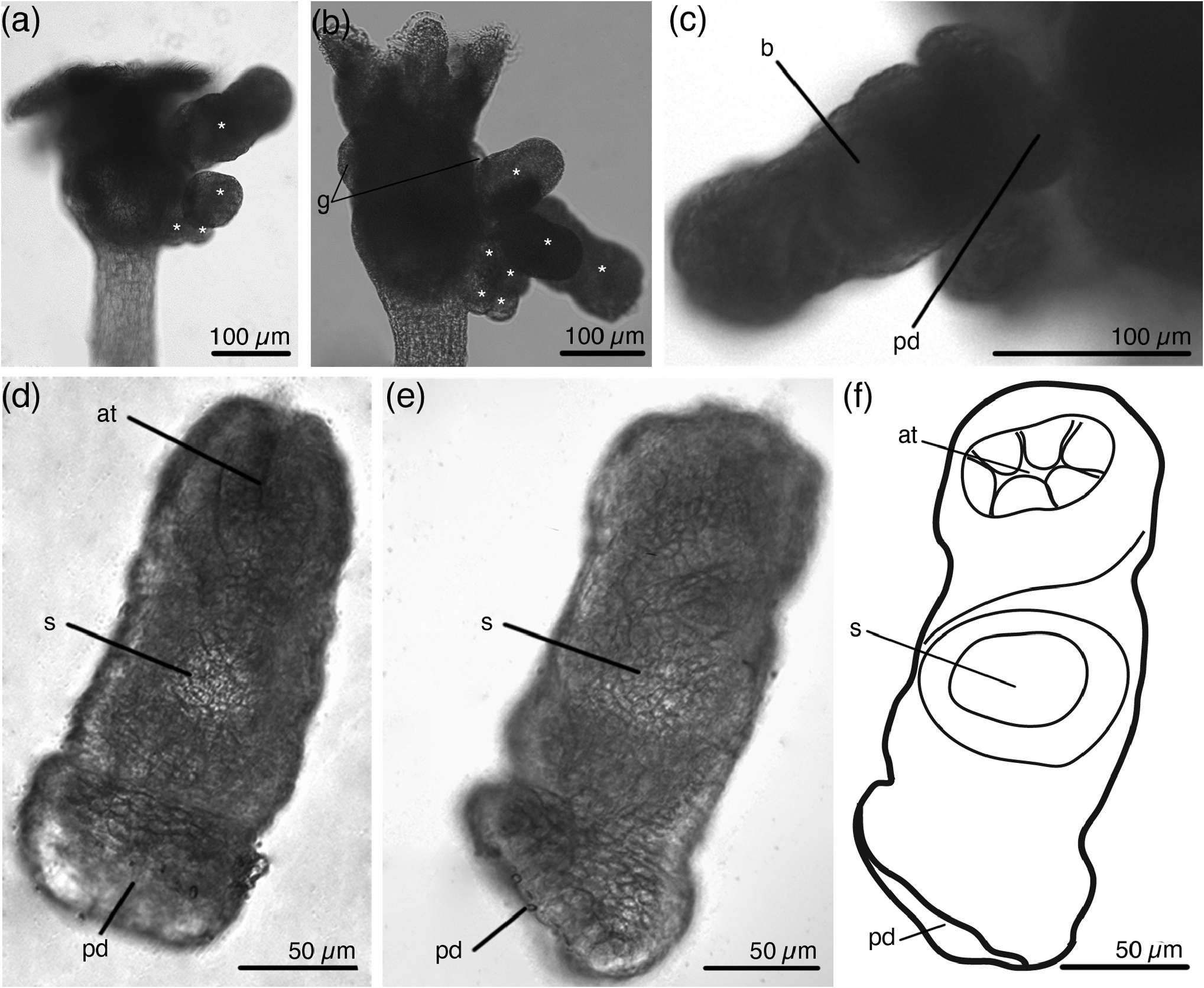
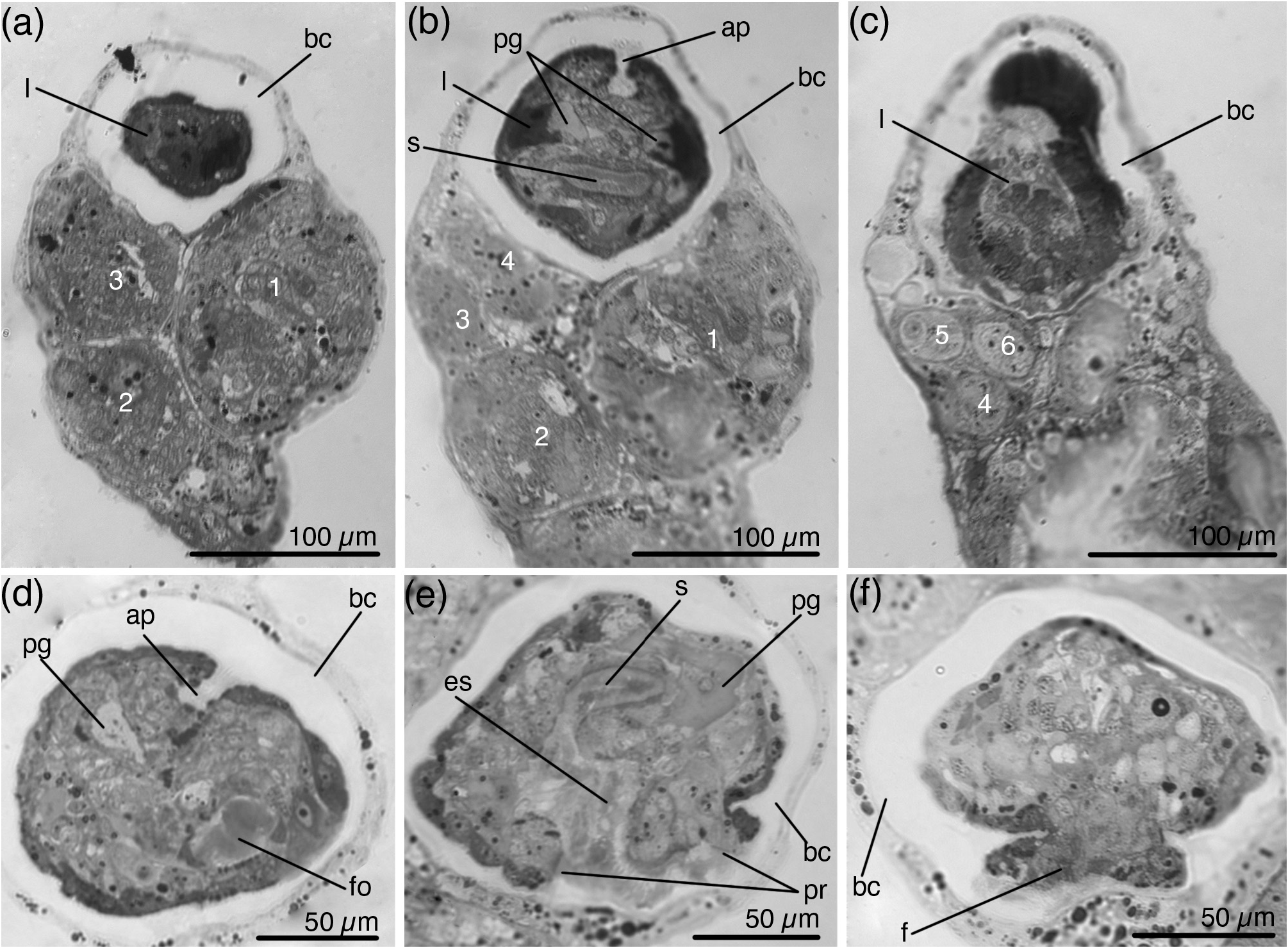
Buds originate from lateral area only on one side of the calyx, up to seven buds at a time ( Figs 2 View FIGURE 2 , 7a, b View FIGURE 7 ). Larger buds are located upper and more laterally than younger ones. The stalk of the fully developed bud ends with a rounded pedal disc ( Fig. 7c–f View FIGURE 7 ). The bud attaches to the maternal specimen by the posterior end of the pedal disc ( Fig. 7c View FIGURE 7 ). Specimens with fully developed buds have paired gonads on both sides of the calyx, but do not have embryos ( Fig. 7b View FIGURE 7 ). Specimens with young buds may have embryos. Embryos, like buds, form only on one side of the calyx, and this is the same side where the buds are located ( Fig. 2a–c, h, i View FIGURE 2 ). In some specimens embryos and buds develop on the left side of a calyx ( Fig. 2a, i View FIGURE 2 ), in other specimens on the right side of a calyx ( Figs 2h View FIGURE 2 , 6a View FIGURE 6 ).
Most specimens that were collected at the end of August had developing embryos in the calyx. When embryos develop, the calyx becomes asymmetric—it swells on one side ( Fig. 2g –i View FIGURE 2 ). One specimen may simultaneously have one fully developed larva in the brood chamber, one or two developing larvae and about five embryos at different stages of development ( Fig. 8a–c View FIGURE 8 ). The creeping-type larva has a well-developed foot, a large paired frontal organ, and a small apical organ ( Fig. 8d–f View FIGURE 8 ).
Remarks. The specimens found in the White Sea attach to the setae of the parapodia of Laonice sp. Several dozen specimens were found on one polychaete. They have some differences from those described from the Bergen area. They are slightly larger (up to 700 µm, while specimens from Bergen are up to 470 µm). The specimens from Bergen have transverse furrows on the base of the stalk caused by the setae of the polychaete ( Nielsen 1964b), which are lacking on the specimens from the White Sea. In the White Sea sexually reproduced specimens were found in August, while in Bergen was September. Despite these differences, we still assume that specimens from Bergen and from the White Sea belong to the same species. They share the unique features: buds and embryos develop only on one side of the calyx, which becomes asymmetrical when embryos are large; the calyx bears six short and wide tentacles (specimens with four tentacles are also described from Bergen). Loxosomatids rarely have six tentacles. Only calyxes of Loxosoma axisadversum Konno 1972 , Loxosomella sextentaculata Borisanova & Chernyshev & Ekimova, 2018 and Loxosomella discopoda Nielsen & Ryland, 1961 bear six tentacles, and calyx of Loxosomella brachystipes Franzén, 1973 can bear from six to twelve tentacles. The tentacles of Loxosoma (Loxosomina) aripes n. comb. differ from all other studied entoprocts in the structure of the frontal surface. It consists of nine rows of ciliated cells instead of five rows as in other entoprocts ( Nielsen & Jespersen 1997; Riisgard et al. 2000; Borisanova 2020). There are two additional rows of cells similar in ultrastructure to the frontal cells that form the lateral walls of the frontal groove. In other entoprocts, the frontal groove is formed by a single frontal cell. There are also two additional rows of lateral cells, which create a water current.
| ZMMU |
Zoological Museum, Moscow Lomonosov State University |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Loxosoma (Loxosomina) aripes ( Nielsen, 1964b )
| Borisanova, Anastasia & Schepetov, Dimitry 2023 |
Loxosomella aripes
| Nielsen, C. 1964: 4 |