Bittacus acutus, Zhang & Du & Hua, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4718.3.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:40857F32-81DA-4DFC-A3B9-F2AA1B485542 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5919218 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03802B15-E579-BF15-FF0E-7591FE60FED7 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Bittacus acutus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Bittacus acutus View in CoL sp. n.
( Figs. 2–3 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 )
Type material. Holotype. ♂, CHINA: Guangxi: Mao’ershan Nature Reserve (25°53′25″N, 110°29′08″E, elev. 1100 m), 25 July 2015, Ji-Shen Wang leg. GoogleMaps Paratype. 1♀, same data as for the holotype GoogleMaps .
Diagnosis. The new species can be distinguished from its congeners by the following characters: 1) wing with four brown markings, one each at OM, ORs, FRs and end of CuP ( Fig. 2C View FIGURE 2 ); and 2) epandrial lobe hat-shaped in lateral view, with a sharp process at ventro-distal apex ( Fig. 3A View FIGURE 3 ).
Etymology. The specific epithet “ acutus ” (sharpened) is a Latin participle, referring to the sharp distal process of the male epandrial lobe.
Description. Head ( Fig. 2B View FIGURE 2 ). Vertex yellowish brown. Ocellar triangle blackish brown. Antennae yellowish brown, filiform and ciliated; flagellum with segments distinct basally and obscure beyond the 15th segment. Frons slightly concave below the antennal socket. Compound eyes blackish brown. Rostrum three times as long as wide. Clypeus yellowish brown; labrum fuscous; maxillary and labial palps yellowish brown; third maxillary palpomere the longest, and the fifth slightly shorter than the fourth.
Thorax ( Fig. 2A, D, E View FIGURE 2 ). Pronotum yellowish brown, with a pair of long setae on anterior margin. Mesonotum and metanotum yellowish brown. Pleura unevenly pale yellowish. Legs yellow; hind basitarsus longer than tarsomeres II and III combined. Tibia with two apical spurs, the longer one about 1.5 times as long as the shorter one in middle leg. Tarsomere IV bearing 24–27 prominent black ventral teeth, with three setae on each side subbasally; tarsomere V with 26–28 ventral teeth.
Wings ( Fig. 2C View FIGURE 2 ). Forewing length 18.9 mm in male, 18.8 mm in female; width 4.6 mm in male, 4.2 mm in female. Pterostigma brown. Four brown markings, one each at ORs, FRs, OM and subapical portion of CuP; thyridium at FM; two Pcv; Av absent. Sc terminating beyond the origin of FRs; FM at the level of FRs; CuP ending before the origin of FM 3+4; 1A long, ending before FM. Hindwing length 16.5 mm in male, 15.0 mm in female; width 4.0 mm in male, 3.8 mm in female. Wing pattern similar to forewing, but Sc ending before the level of FRs; 1A coalesced with CuP basally.
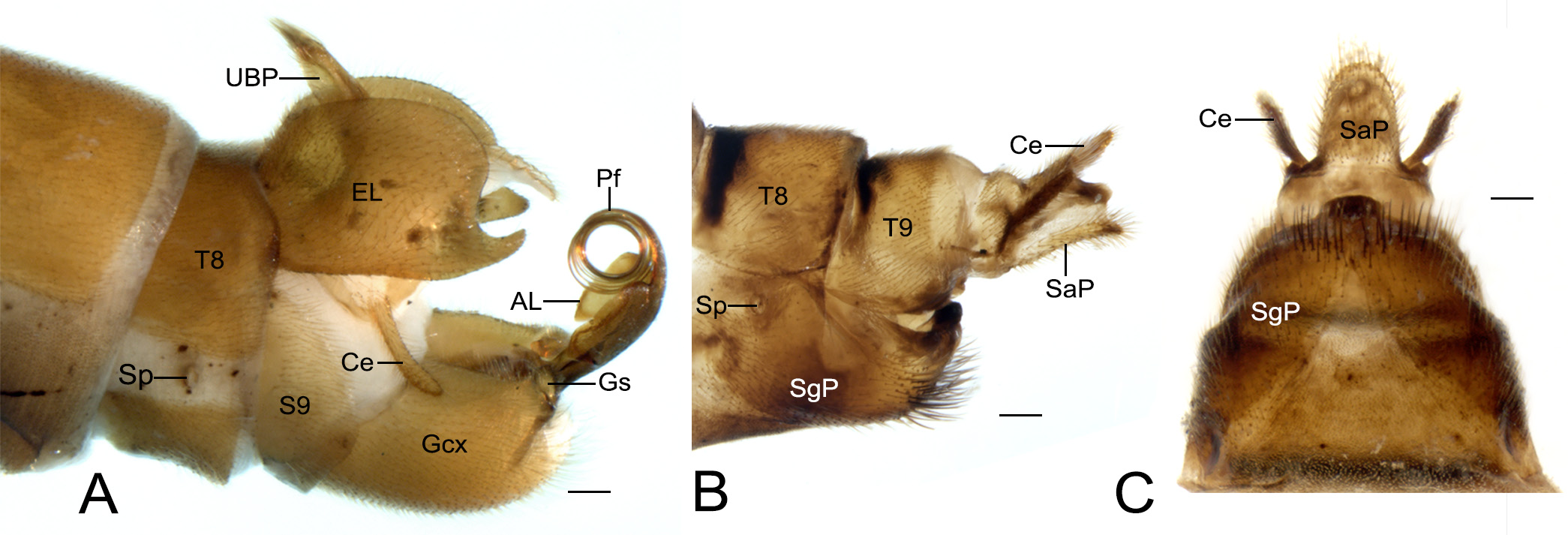
Abdomen of male ( Figs. 2A View FIGURE 2 , 3A View FIGURE 3 ). Terga and sterna yellowish brown; terga III−VIII each with a narrow black antecosta; tergum VIII emarginate slightly on posterior margin. Epandrial lobe yellowish brown, slightly longer than gonocoxite, hat-shaped in lateral view, with a sharp process at ventro-distal apex and dense black spines along the distal inner surface. Tergum X saddle-like. Upper branch of proctiger digitate, with long setae distally; lower branch of proctiger curved ventrally, broad basally and tapering toward apex. Cerci clavate, approximately as long as half length of gonocoxites. Gonocoxites yellowish brown, separated by a V-shaped membranous median area caudally; gonostylus short, blunt distally with a process on inner side. Penisfilum slender and greatly coiled; aedeagal lobe broad, with its ventral portion enlarged and separated from aedeagus.
Abdomen of female ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 B–C). Terga and sterna yellowish brown; each tergum with a narrow black antecosta. Subgenital plate sclerotized, yellowish brown, with a patch of black setae apically, and separated medially by a broad triangular membranous area, and with a prominent blunt distal process; dorsal margin concave apically in lateral view, with a slender process extending to the anterior portion of tergum IX. Tergum X yellowish brown, not extending ventrally. Anal plates consistent in length, blunt apically. Cerci slightly shorter than subanal plate.
Distribution. China (Guangxi).
Remarks. Bittacus acutus sp. n. resembles B. diaoluoshanus Chen & Hua, 2011 in appearance, but can be readily separated from the latter by the following characters: 1) wing with only four brown markings, each at ORs, FRs, OM and CuP (cf. four brown markings and one distinct tawny stripe along apical margin extending from pterostigma to beyond the apex); and 2) male epandrial lobe with a sharp distal process (cf. epandrial lobe subtrapezoidal, without process).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |