Culeolus anonymus Monniot C. & Monniot F., 1976
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5093.3.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:EC380383-C960-4473-92DD-A46699E07FA2 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5911117 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0075879C-FFB7-FF8C-FF09-87F8456CFCE0 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Culeolus anonymus Monniot C. & Monniot F., 1976 |
| status |
|
Culeolus anonymus Monniot C. & Monniot F., 1976 View in CoL
Figure 6 View FIGURE 6
Culeolus anonymus Monniot C. & Monniot F. 1976 View in CoL ; Sanamyan K. & Sanamyan N. 2002: 344, fig 25, and synonymy.
Culeolus suhmi: Millar, 1959: 199 View in CoL , figs. 11B and 11F (part: stations 663 y 668); Millar, 1970: 136, fig. 28.
? Culeolus wivylle-thomsoni Herdman, 1881
Material examined: 68°32’S, 20°34’W, station 9, 4930 m, 27 Feb 2005, one specimen.
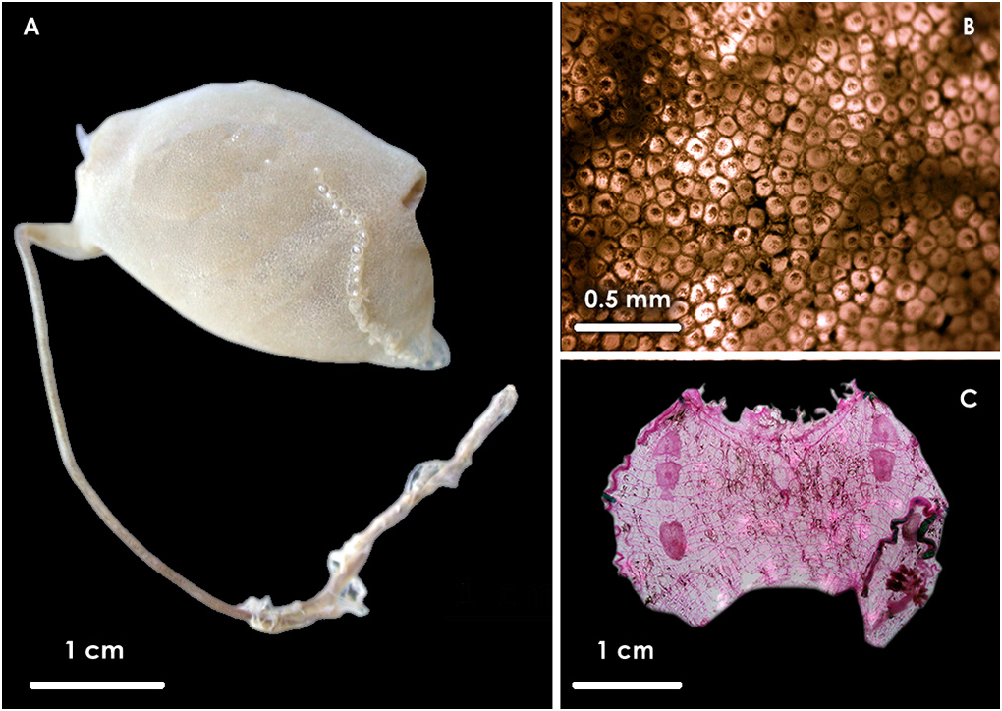
Description. The only specimen collected was found attached to the peduncle of Culeolus suhmi . Its body measures 1.8 cm long and 2.7 cm wide while the length of the peduncle reaches 6.5 cm, the shortest measure reported so far. The tunic is white ( Fig. 6A View FIGURE 6 ). It is completely covered by tiny rounded-tipped vesicles, which give the surface of the animal a granulated aspect ( Fig. 6B View FIGURE 6 ). The atrial aperture is surrounded by a crest of papillae interrupted dorsally. In the ventral region, the papillae of the crest are thicker and attached by their sides, creating a sort of stout lamella. There are no papillae in the mid-ventral region nor in any other region of the body ( Figs. 6A, B View FIGURE 6 ). There are 32 oral tentacles, with ramifications of the one order, disposed in a circle. Bigger tentacles with wide bases are distributed interspaced with smaller and thinner tentacles. Some of the bases of the bigger tentacles are so wide that they extend beyond the line of insertion towards the oral aperture. There is no oral velum. The dorsal tubercle has a “C” shape. The pre-pharyngeal band is simple. It makes a pronounced V around the dorsal tubercle. The dorsal lamina is composed of 20 triangular languets. Strong muscle fibers form a gridded network over the mantle. The branchial sac has six folds on each side. The branchial formula for the left side is:
DL - 2 (7) 2 (6) 3 (9) 3 (7) 3 (6) 2 (4) 4 - E
There is a short esophagus that connects with a small stomach, which is covered by two rows of hepatic diverticula. The intestine is long and thick. The border of the anus has multiple lobes. A short atrial velum was observed. There are two gonads on each side of the body. On the left side, the posterior gonad is located inside the gut-loop, while the anterior gonad is located antero-dorsal to the gut-loop. Both right gonads are located parallel to the endostyle, in one line, one after another. The anterior gonads on both sides of the body have two lobes, while the ventral gonads have only one ( Fig. 6C View FIGURE 6 ).
Stomach contents. In the stomach of this specimen we found pellet-shaped material (fecal pellets).
Remarks. Millar (1959) was the first who recognized two different species based on the morphologies of the postero-ventral crests of several specimens of Culeolus , which he temporarily identified as Culeolus suhmi . After the study of new material, Monniot C. & Monniot F. (1976) identified all specimens with postero-ventral crests interrupted dorsally as Culeolus anonymus . The authors originally described two populations based on the shape of the crest: one group with a continuous crest and the other with a crest composed of separate papillae. However, subsequent samples showed the existence of intermediate forms (Monniot C. & Monniot F. 1982). The number of branchial folds may also vary in C. anonymus . Although the most frequent is six folds per side, Sanamyan K. & Sanamyan N. (1999) observed five folds in specimens collected in the Indo-Pacific.
Other species of Culeolus recorded in the Southern Ocean are: Culeolus antarcticus Vinogradova, 1962 ; Culeolus likae Sanamyan K. & Sanamyan N., 2002 ; Culeolus pinguis Monniot C. & Monniot F., 1982 ; and Culeolus recumbens Herdman, 1881 . Culeolus anonymus is clearly distinguished from C. antarcticus and C. likae by the shape of the postero-ventral crest and by the number of gonads. The crest of both, C. antarcticus and C. likae , consists of a lamella that completely surrounds the atrial aperture and is interrupted dorsally, and extends along the mid-ventral side of the body. Moreover, C. antarcticus has one gonad consisting of one lobe on each side of the body, while C. likae presents three gonads per side. Culeolus pinguis presents a postero-ventral crest that surrounds the atrial aperture and two gonads with two lobes on each side. Finally, C. recumbens does not present gonads outside the gut-loop, and the postero-ventral crest completely surrounds the atrial aperture.
In a revision of the genus, Kott (2002) proposed the synonymy between C. anonymus and Culeolus suhmi . This statement, although possible, is difficult to maintain based on the present available data. As such, the position and morphology of the gonads of the present specimen of C. anonymus is almost identical to the figure presented by Monniot C. & Monniot F. (1973) for specimens of Culeolus suhmi from the North Atlantic. However, the gonads of C. anonymus and Culeolus suhmi are extremely variable and, in some cases, almost identical. Although the only robust feature to differentiate between Culeolus suhmi and C. anonymus is the configuration of the postero-ventral crest (Sanamyan K. & Sanamyan N. 2002), the finding of two species in the Weddell Sea, one with internal characters more frequently found in the other, could be indicating that these species are, in fact, conspecific. However, until more material is available and completed with molecular studies, we propose to maintain C. anonymus and C. suhmi as separate species.
In the most recent revision of the genus, Sanamyan et al. (2018) suggested that C. wivylle-thomsoni and C. anonymus could be conspecific based on a commentary by Monniot C. & Monniot F. (1982). According to the latter authors, the type specimen of C. wivylle-thomsoni could be an abnormal specimen of C. anonymus . Culeolus wivylle-thomsoni has not been collected since its original finding (see Herdman, 1881).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
SubPhylum |
Tunicata |
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Culeolus anonymus Monniot C. & Monniot F., 1976
| Maggioni, Tamara, Rimondino, Clara, Taverna, Anabela, Reyna, Paola, Lagger, Cristian, Alurralde, Gastón, Calcagno, Emilia & Tatián, Marcos 2022 |
Culeolus anonymus
| Monniot C. & Monniot F. 1976 |
Culeolus suhmi
| : Millar 1959: 199 |
Culeolus wivylle-thomsoni
| Herdman 1881 |