Pseudechiniscus facettalis Petersen, 1951
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4410.1.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:0944C1F0-1405-43E0-80B7-03438A19F334 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5998755 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/00108791-0D0A-FF9D-D399-FB00FB23FF3F |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Pseudechiniscus facettalis Petersen, 1951 |
| status |
|
Pseudechiniscus facettalis Petersen, 1951 View in CoL
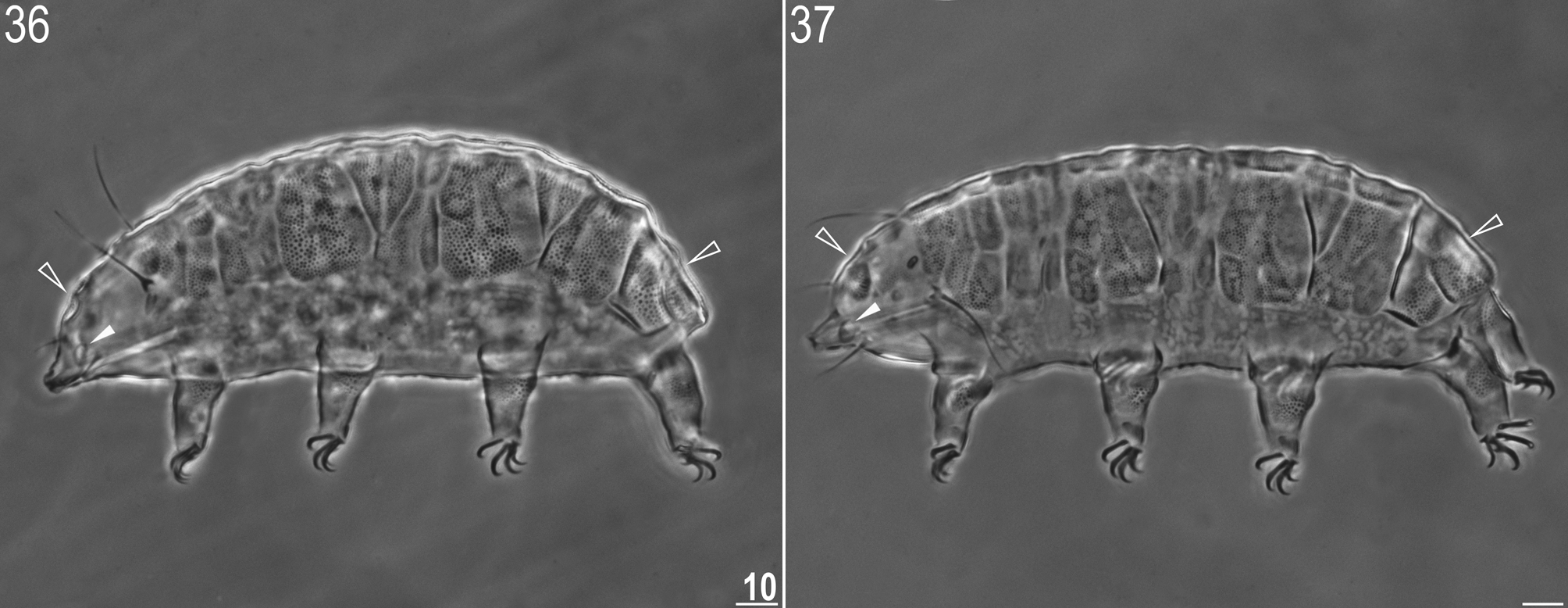
( Figs 36–37 View FIGURES 36–37 )
Terra typica. Greenland.
Material examined. Eleven females, two males, and one juvenile, found together with Echiniscus granulatus , Testechiniscus spitsbergensis , and Hypsibius convergens ( Urbanowicz, 1925) (PL.247, 248, 252, and 274; Kościeliska Valley, Ciemniak hillside, Kobylarzowy Coulouir).
Description. Small (females 152–201 µm, males 180–205 µm), light-orange. Black eyes present. Primary clavae long, secondary clavae large (females: 20.6–22.7%, male: 35.1%; Figs 36–37 View FIGURES 36–37 , arrowheads). Cirrus A very short (24.6–32.7 µm, cirrus A/body length ratio 14–20%). All plates weakly sclerotized, covered with fine granulation of suillus type. Cephalic and caudal plates clearly facetted ( Figs 36–37 View FIGURES 36–37 , empty arrowheads). Pseudosegmental plate always divided longitudinally. Pedal (leg) plates present. Spine on the leg I absent. Venter with developed sculpture consisting of intracuticular pillars. Claws I–IV 7.7–11.0 µm long ( 34.0–46.2%), the internal claws with spurs, 1.2 – 2.1 µm long ( 4.7–9.3%).
Remarks. Additional Polish record. Dastych (1970) was the first to report this taxon from Poland (as P. suillus facettalis ), but in his later monograph he synonymised it with P. suillus ( Dastych 1988) . Since one of the primary characters separating these two species is the presence of cephalic and caudal plate faceting, the status of P. facettalis as an element of the Polish fauna is restored.
Kristensen (1987) gave two features that allow differentiation of the sexes in the genus Pseudechiniscus : body shape (males are more elongate than females) and enlarged male secondary clavae. There are two additional qualitative traits which can be used to distinguish the sexes in P. facettalis , i.e. males are more flattened than females (compare Figs 36 and 37 View FIGURES 36–37 ), and the faceting of the caudal plate in males is not as deep as that observed in females (visible only when specimens are laterally or dorso-laterally oriented). Similar sexual dimorphism was observed in the two populations from Norway and Tunisia used for comparisons (see Table 2).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |